The Legacy of Ancient African Kingdoms
Exploring the rich tapestry of ancient African kingdoms unveils a captivating narrative that has woven its way through time, leaving an indelible mark on modern societies, culture, and traditions. From the towering pyramids of Egypt to the bustling markets of Ghana, these civilizations have bequeathed a legacy that resonates across continents and centuries.
One of the most formidable kingdoms of ancient Africa was the Great Kingdom of Kush, renowned for its mastery of architecture, intricate trade networks, and profound influence on the neighboring realm of ancient Egypt. The legacy of Kushite rulers, including the legendary Queen Amanirenas, stands as a testament to their enduring contributions to African history and civilization.
Delving deeper into the annals of time, the Kingdom of Aksum emerges as a beacon of innovation and prosperity in East Africa. Its pioneering coinage system, towering obelisks, and the enduring presence of Christianity in the region underscore the kingdom's lasting impact on the cultural landscape of Africa.
The Mali Empire, with its opulent wealth and illustrious ruler Mansa Musa, shines as a beacon of prosperity and cultural achievement in West Africa. The legendary city of Timbuktu, a hub of learning and commerce, stands as a testament to the empire's golden age and enduring influence on the region.
Turning our gaze to the Kingdom of Benin, we uncover a realm of artistic brilliance and military prowess, exemplified by its intricate bronze sculptures and formidable army. The kingdom's unique political system, vibrant trade relations, and rich cultural heritage continue to captivate scholars and enthusiasts alike.
Tracing the rise and fall of the ancient Kingdom of Ghana, we unearth a pivotal center of trade and wealth in West Africa. Its strategic position along the trans-Saharan trade routes, powerful rulers, and the enduring legacy of its gold-rich empire illuminate Ghana's historical significance in the region.
Embarking on a journey to the ancient Kingdom of Axum, we encounter a dominant force in the Horn of Africa celebrated for its towering stelae and legendary connections to the Queen of Sheba. The kingdom's extensive trade networks, early embrace of Christianity, and enduring influence underscore its pivotal role in shaping the region's history.
Unveiling the mysteries of the Kingdom of Zimbabwe, we are greeted by an ancient civilization renowned for its impressive stone structures and intricate trade networks. The enigmatic Great Zimbabwe ruins, the kingdom's sophisticated political organization, and its enduring impact on Southern Africa beckon us to explore further.
Lastly, the artistic and spiritual enclave of the Kingdom of Ife beckons us with its exquisite bronze and terracotta sculptures, offering a glimpse into its unique cultural practices and religious beliefs that continue to influence the Yoruba civilization to this day.
The Great Kingdom of Kush
Exploring the rich history and lasting impact of ancient African kingdoms on modern societies, culture, and traditions. From Egypt to Ghana, these civilizations left behind a legacy that continues to shape Africa and the world today.
Known for its powerful civilization, the Kingdom of Kush thrived in the region of Nubia, present-day Sudan. The Kushites built impressive pyramids and temples, showcasing their advanced architectural skills. Their strategic location along the Nile River enabled them to establish extensive trade networks with neighboring regions, including ancient Egypt.
The legacy of the Kingdom of Kush extends beyond its architectural achievements. The Kushite rulers, such as the renowned Queen Amanirenas, played a significant role in shaping African history. Queen Amanirenas led successful military campaigns against the Roman Empire, demonstrating the strength and resilience of the Kushite civilization.
Moreover, the Kingdom of Kush exerted a profound influence on ancient Egypt, particularly during the period of the Twenty-Fifth Dynasty when Kushite pharaohs ruled over Egypt. This cultural exchange between Kush and Egypt enriched both civilizations, leaving a lasting impact on the history of the region.
In addition to their military prowess and architectural marvels, the Kushites were known for their rich cultural heritage, including distinctive art forms and religious practices. The Kingdom of Kush stands as a testament to the ingenuity and sophistication of ancient African civilizations, highlighting their contributions to world history.

