The Mystery of the Lost Roman City of Pompeii
Have you ever wondered what secrets lie beneath the ancient city of Pompeii, frozen in time by the catastrophic eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD? The lost Roman city of Pompeii continues to intrigue and captivate both historians and tourists alike with its mysterious past and ongoing archaeological discoveries.

History of Pompeii
Exploring the ancient city of Pompeii is like stepping into a time machine, where the past comes alive in astonishing detail. Founded by the Oscan people around the 6th century BC, Pompeii thrived as a bustling Roman city until its tragic fate was sealed by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. This catastrophic event buried the city under layers of ash and pumice, freezing it in time and preserving its secrets for centuries to come.
The history of Pompeii is a tapestry woven with threads of triumph and tragedy. From its humble beginnings as a trading hub to its transformation into a prosperous Roman municipality, Pompeii's story is one of resilience and resilience in the face of adversity. The city's strategic location near the Bay of Naples made it a vital center for commerce and culture, attracting merchants, artisans, and dignitaries from far and wide.
Excavations of Pompeii began in the 18th century, uncovering a treasure trove of artifacts that shed light on the daily lives of its inhabitants. The meticulous work of archaeologists has revealed a city frozen in time, with its streets, homes, and public buildings offering a glimpse into the vibrant world of ancient Rome. The preserved art and architecture of Pompeii stand as a testament to the ingenuity and creativity of its people, showcasing their mastery of engineering, painting, and sculpture.
Everyday life in Pompeii was a vibrant tapestry of activities, from bustling markets to lively theaters. The remains of bakeries, taverns, and baths provide insight into the social fabric of the city, highlighting the diversity and sophistication of its population. The discovery of graffiti, mosaics, and frescoes offers a window into the beliefs, values, and aspirations of Pompeii's residents, painting a vivid picture of a society rich in culture and tradition.
The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD was a cataclysmic event that forever altered the course of Pompeii's history. The volcanic ash that engulfed the city preserved it in a time capsule, but at a devastating cost. Thousands of lives were lost in the disaster, leaving behind a haunting reminder of the fragility of human existence in the face of nature's fury.
The destruction of Pompeii reverberated throughout the Roman Empire, reshaping attitudes towards natural disasters and inspiring a wave of artistic and literary expressions. The ruins of Pompeii became a symbol of both tragedy and resilience, serving as a cautionary tale of the consequences of hubris and the impermanence of human achievements.
Today, modern preservation efforts are underway to safeguard the ruins of Pompeii for future generations. Conservationists employ cutting-edge techniques to protect the fragile structures from environmental degradation, balancing the need for restoration with the imperative of maintaining historical authenticity. The ongoing challenge of preserving Pompeii's legacy is a testament to the enduring allure and significance of this ancient city.
The tourism industry around Pompeii has flourished, drawing visitors from around the globe to witness its wonders firsthand. As a UNESCO World Heritage Site, Pompeii holds immense cultural importance, serving as a living museum of ancient Roman civilization. However, the ethical considerations of managing tourism and preservation pose a delicate balancing act, requiring thoughtful stewardship to ensure the longevity and integrity of this remarkable archaeological site.

Excavations and Discoveries
Exploring the ancient city of Pompeii, frozen in time by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, and the ongoing archaeological discoveries that continue to unravel its secrets.
Discover the rich history of Pompeii, from its founding by the Oscan people to its destruction and preservation under layers of volcanic ash.
The excavations of Pompeii, which commenced in the 18th century, have unearthed remarkable findings shedding light on daily life in ancient Rome. Archaeologists have meticulously excavated the city's ruins, revealing a treasure trove of insights into the past. Through these excavations, Pompeii's secrets have slowly been brought to light, offering a glimpse into a civilization long lost to time.
Exploring Pompeii allows us to witness the well-preserved art, buildings, and infrastructure that showcase the advanced civilization that once thrived there. The intricate frescoes, mosaics, and architectural marvels provide a window into the artistic and engineering prowess of the ancient Romans.
Delving into the details of Pompeii's daily life reveals insights into the inhabitants' homes, food, entertainment, and social structure. From the layout of the streets to the remains of taverns and bathhouses, each discovery paints a vivid picture of the bustling city and its vibrant community.
