The Mystery of the Ancient Greek Philosopher Pythagoras
Pythagoras, a name that resonates through the corridors of time, holds within it a veil of mystery that captivates the curious minds of scholars and enthusiasts alike. Born in ancient Greece, this enigmatic philosopher and mathematician left a legacy shrouded in intrigue and intellectual prowess. As we embark on a journey to unravel the enigma that is Pythagoras, we are drawn into a realm where numbers dance with the divine, and philosophy intertwines with the fabric of reality.

Early Life and Education
Pythagoras, one of the most enigmatic figures in ancient Greek philosophy and mathematics, was believed to have been born around 570 BC on the island of Samos. Little is known about his early life, with some accounts suggesting that he traveled extensively in his youth, visiting Egypt and other centers of learning to acquire knowledge and wisdom. Growing up in a society rich in intellectual pursuits, Pythagoras showed a keen interest in mathematics and philosophy from a young age, laying the foundation for his future teachings and theories.
His education was diverse and extensive, encompassing a wide range of subjects including mathematics, music, astronomy, and metaphysics. Pythagoras is said to have studied under various teachers, absorbing their teachings and incorporating them into his own philosophical framework. His travels and interactions with different cultures and schools of thought contributed to the development of his unique philosophical beliefs and mathematical insights.
Despite the scarcity of historical records detailing his formal education, Pythagoras' deep understanding of numbers, geometry, and the natural world suggests a rigorous and comprehensive training in both theoretical and practical disciplines. His early years were marked by a thirst for knowledge and a relentless pursuit of truth, shaping the intellectual foundations upon which his later teachings would be built.

Philosophical Beliefs
Exploring the life, teachings, and enigmatic legacy of Pythagoras, a revered figure in ancient Greek philosophy and mathematics, whose contributions continue to influence various fields of study today.
Delving into the obscure details surrounding Pythagoras' birth, upbringing, and the philosophical and mathematical knowledge he acquired during his formative years.
Pythagoras was not merely a mathematician but also a profound philosopher, delving into the depths of metaphysics and ethics. His philosophical beliefs were as enigmatic as his mathematical theorems. He saw mathematics as the language of the universe, a key to understanding the fundamental principles that govern our reality. For Pythagoras, numbers held a mystical significance, representing the harmony and order of the cosmos. He believed in the immortality of the soul, viewing life as a journey towards the purification and liberation of the spirit. Pythagoras' philosophical musings continue to intrigue and inspire thinkers across the ages, prompting deep reflections on the nature of existence and the interconnectedness of all things.
Unraveling the significance and applications of the famous Pythagorean theorem in geometry, a mathematical principle attributed to Pythagoras and his followers.
Investigating the secretive nature of the Pythagorean brotherhood, its rituals, teachings on numerology, music theory, and the influence it had on ancient Greek society.
Exploring Pythagoras' mathematical discoveries, such as the theory of proportions, geometric theorems, and his influence on the development of Greek mathematics.
Discussing the concept of the Golden Ratio, its prevalence in nature, art, and architecture, and its association with Pythagoras and his mathematical principles.
Analyzing the enduring impact of Pythagoras' teachings on philosophy, mathematics, science, and the arts, highlighting how his ideas have shaped intellectual thought throughout history.
Examining contemporary perspectives on Pythagoras' legacy, including reinterpretations of his teachings in the context of modern science, spirituality, and philosophy.
Stay tuned for answers to common queries about Pythagoras and his teachings!

Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean Theorem is one of the most famous and fundamental principles in geometry, attributed to the ancient Greek philosopher Pythagoras and his followers. This theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. In mathematical terms, it can be expressed as a² + b² c², where 'a' and 'b' represent the lengths of the two shorter sides, and 'c' represents the length of the hypotenuse.
Imagine a right triangle where you have one side that is 3 units long and another side that is 4 units long. According to the Pythagorean Theorem, the square of the hypotenuse should be equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. Therefore, 3² + 4² 5². This simplifies to 9 + 16 25, which is indeed true, as 25 is the square of 5.
The Pythagorean Theorem has numerous practical applications in various fields, including architecture, engineering, physics, and even computer graphics. It provides a fundamental relationship that allows for the calculation of distances, the determination of angles, and the verification of shapes in a geometric context.

