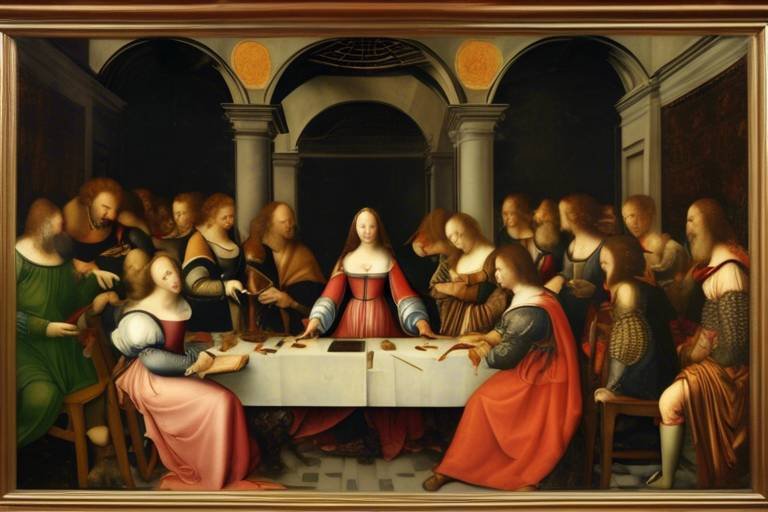
The Influence of the Renaissance on Art and Science
The Renaissance period stands as a pivotal juncture in human history, where creativity and knowledge intertwined to spark a revolution in art and science. This transformative era, spanning from the 14th to the 17th century, witnessed a surge of innovation and exploration that reshaped the trajectory of human civilization.
Artists of the Renaissance, such as the legendary Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo, pioneered revolutionary techniques and styles that continue to inspire awe and admiration centuries later. Their masterpieces not only captured the essence of human emotion and beauty but also pushed the boundaries of artistic expression to new heights.
Simultaneously, the Renaissance ushered in a scientific revolution led by visionaries like Copernicus and Galileo, who dared to challenge conventional wisdom and explore the mysteries of the cosmos. Through their groundbreaking discoveries and observations, these trailblazers laid the foundation for modern science and transformed our understanding of the universe.
One of the most remarkable aspects of the Renaissance was the seamless integration of art and science, where boundaries between disciplines blurred to foster interdisciplinary innovations. This cross-pollination of ideas and methods led to remarkable advancements in both fields, enriching human knowledge and creativity.
Central to the Renaissance ethos was humanism, a philosophy that celebrated the inherent dignity and worth of the individual. This human-centered approach permeated artistic expression and scientific inquiry, emphasizing the importance of empirical observation and critical thinking in the pursuit of truth.
Artists of the Renaissance, driven by a fascination with the human form, undertook detailed anatomical studies and dissections that deepened our understanding of the human body. Their meticulous drawings and observations not only enriched artistic representation but also contributed significantly to the field of anatomy and medical science.
Moreover, the Renaissance witnessed the development of new scientific instruments that revolutionized the way we perceive the world. From the telescope to the microscope, these innovative tools enabled scientists to make groundbreaking discoveries and unravel the mysteries of the natural world.
Behind the flourishing of art and science during the Renaissance stood wealthy patrons who generously supported artists and scientists in their creative endeavors. Their patronage not only fueled the production of masterpieces but also nurtured a culture of innovation and exploration that defined the era.
The legacy of the Renaissance endures to this day, shaping the realms of art, science, and society in profound ways. The spirit of curiosity, creativity, and humanism that defined this remarkable period continues to inspire and influence generations of artists, scientists, and thinkers, leaving an indelible mark on the fabric of human civilization.

Renaissance Art Innovations
Exploring how the Renaissance period catalyzed advancements in both art and science, shaping the trajectory of human creativity and knowledge.
During the Renaissance, artists embarked on a journey of innovation and creativity that transformed the art world forever. Visionaries like Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo pioneered revolutionary techniques and styles that continue to inspire and awe us today. Their mastery of light, perspective, and anatomy elevated art to new heights, capturing the essence of human emotion and beauty on canvas like never before.