Understanding the catastrophic eruption of Mount Vesuvius that buried Pompeii under ash and pumice is crucial to grasping the city's fate. While the tragedy led to the loss of thousands of lives, it also preserved Pompeii in a time capsule, offering a unique perspective on the ancient world.
Examining the aftermath of Pompeii's destruction unveils how it reverberated through Roman society. The event not only reshaped perceptions of natural disasters but also influenced art, literature, and urban planning in profound ways, leaving a lasting mark on the Empire.
Today, ongoing conservation efforts aim to protect and preserve the ruins of Pompeii for future generations. Despite facing challenges such as weathering, tourism impact, and limited resources, innovative techniques in restoration ensure that this ancient city continues to be safeguarded and appreciated.
The tourism industry surrounding Pompeii highlights its cultural importance as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Balancing the preservation of the site with public access raises ethical considerations, as the world seeks to appreciate and learn from this archaeological marvel while safeguarding its integrity for the future.
Stay tuned for answers to common queries about Pompeii and its fascinating history!
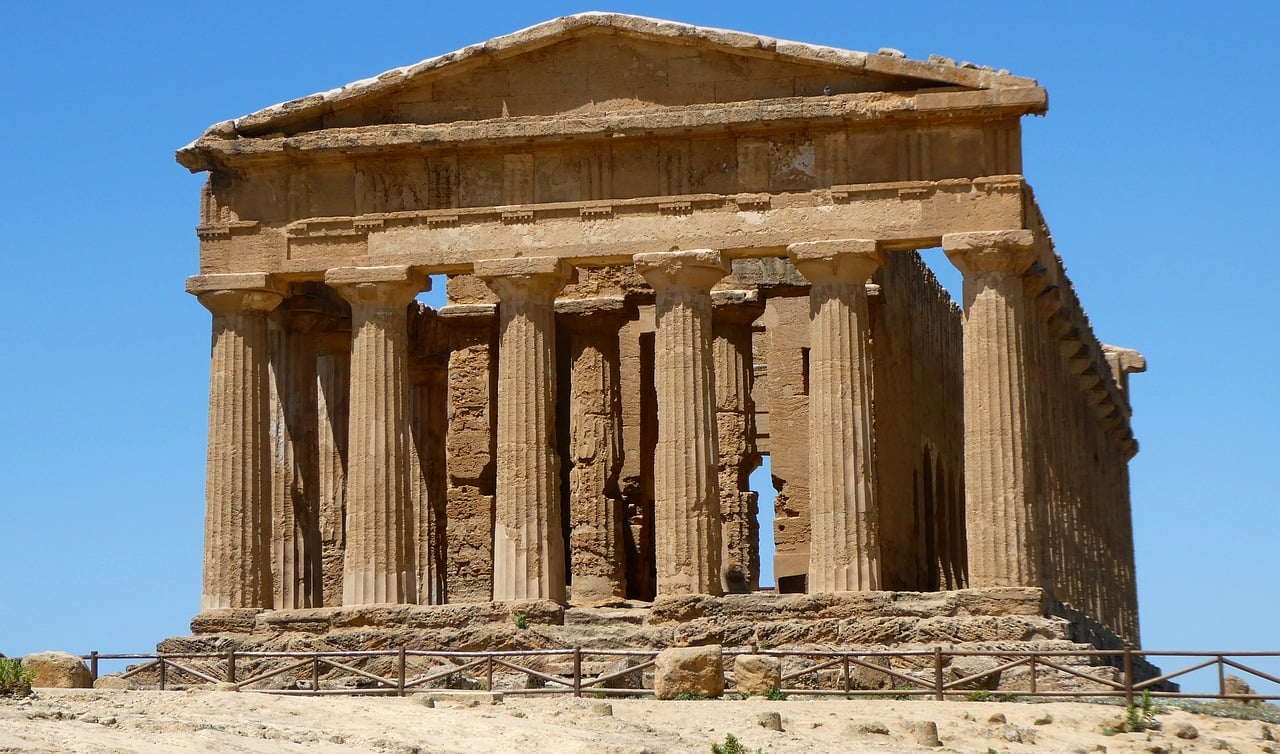

Preserved Art and Architecture
Exploring the ancient city of Pompeii, frozen in time by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, and the ongoing archaeological discoveries that continue to unravel its secrets.