Secret Society and Teachings
Delving into the mysterious realm of Pythagoras' teachings unveils a world shrouded in secrecy and intellectual depth. Central to his enigmatic legacy is the existence of the Pythagorean brotherhood, a clandestine society known for its esoteric rituals and profound philosophical insights. Within the confines of this exclusive group, Pythagoras imparted his teachings on numerology, music theory, and the interconnectedness of mathematics with the fabric of the universe.
Imagine a hidden sanctuary where disciples gathered to unravel the mysteries of numbers, exploring their symbolic meanings and cosmic significance. The teachings of Pythagoras went beyond mere mathematical equations; they delved into the very essence of reality, seeking to uncover the harmonious relationships that governed the natural world.
Through the lens of Pythagorean philosophy, numbers were not mere tools for calculation but gateways to profound truths about existence. The brotherhood's emphasis on numerical symbolism and the mystical properties of numbers reflected Pythagoras' belief in the divine nature of mathematics, viewing it as a sacred language that unlocked the secrets of the universe.
As initiates delved deeper into the teachings of Pythagoras, they discovered a world where music was not just an art form but a manifestation of cosmic harmony. The Pythagorean concept of the "music of the spheres" posited that celestial bodies moved in accordance with mathematical ratios, producing a celestial symphony that resonated throughout the cosmos.
The influence of the Pythagorean brotherhood extended beyond the realm of mathematics and philosophy, permeating ancient Greek society with its teachings on ethics, virtue, and the pursuit of knowledge. By embracing a life of contemplation and intellectual inquiry, Pythagoras and his followers sought to elevate the human spirit and cultivate a deeper understanding of the interconnectedness of all things.
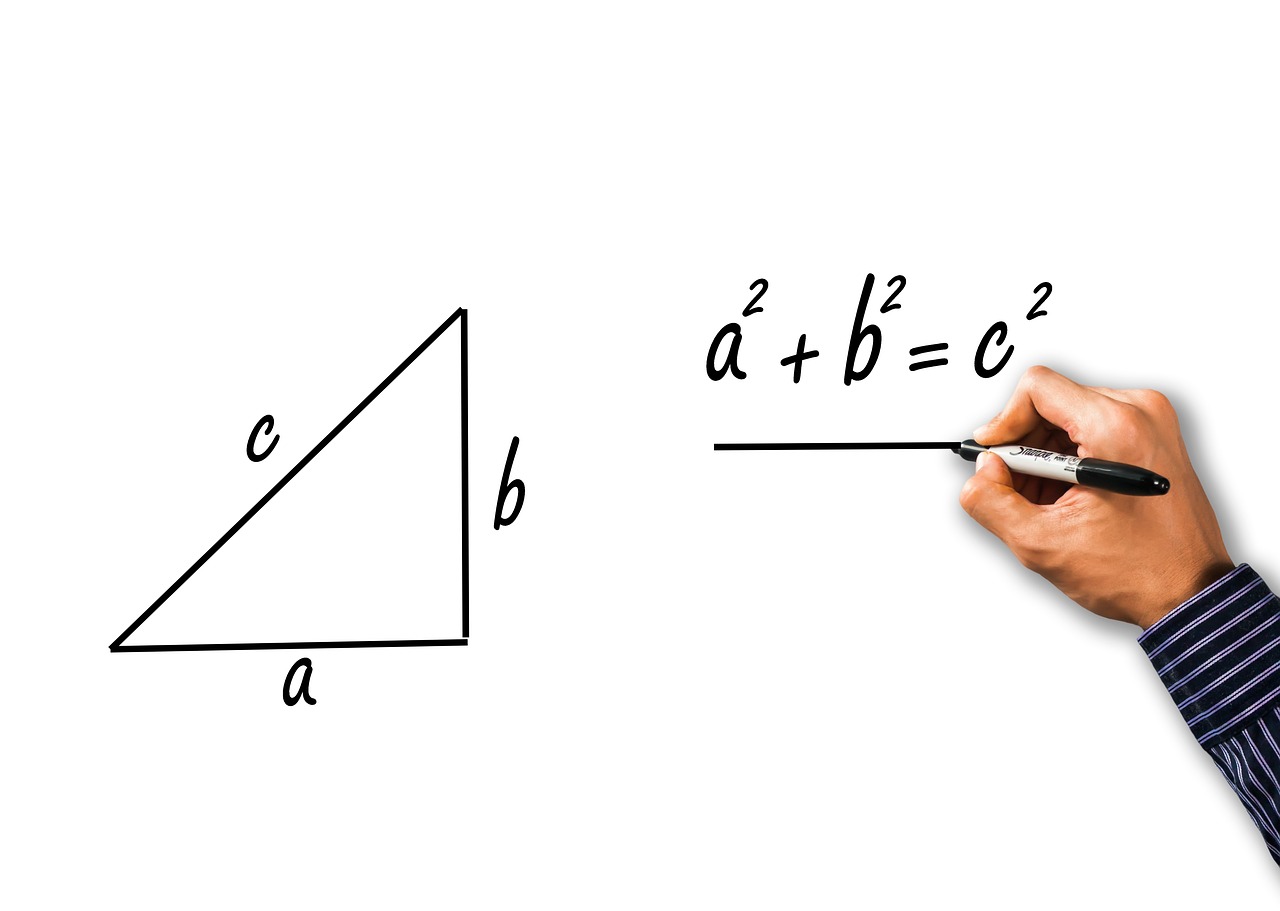
Mathematical Contributions
Pythagoras, the ancient Greek philosopher and mathematician, made significant mathematical contributions that laid the foundation for future developments in the field. One of his notable achievements was the theory of proportions, which revolutionized the understanding of numerical relationships. Through his work, Pythagoras introduced geometric theorems that expanded the knowledge of shapes and spatial relationships.
Furthermore, Pythagoras' influence extended to the realm of Greek mathematics, where his teachings inspired generations of scholars to explore the intricacies of numbers and geometric principles. His emphasis on the importance of mathematical reasoning and deduction paved the way for advancements in mathematical theory and practice.