The Kingdom of Aksum
The Kingdom of Aksum, also known as the Aksumite Empire, was a powerful trading civilization located in East Africa. This ancient kingdom flourished from around the 1st century AD to the 7th century AD, with its capital city in present-day Ethiopia. Aksum was renowned for its strategic location along major trade routes, connecting Africa with the Mediterranean world, Arabia, Persia, and India.
One of the remarkable features of the Kingdom of Aksum was its innovative coinage system. Aksum was one of the first civilizations in the world to issue its own currency, which played a crucial role in facilitating trade and economic prosperity. The use of coins also reflected the advanced level of economic development and organization within the kingdom.
In addition to its economic prowess, the Kingdom of Aksum was known for its impressive obelisks, towering stone monuments that served as symbols of royal power and religious significance. These monumental structures, some of which still stand today, reflected the sophisticated architectural skills of the Aksumites and their cultural achievements.
Furthermore, the Kingdom of Aksum played a significant role in the spread of Christianity in the region. Aksum embraced Christianity in the 4th century AD, making it one of the earliest Christian kingdoms in the world. The adoption of Christianity had a lasting impact on the culture, traditions, and identity of the Aksumite people, shaping the religious landscape of East Africa.
Overall, the Kingdom of Aksum left a lasting legacy that continues to resonate in modern-day Ethiopia and beyond. Its innovative economic practices, architectural marvels, and religious contributions have contributed to the rich tapestry of African history and heritage.

The Mali Empire
The Mali Empire, one of the most renowned ancient African kingdoms, flourished in West Africa during its golden age. Led by the legendary ruler Mansa Musa, Mali was a beacon of wealth and grandeur, attracting traders and scholars from far and wide. The city of Timbuktu, a bustling hub of commerce and learning, epitomized the empire's prosperity and cultural achievements. Mansa Musa's famous pilgrimage to Mecca, where he displayed his immense wealth, solidified Mali's reputation as a land of opulence and power.
At the heart of Mali's success was its control over lucrative trade routes, especially in gold and salt. The empire's strategic location allowed it to amass vast wealth through trade with North Africa and the Mediterranean. This economic prosperity fueled the growth of cities like Timbuktu, which became centers of learning and culture, attracting scholars, poets, and artisans from across the Islamic world.
Mansa Musa's extravagant spending during his pilgrimage to Mecca, where he distributed gold and gifts lavishly, not only showcased Mali's wealth but also established diplomatic ties with other powerful empires. The Mali Empire's influence extended beyond its borders, shaping the political and economic landscape of West Africa for centuries to come.
Moreover, Mali's embrace of Islam under Mansa Musa's rule left a lasting impact on the region's religious landscape. The spread of Islam brought new ideas, technologies, and cultural practices to Mali, enriching its society and fostering a sense of unity among its diverse population.
Despite its eventual decline due to internal strife and external pressures, the legacy of the Mali Empire endures in the traditions, art, and architecture of West Africa. The grandeur of Timbuktu, the stories of Mansa Musa's wealth, and the cultural richness of Mali continue to captivate historians and enthusiasts, offering a glimpse into a bygone era of African greatness.

The Kingdom of Benin
The Kingdom of Benin, located in present-day Nigeria, was a civilization renowned for its remarkable artistic achievements and military organization. The kingdom flourished between the 11th and 19th centuries, leaving a lasting impact on the region's culture and history. One of the most distinctive features of the Kingdom of Benin was its intricate bronze sculptures, which showcased the artistic prowess of its craftsmen. These sculptures depicted scenes of court life, rituals, and warfare, reflecting the kingdom's rich cultural heritage.
Furthermore, the Kingdom of Benin boasted a well-organized army that played a crucial role in protecting the kingdom's borders and ensuring its dominance in the region. The military prowess of Benin's warriors was evident in their strategic warfare tactics and disciplined approach to combat. This strength allowed the kingdom to maintain its sovereignty and defend against external threats effectively.
In addition to its artistic and military achievements, the Kingdom of Benin had a unique political system characterized by a centralized monarchy. The Oba, or king, held significant power and authority, overseeing the administration of the kingdom and maintaining social order. The kingdom's political structure facilitated governance and decision-making, contributing to its stability and prosperity.
Trade relations were also vital to the Kingdom of Benin's success, as it engaged in commercial activities with neighboring regions and European traders. The kingdom's position as a trading hub enabled it to acquire valuable resources, such as ivory, palm oil, and textiles, which further enriched its economy and cultural exchange.
The enduring cultural heritage of the Kingdom of Benin continues to fascinate scholars and enthusiasts alike, offering insights into the complexities of African civilizations and their contributions to global history. From its artistic masterpieces to its military achievements and political organization, Benin stands as a testament to the ingenuity and resilience of ancient African kingdoms.