Discover the rich history of Pompeii, from its founding by the Oscan people to its destruction and preservation under layers of volcanic ash.
Learn about the excavations of Pompeii that began in the 18th century and the remarkable findings that have provided insights into daily life in ancient Rome.
When we delve into the preserved art and architecture of Pompeii, we are transported back in time to witness the grandeur of an ancient civilization. The intricate frescoes adorning the walls of villas, the majestic temples dedicated to Roman gods, and the well-preserved amphitheaters all stand as testaments to the artistic and architectural prowess of Pompeii's inhabitants.
Walking through the streets of this ancient city, one can't help but marvel at the advanced engineering techniques employed in the construction of aqueducts, baths, and public buildings. The meticulous attention to detail in the design of homes and public spaces reflects a society that valued aesthetics and functionality in equal measure.
The art and architecture of Pompeii not only showcase the skills of its craftsmen but also provide valuable insights into the daily lives and cultural beliefs of its residents. From the colorful mosaics depicting scenes of everyday life to the imposing structures dedicated to deities, each piece of art and architecture tells a story of a civilization tragically frozen in time.
Uncover details about the daily lives of Pompeii's inhabitants, including their homes, food, entertainment, and social structure revealed through archaeological evidence.
Understand the catastrophic eruption of Mount Vesuvius that buried Pompeii under ash and pumice, preserving the city but causing the tragic loss of thousands of lives.
Examine how the destruction of Pompeii affected the Roman Empire, shaping perceptions of natural disasters and influencing art, literature, and urban planning.
Learn about current conservation efforts to protect and preserve the ruins of Pompeii for future generations, including challenges and innovative techniques used in restoration.
Discuss the tourism industry around Pompeii, its cultural importance as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and the ethical considerations of balancing preservation with public access.

Everyday Life in Pompeii
Imagine walking through the cobbled streets of ancient Pompeii, a bustling city frozen in time by the catastrophic eruption of Mount Vesuvius. As you explore the remnants of daily life, you can't help but marvel at the intricate details that offer a glimpse into the everyday existence of its inhabitants.
One of the most fascinating aspects of Pompeii is the well-preserved homes that reveal the living conditions of its residents. From modest dwellings to elaborate villas, each building tells a story of social hierarchy and architectural sophistication. The colorful frescoes adorning the walls transport you to a world where art and daily life intertwine seamlessly.
Food played a significant role in Pompeian culture, as evidenced by the remains of bakeries, taverns, and street food stalls. The thermopolia, ancient fast-food outlets, offer insight into the culinary preferences of the time, showcasing a diverse menu that catered to the eclectic tastes of the population.
Entertainment was also a vital part of daily life in Pompeii, with amphitheaters, theaters, and public baths serving as hubs of social activity. The amphitheater, where gladiatorial contests took place, stands as a testament to the city's fascination with spectacles that captivated the masses.
Moreover, the social structure of Pompeii is unveiled through the layout of the city, with distinct neighborhoods reflecting the divisions of class and occupation. From the bustling markets of the Forum to the tranquil gardens of the wealthy, each area paints a picture of a vibrant society that thrived in the shadow of the looming volcano.

Volcanic Eruption and Destruction
The volcanic eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD is a cataclysmic event that forever altered the landscape of Pompeii, freezing the city in time under layers of ash and pumice. The eruption, which occurred over a span of two days, buried the thriving Roman city and its inhabitants, preserving them for centuries to come.
The destruction caused by the volcanic eruption was immense, with ash and debris raining down on Pompeii, blanketing the city in a thick layer of volcanic material. The sheer force of the eruption led to the collapse of roofs and buildings, trapping many residents in their homes and ultimately sealing their fate.
As the ash settled, it formed a protective layer over Pompeii, creating a natural time capsule that would later be unearthed by archaeologists, offering a glimpse into the daily life and customs of an ancient civilization. The tragic loss of thousands of lives during the eruption is a stark reminder of the raw power of nature and the fragility of human existence in the face of such natural disasters.