In addition to his theoretical contributions, Pythagoras also delved into practical applications of mathematics, demonstrating the relevance of mathematical concepts in everyday life. His insights into the mathematical underpinnings of music and harmonics showcased the interconnectedness of mathematics and the arts, highlighting the universal nature of mathematical principles.
Moreover, Pythagoras' mathematical legacy transcended his own time, influencing subsequent mathematical developments and shaping the course of mathematical history. His innovative approach to problem-solving and his dedication to exploring the mysteries of numbers continue to inspire mathematicians and scholars to this day.

The Golden Ratio
The Golden Ratio, often symbolized by the Greek letter phi (φ), is a mathematical concept that has captivated the minds of artists, architects, and mathematicians for centuries. This ratio, approximately equal to 1.618, is considered aesthetically pleasing and harmonious to the human eye, leading to its widespread use in art, design, and even nature itself. The Golden Ratio is found in various natural phenomena, from the spiral arrangements of shells to the branching patterns of trees, showcasing its ubiquity in the world around us.
Pythagoras, the ancient Greek philosopher and mathematician, is often associated with the Golden Ratio due to its mathematical significance and aesthetic appeal. The ratio's prevalence in the Parthenon's architecture in ancient Greece and the works of renowned artists like Leonardo da Vinci further solidify its reputation as a symbol of beauty and balance.
Mathematically, the Golden Ratio exhibits unique properties that make it intriguing to mathematicians and artists alike. It appears in the Fibonacci sequence, where each number is the sum of the two preceding ones, creating a spiral that approximates the Golden Ratio. This spiral, known as the Fibonacci spiral, is a visual representation of the ratio's harmonious proportions and infinite nature.
Furthermore, the Golden Ratio is not merely a mathematical curiosity but a guiding principle in design and composition. Artists and architects have utilized the ratio to create visually appealing compositions that resonate with viewers on a subconscious level. By incorporating the Golden Ratio into their works, creators seek to evoke a sense of balance, harmony, and beauty that transcends cultural and temporal boundaries.
In conclusion, the Golden Ratio stands as a testament to the interconnectedness of mathematics, art, and nature. Its allure lies in its ability to bridge the gap between the abstract realm of numbers and the tangible world of aesthetics, inspiring generations of thinkers and creators to seek harmony and proportion in their endeavors.