Leonardo da Vinci, known for his iconic works such as the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper, delved into the realms of science and art, seamlessly blending the two disciplines. His meticulous attention to detail and unparalleled skill in capturing human expression set a standard that artists aspire to even centuries later. Michelangelo, on the other hand, sculpted masterpieces like David and the Sistine Chapel ceiling, showcasing the power and grace of the human form in ways previously unseen.
The Renaissance era was a time of experimentation and bold artistic expression, with artists pushing boundaries and challenging conventions. Techniques like sfumato, chiaroscuro, and perspective transformed the way we perceive art, inviting viewers to immerse themselves in rich, lifelike compositions that seemed to leap off the canvas.
Artists of the Renaissance not only captured the external world with unparalleled precision but also delved into the depths of human emotion and spirituality, infusing their works with layers of meaning and symbolism. The era marked a profound shift in artistic philosophy, emphasizing individual creativity, expression, and the celebration of human potential.
Through their innovations and daring spirit, Renaissance artists laid the foundation for future generations, inspiring countless creators to explore new horizons and push the boundaries of artistic possibility.

Renaissance Scientific Revolution
The Renaissance period was not only a time of artistic flourishing but also a pivotal moment in the history of science. Visionaries like Copernicus and Galileo spearheaded a scientific revolution that challenged existing beliefs and paved the way for modern scientific inquiry. These bold thinkers dared to look beyond the conventional wisdom of their time, gazing up at the stars and unlocking the mysteries of the universe.
One of the key aspects of the Renaissance Scientific Revolution was the emphasis on observation and experimentation. Instead of relying solely on ancient texts and traditional teachings, scientists began to conduct their own investigations, testing hypotheses and refining their understanding of the natural world. This hands-on approach marked a significant departure from the dogma that had long dominated scientific thought.
Through the development of new tools and instruments, such as the telescope and the astrolabe, Renaissance scientists were able to make groundbreaking discoveries that forever altered our perception of the cosmos. Galileo's observations of the moons of Jupiter and the phases of Venus, for example, provided compelling evidence for the heliocentric model of the solar system proposed by Copernicus.
Moreover, the Renaissance Scientific Revolution was not confined to astronomy alone. Scholars across various disciplines, from mathematics to anatomy, made significant contributions that laid the foundation for modern science. The era saw advancements in fields such as biology, chemistry, and physics, setting the stage for the scientific breakthroughs that would follow in the centuries to come.
By challenging the prevailing orthodoxy and embracing a spirit of inquiry and discovery, the pioneers of the Renaissance Scientific Revolution ushered in a new era of intellectual exploration and innovation. Their legacy continues to inspire scientists and scholars to push the boundaries of knowledge, reminding us of the transformative power of curiosity and critical thinking.

Integration of Art and Science
Art and science, two seemingly distinct disciplines, found a harmonious union during the Renaissance, igniting a spark of creativity that illuminated the path of human progress. Imagine a canvas where brushstrokes of artistic expression intertwine with the precise lines of scientific inquiry, creating a masterpiece of innovation and discovery. The Renaissance era witnessed a profound integration of art and science, where artists and scientists collaborated and drew inspiration from each other's work. This fusion of creativity and rationality gave birth to groundbreaking ideas and inventions that transcended traditional boundaries.
One notable example of this integration is the work of Leonardo da Vinci, a polymath whose genius spanned across art and science. Da Vinci's anatomical drawings not only captured the beauty of the human form but also provided invaluable insights into the intricacies of the human body. His meticulous observations laid the foundation for modern anatomy studies, bridging the gap between artistic representation and scientific exploration. Similarly, the celestial observations of astronomers like Galileo Galilei were not merely scientific endeavors but also artistic pursuits, as they sought to unveil the beauty and order of the cosmos through their telescopic observations.