The volcanic eruption not only destroyed Pompeii physically but also had far-reaching implications for Roman society. The event left a lasting impact on the Roman Empire, influencing perceptions of natural disasters and prompting discussions on disaster preparedness and response. The ruins of Pompeii stand as a testament to the destructive forces of nature and the resilience of humanity in the face of adversity.
Impact on Roman Society
When Mount Vesuvius unleashed its fury upon the unsuspecting city of Pompeii in 79 AD, the impact on Roman society was profound and far-reaching. The catastrophic eruption not only buried the city under layers of ash and pumice but also left an indelible mark on the collective consciousness of the Roman Empire.
The destruction of Pompeii served as a stark reminder of the unpredictable and devastating power of nature, leading to a reevaluation of Roman attitudes towards natural disasters. The event spurred discussions on disaster preparedness, urban planning, and the role of government in ensuring the safety and well-being of its citizens.
Furthermore, the tragic fate of Pompeii found resonance in Roman art and literature, inspiring poignant depictions of loss, resilience, and the fragility of human civilization. Artists and writers drew upon the haunting imagery of the buried city to convey themes of mortality, impermanence, and the relentless march of time.
The ruins of Pompeii also influenced architectural styles and urban design in the Roman world, serving as a cautionary tale against unchecked expansion and inadequate infrastructure. The meticulous preservation of the city's remains offered valuable insights into Roman engineering, construction techniques, and city planning, shaping future architectural practices.
Moreover, the rediscovery of Pompeii in the 18th century sparked a renewed interest in ancient history and archaeology, leading to significant advancements in the study of Roman civilization. The excavation of Pompeii's streets, homes, and public buildings provided a tangible connection to the past, fostering a deeper understanding of Roman society and culture.
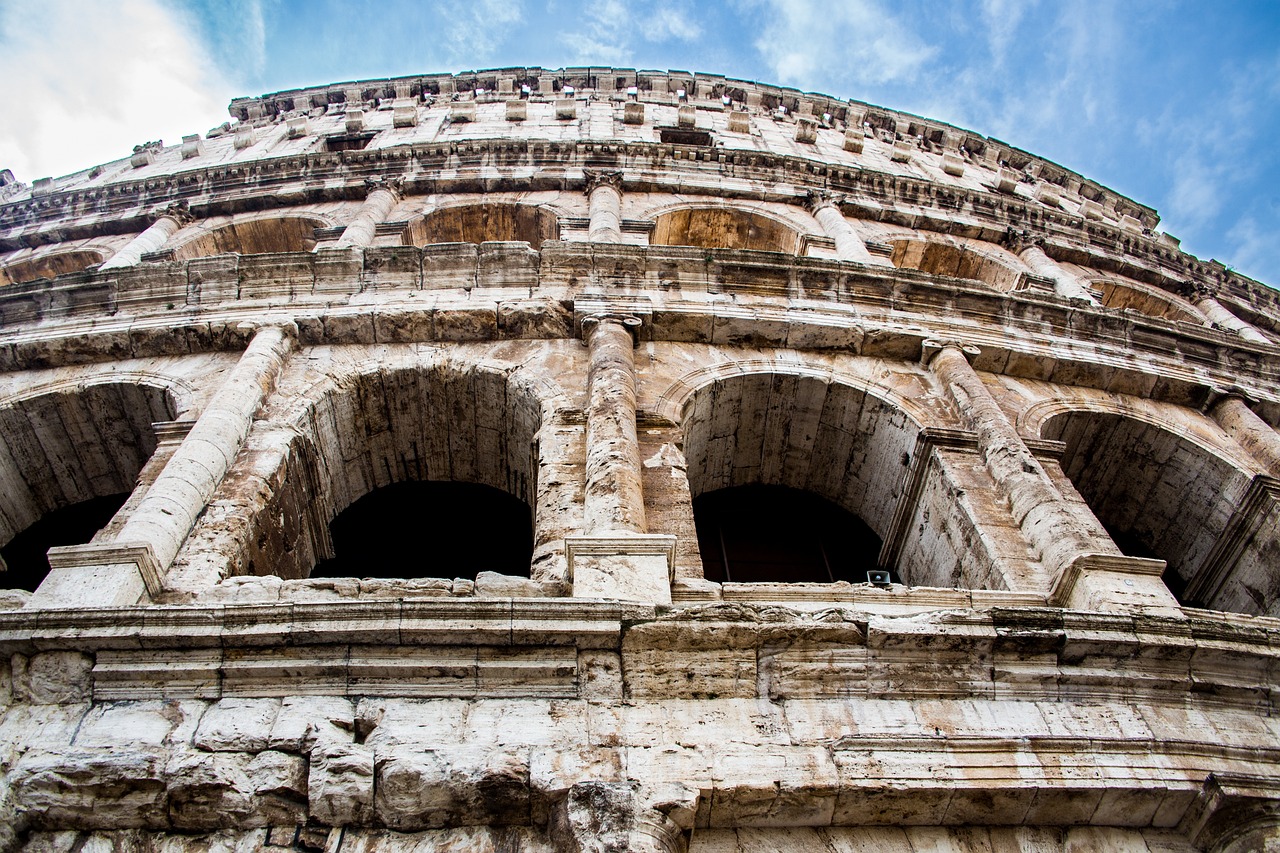

Modern Preservation Efforts