Legacy and Influence
Pythagoras' legacy is a tapestry woven with threads of wisdom, mystery, and innovation that continues to captivate minds across centuries. His influence transcends time, leaving an indelible mark on the realms of philosophy, mathematics, science, and the arts. The enigmatic figure of Pythagoras, shrouded in myth and legend, stands as a beacon of intellectual curiosity and exploration.
Through his teachings, Pythagoras instilled a reverence for the interconnectedness of numbers, shapes, and the universe, fostering a holistic approach to knowledge that resonates to this day. His philosophical musings on the immortality of the soul and the harmony of the cosmos echo through the corridors of intellectual discourse, inspiring generations of thinkers to ponder the profound mysteries of existence.
One of Pythagoras' most enduring contributions is the eponymous Pythagorean theorem, a fundamental principle in geometry that unlocks the secrets of right-angled triangles. This theorem, a cornerstone of mathematical understanding, serves as a testament to Pythagoras' keen insight and analytical prowess, showcasing his ability to unravel the mysteries of the physical world through mathematical abstraction.
Furthermore, Pythagoras' exploration of the Golden Ratio, a mathematical proportion revered for its aesthetic appeal and prevalence in nature, has left an indelible mark on the fields of art, architecture, and design. The allure of this divine ratio, embodied in the spirals of seashells and the petals of flowers, speaks to the universal harmony embedded in the fabric of creation, a concept that Pythagoras held dear in his philosophical and mathematical pursuits.
As we gaze upon the legacy of Pythagoras, we are reminded of the transformative power of ideas, the enduring legacy of intellectual inquiry, and the timeless quest for knowledge that defines the human experience. His influence, like a ripple in the vast ocean of human thought, continues to inspire, challenge, and provoke us to seek deeper truths and contemplate the mysteries that lie beyond the veil of perception.
Modern Interpretations
Modern Interpretations of Pythagoras' teachings have sparked a diverse range of perspectives and applications in contemporary society. While Pythagoras' influence originated in ancient Greece, his ideas continue to resonate with modern thinkers across various disciplines. One notable reinterpretation involves the integration of Pythagorean principles into the realm of spirituality and self-discovery. Many individuals today draw parallels between Pythagorean concepts of harmony and balance with practices such as meditation and holistic healing.
Furthermore, Pythagoras' mathematical theories have found new relevance in fields such as architecture and design. Architects and artists often reference the Golden Ratio, a concept closely associated with Pythagoras, to create aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound compositions. The enduring appeal of the Golden Ratio lies in its mathematical precision and its perceived connection to natural beauty.
In the realm of science, Pythagorean principles have influenced theories of symmetry and order in the natural world. Scientists and researchers continue to explore the mathematical patterns and relationships championed by Pythagoras, seeking to uncover universal truths that govern the cosmos. The legacy of Pythagoras serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of mathematics, philosophy, and the physical world.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Who was Pythagoras and why is he important?
Pythagoras was an ancient Greek philosopher and mathematician known for his contributions to various fields of study, including mathematics, philosophy, and music theory. He is famous for the Pythagorean theorem and his beliefs in the immortality of the soul. Pythagoras' teachings have had a lasting impact on intellectual thought throughout history.
- What is the Pythagorean theorem?
The Pythagorean theorem is a fundamental principle in geometry attributed to Pythagoras and his followers. It states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. This theorem has numerous applications in mathematics, science, and engineering.
- Did Pythagoras really have a secret society?
Yes, Pythagoras is believed to have founded a secretive brotherhood known as the Pythagoreans. This society was known for its strict rules, rituals, and teachings on subjects like numerology, music theory, and ethical principles. The Pythagoreans had a significant influence on ancient Greek society and philosophy.
- What is the Golden Ratio and why is it associated with Pythagoras?
The Golden Ratio is a mathematical ratio that appears in nature, art, and architecture, often denoted by the Greek letter phi (φ). It is closely linked to Pythagoras due to its prevalence in geometric proportions and aesthetics. Pythagoras and his followers studied the Golden Ratio and its applications in various disciplines.
- How has Pythagoras' legacy influenced modern interpretations?
Pythagoras' legacy continues to inspire contemporary perspectives in fields such as science, spirituality, and philosophy. His mathematical principles, philosophical beliefs, and ideas about harmony and balance have been reinterpreted in the context of modern knowledge, contributing to ongoing discussions on the interconnectedness of the universe.



