The Kingdom of Ghana
Located in West Africa, the ancient Kingdom of Ghana holds a significant place in the history of the continent. Flourishing between the 6th and 13th centuries, Ghana was a powerful empire known for its wealth, advanced military, and strategic location along the trans-Saharan trade routes. The kingdom's prosperity was built on its control of the lucrative gold trade, which attracted merchants from far and wide.
One of the key aspects of Ghana's success was its efficient system of taxation on trade, allowing the empire to accumulate vast wealth. This wealth, in turn, funded the development of thriving urban centers, such as the capital city of Kumbi Saleh, which served as a hub for commerce and culture. The kingdom's rulers, including the legendary Ghana kings, wielded significant power and influence, further solidifying Ghana's position as a dominant force in the region.
Ghana's decline, attributed to various factors including internal strife and external pressures, marked the end of an era. However, the legacy of the Kingdom of Ghana lives on in the traditions, art, and cultural practices of the region. The remnants of ancient Ghana serve as a reminder of the empire's once-great influence and continue to fascinate historians and archaeologists alike.

The Kingdom of Axum
The Kingdom of Axum, situated in the Horn of Africa, held significant influence and power during ancient times. Renowned for its impressive stelae, Axum was a dominant force in the region, with connections to the legendary Queen of Sheba adding to its mystique. The kingdom's strategic location allowed it to establish extensive trade networks that extended both locally and internationally. Axum's early adoption of Christianity further solidified its cultural and religious significance, leaving a lasting impact on the region.
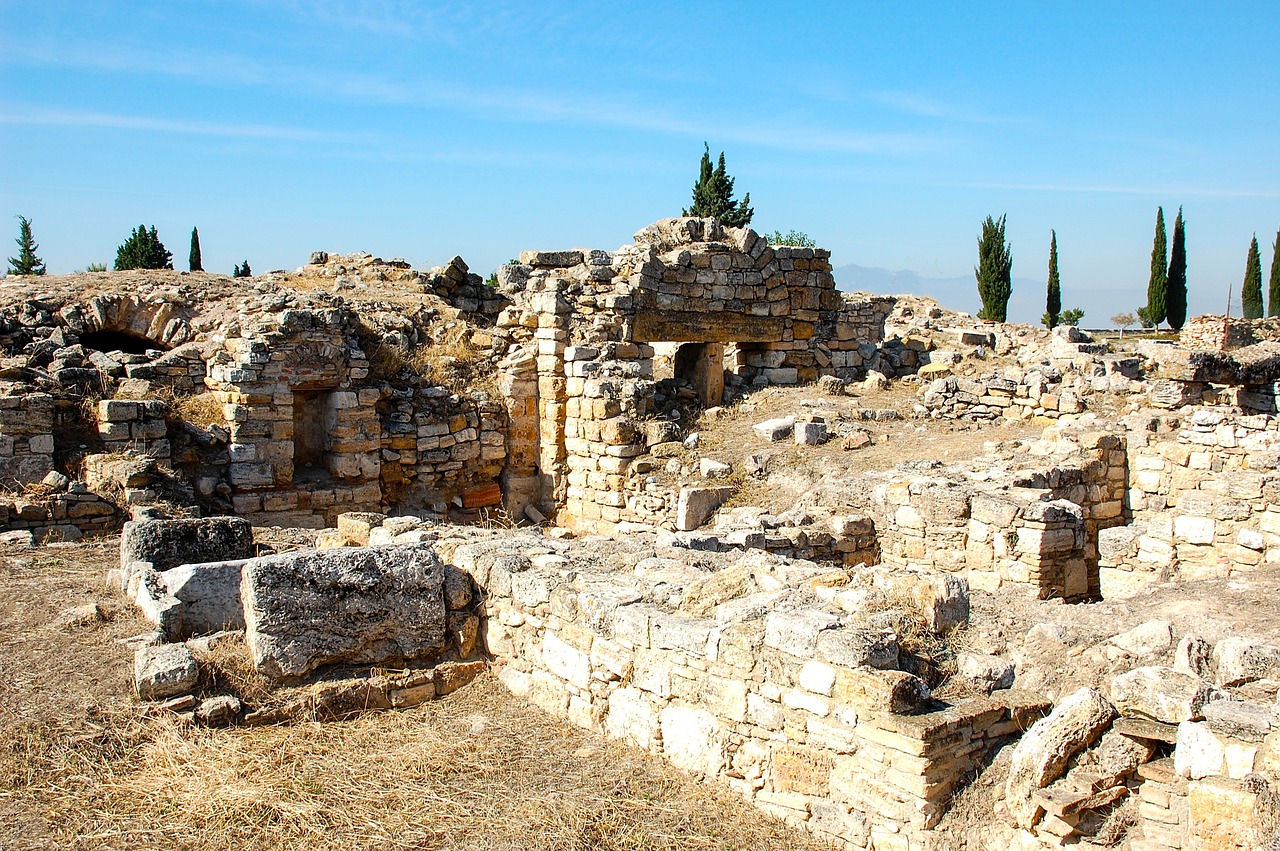