The Renaissance period encouraged a holistic approach to knowledge, where artists and scientists collaborated on projects that encompassed both artistic and scientific elements. This interdisciplinary approach gave rise to innovations such as perspective in art, which mirrored the precision and depth of scientific observation. The blending of art and science during the Renaissance not only enriched the creative landscape but also paved the way for future generations to explore the interconnectedness of different fields of study.
In essence, the integration of art and science during the Renaissance was not just a convergence of disciplines but a celebration of human ingenuity and curiosity. It exemplified the power of collaboration and cross-pollination of ideas, demonstrating that when art and science intertwine, the possibilities are limitless. The legacy of this integration continues to inspire and influence contemporary artists and scientists, reminding us of the transformative impact that creativity and knowledge can have when they work hand in hand.

Renaissance Humanism
Renaissance Humanism, a pivotal aspect of the Renaissance period, delved into the profound exploration of human potential and capabilities. It was a philosophical movement that emphasized the importance of human values, achievements, and dignity. Imagine a tapestry where artistry and intellect intertwine seamlessly, creating a vibrant mosaic of human experience. Artists and scientists alike were inspired by the belief in the boundless potential of humanity, shaping their works with a deep appreciation for the human form and intellect.
Humanism during the Renaissance era encouraged a shift towards individualism and critical thinking, fostering a culture that celebrated human creativity and rational inquiry. It was a time when the human spirit soared, reaching new heights of artistic expression and scientific discovery. Think of it as a symphony where each note represents a unique aspect of human existence, harmonizing to create a masterpiece of innovation and enlightenment.
Artists such as Leonardo da Vinci embodied the essence of Renaissance Humanism, infusing their works with a profound understanding of human anatomy and emotion. Scientists like Galileo Galilei embraced humanist ideals by challenging traditional beliefs and expanding the boundaries of knowledge. The Renaissance Humanism movement paved the way for a renaissance of the human spirit, igniting a spark of curiosity and creativity that continues to inspire us today.

Impact on Anatomy Studies
During the Renaissance, the study of anatomy experienced a profound transformation, thanks to the meticulous anatomical drawings and dissections carried out by artists such as Leonardo da Vinci. These detailed illustrations not only captured the intricacies of the human body but also provided valuable insights for medical practitioners and scientists. By merging artistry with scientific inquiry, artists like da Vinci revolutionized the understanding of human anatomy, laying the groundwork for modern anatomical studies.
Scientific Instruments Development
Exploring how the Renaissance period catalyzed advancements in both art and science, shaping the trajectory of human creativity and knowledge.
Discovering the revolutionary techniques and styles developed by artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo during the Renaissance.
Examining how figures such as Copernicus and Galileo challenged traditional beliefs and laid the foundation for modern science.
Exploring how the Renaissance era blurred the lines between art and science, leading to interdisciplinary innovations.
Understanding the human-centered approach of the Renaissance that influenced both artistic expression and scientific inquiry.
Investigating how artists' anatomical drawings and dissections influenced the understanding of the human body in science.
During the Renaissance, the development of scientific instruments marked a significant leap forward in the pursuit of knowledge. Innovations in instrument-making allowed scientists to observe the world with newfound clarity and precision. From the invention of the telescope by Galileo Galilei to the refinement of the microscope, these tools revolutionized scientific exploration. The ability to magnify and analyze objects at a microscopic and macroscopic level opened up new frontiers of discovery, enabling researchers to delve deeper into the mysteries of the natural world.
Discussing the role of wealthy patrons in fostering artistic and scientific endeavors during the Renaissance.
Reflecting on how the innovations of the Renaissance continue to shape art, science, and society in the modern world.