Modern preservation efforts at Pompeii are a delicate balance between conserving the ancient ruins and ensuring their accessibility to the public. The site faces numerous challenges, including environmental factors, tourism impact, and the need for ongoing restoration work. One of the key strategies employed is the use of innovative technologies to monitor and protect the fragile structures from further decay.
Archaeologists and conservationists work tirelessly to stabilize the excavated buildings, frescoes, and artifacts to prevent further deterioration. Advanced techniques such as laser scanning, 3D modeling, and digital mapping are utilized to document the site comprehensively and aid in conservation planning. These methods allow experts to monitor changes in the structures over time and develop targeted intervention strategies.
In addition to technological advancements, preservation efforts also rely on traditional conservation methods and materials. Skilled craftsmen meticulously restore damaged mosaics, sculptures, and wall paintings to their former glory, using historical techniques and authentic materials. The goal is to maintain the authenticity of the ancient city while ensuring its structural integrity for future generations to appreciate.
Furthermore, educational programs and community engagement initiatives play a crucial role in raising awareness about the importance of preserving Pompeii. Local residents, schools, and volunteers are involved in various conservation projects, fostering a sense of ownership and pride in safeguarding this invaluable cultural heritage.
Collaboration with international organizations and experts in the field of heritage conservation also contributes to the long-term sustainability of Pompeii. Knowledge sharing, best practices exchange, and joint research projects help enhance the preservation efforts and ensure that the site remains a beacon of ancient history for years to come.
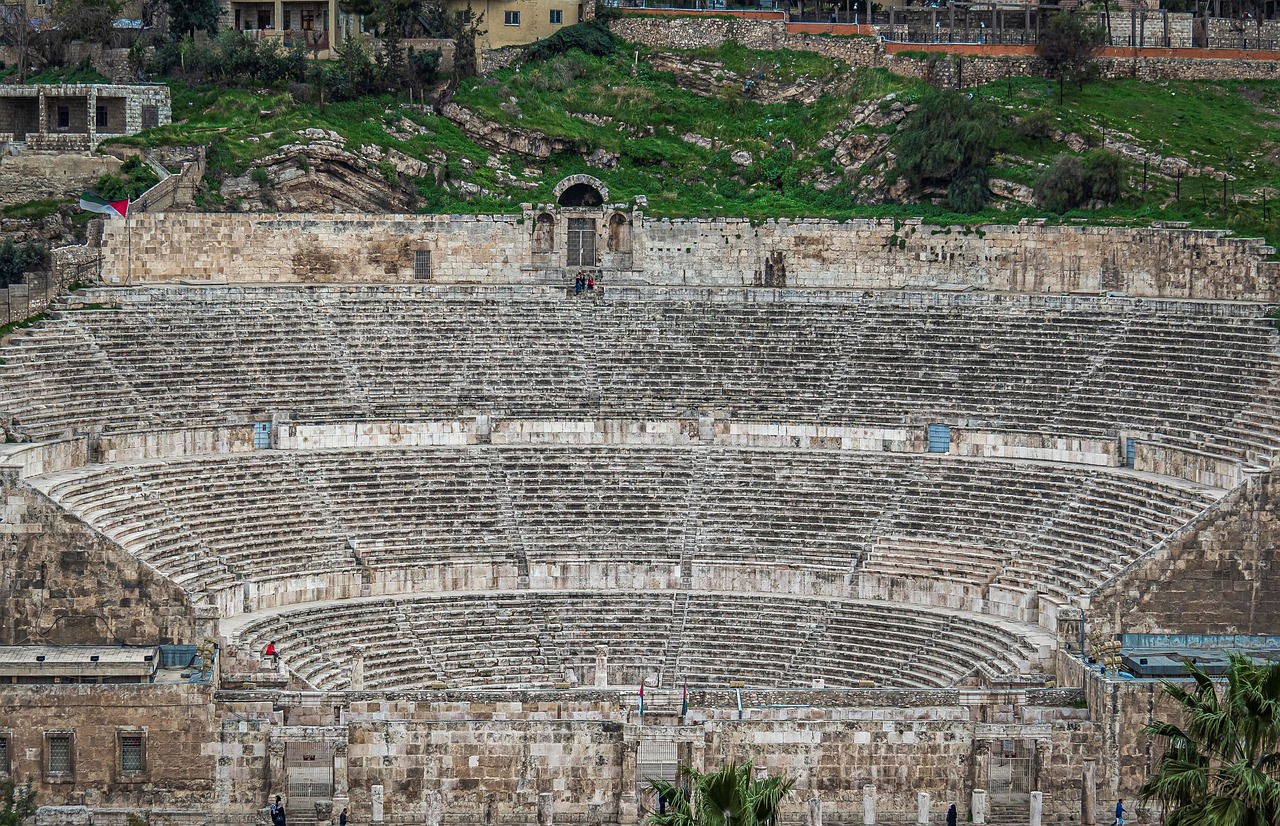

Tourism and Cultural Significance
When it comes to tourism and cultural significance, Pompeii stands as a beacon of ancient history and archaeological wonder. Visitors from around the world flock to this UNESCO World Heritage Site to walk in the footsteps of ancient Romans and witness firsthand the tragic yet captivating story of Pompeii's destruction and preservation.