The Kingdom of Zimbabwe
The Kingdom of Zimbabwe, an ancient civilization shrouded in mystery and grandeur, stands as a testament to the ingenuity and sophistication of African kingdoms. Nestled in Southern Africa, the Kingdom of Zimbabwe flourished with its impressive stone structures and intricate trade networks. At the heart of this kingdom lies the awe-inspiring Great Zimbabwe ruins, a symbol of power and architectural marvel.
The political organization of the Kingdom of Zimbabwe was characterized by a central hub surrounded by smaller satellite communities, showcasing a well-developed system of governance and administration. This structure facilitated efficient trade relations and cultural exchange, contributing to the kingdom's prosperity and influence in the region.
One of the defining features of the Kingdom of Zimbabwe was its mastery of trade, connecting distant regions and fostering economic growth. The kingdom's strategic location allowed it to establish lucrative trade routes, exchanging goods such as gold, ivory, and copper with neighboring civilizations.
Artistic expression thrived in the Kingdom of Zimbabwe, as evidenced by the intricate sculptures and artifacts discovered within its borders. Skilled artisans crafted elaborate pieces that reflected the cultural richness and spiritual beliefs of the kingdom, leaving a lasting legacy of artistic excellence.
Despite the passage of time, the Kingdom of Zimbabwe continues to captivate historians and archaeologists, offering glimpses into a bygone era of innovation and prosperity. Its legacy endures in the collective memory of Southern Africa, reminding us of the remarkable achievements of ancient African civilizations.

The Kingdom of Ife
The Kingdom of Ife holds a special place in the history of ancient African kingdoms as an artistic and spiritual center that flourished in what is now Nigeria. Renowned for its exquisite bronze and terracotta sculptures, Ife's artistic achievements continue to captivate historians and art enthusiasts alike. The kingdom's skilled artisans crafted intricate sculptures that depicted both human and divine figures, showcasing a sophisticated level of craftsmanship and artistic expression.
One of the most remarkable aspects of Ife's cultural legacy is its unique religious practices and beliefs. The kingdom's spiritual traditions revolved around the worship of deities and ancestors, with elaborate rituals and ceremonies playing a central role in Ife society. These religious beliefs not only influenced daily life in the kingdom but also left a lasting impact on the broader Yoruba civilization, shaping cultural practices and spiritual beliefs for generations to come.
Aside from its artistic and spiritual significance, Ife also served as a political and economic hub in ancient Africa. The kingdom's strategic location allowed it to thrive as a center of trade and commerce, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas with neighboring regions. Through its trade networks, Ife established connections with distant lands, contributing to the cultural diversity and prosperity of the kingdom.
Furthermore, Ife's political organization was characterized by a system of governance led by powerful rulers who oversaw the administration of the kingdom. These rulers, known as Oonis, wielded authority and influence over Ife society, guiding the kingdom through periods of growth and change. Their leadership and diplomatic skills played a crucial role in maintaining stability and prosperity within Ife.
In conclusion, the Kingdom of Ife stands as a testament to the ingenuity, creativity, and spiritual richness of ancient African civilizations. Its artistic masterpieces, religious practices, and political achievements reflect the depth of Ife's cultural heritage and its enduring influence on the development of African societies. By exploring the legacy of Ife, we gain valuable insights into the complexities and achievements of one of Africa's most revered kingdoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What were the main achievements of the Kingdom of Kush?
The Kingdom of Kush was known for its advanced architecture, prosperous trade networks, and significant influence on ancient Egypt. The Kushite rulers, including Queen Amanirenas, made remarkable contributions to African history.
- What made the Mali Empire famous?
The Mali Empire gained fame for its wealth and grandeur, particularly under the rule of Mansa Musa. The city of Timbuktu flourished during this time, showcasing the empire's cultural achievements and lasting impact on West Africa.
- What is the significance of the Kingdom of Benin's bronze sculptures?
The Kingdom of Benin was renowned for its intricate bronze sculptures, reflecting its artistic and military prowess. These sculptures, along with the kingdom's well-organized army and unique political system, contribute to its enduring cultural heritage.
- How did the Kingdom of Ghana influence trade in West Africa?
The ancient Kingdom of Ghana played a crucial role in the trans-Saharan trade routes, establishing itself as a major center of trade and wealth in West Africa. Its gold-rich empire and powerful rulers left a lasting legacy on the region.
- What are the main features of the Kingdom of Zimbabwe?
The Kingdom of Zimbabwe was known for its impressive stone structures, intricate trade networks, and the Great Zimbabwe ruins. Its political organization and lasting impact on Southern Africa make it a fascinating ancient civilization to explore.



