The tourism industry surrounding Pompeii has flourished, offering guided tours, educational exhibits, and immersive experiences that bring the city's past to life. From the haunting remains of the Forum to the well-preserved frescoes in the House of the Vettii, every corner of Pompeii holds a piece of history waiting to be discovered.
However, with great tourism comes great responsibility. The delicate balance between preservation and public access is a constant challenge faced by authorities and conservationists. Efforts to protect the ruins from wear and tear while ensuring a meaningful experience for visitors require innovative strategies and careful planning.
Moreover, the cultural significance of Pompeii extends beyond its archaeological value. The city's tragic fate serves as a poignant reminder of the unpredictable forces of nature and the fragility of human civilization. Artists, writers, and scholars have drawn inspiration from Pompeii's story, creating works that immortalize the city's legacy in the annals of history.
Ultimately, Pompeii's tourism and cultural significance offer a unique opportunity to engage with the past, contemplate the complexities of ancient societies, and reflect on the enduring impact of natural disasters on human history.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the history of Pompeii?
The ancient city of Pompeii was founded by the Oscan people and later became a thriving Roman city. It met its tragic end in 79 AD when Mount Vesuvius erupted, burying the city under layers of ash and preserving it for centuries.
- What can visitors see in Pompeii today?
Visitors to Pompeii can explore well-preserved ruins, including temples, theaters, villas, and even ancient graffiti on the walls. The city offers a unique glimpse into daily life in ancient Rome.
- How were the excavations of Pompeii conducted?
Excavations of Pompeii began in the 18th century and have continued to this day. Archaeologists carefully unearthed the city, revealing artifacts, mosaics, and even the remains of its unfortunate inhabitants.
- What caused the destruction of Pompeii?
The catastrophic eruption of Mount Vesuvius spewed ash and pumice over Pompeii, causing buildings to collapse and trapping its residents. The city was abandoned and forgotten until its rediscovery centuries later.



