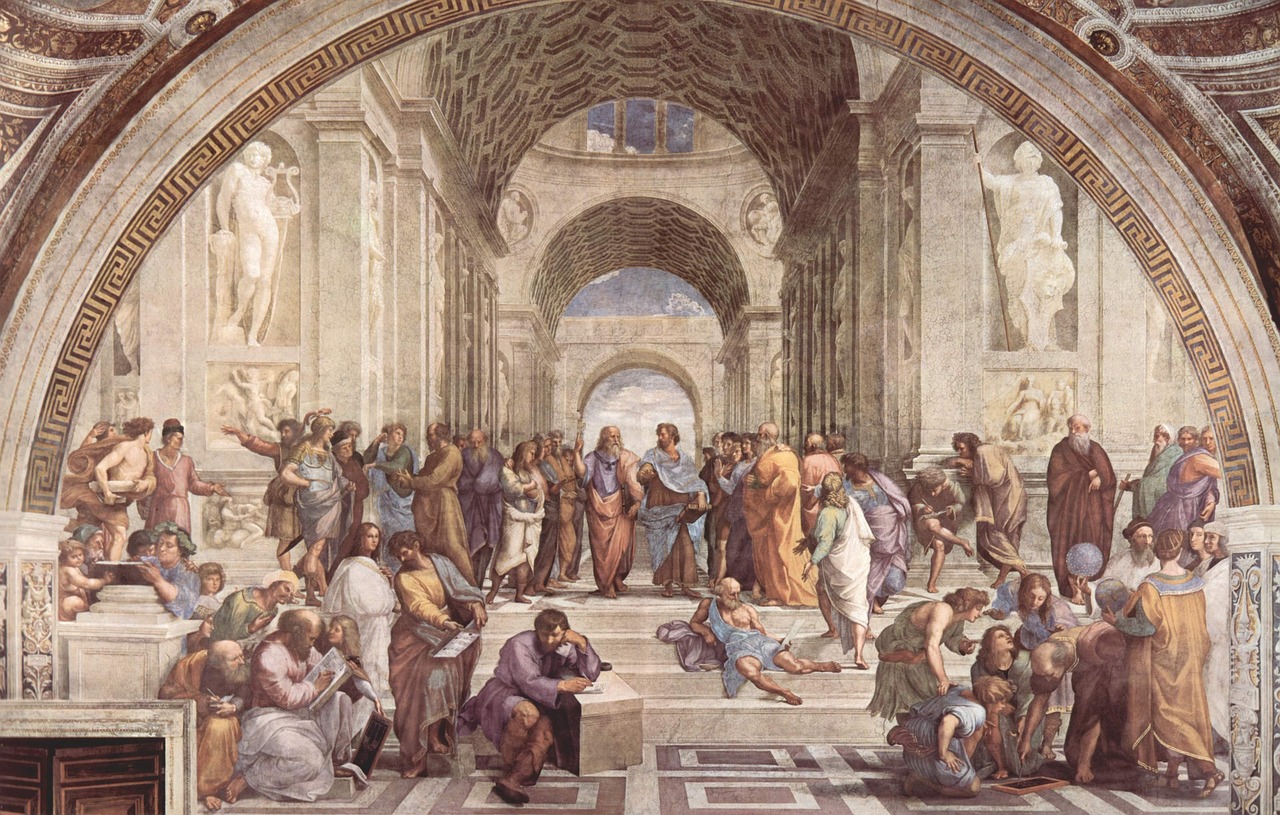

Renaissance Artistic Patronage
Renaissance Artistic Patronage played a pivotal role in fueling the flourishing art and scientific endeavors of the Renaissance period. Wealthy patrons, including powerful rulers, aristocrats, and influential families, provided financial support and commissioned artworks that propelled artistic innovation and scientific exploration. These patrons not only funded the creations of renowned artists such as Leonardo da Vinci and Raphael but also encouraged experimentation and creativity in both art and science.
One notable example of Renaissance Artistic Patronage is the Medici family of Florence, known for their unwavering support of artists, scientists, and scholars. Through their patronage, the Medici family transformed Florence into a vibrant hub of artistic and intellectual activity, attracting some of the most talented minds of the time. Artists like Botticelli and Michelangelo found patronage under the Medici, allowing them to produce masterpieces that continue to captivate audiences today.
Moreover, the patronage system of the Renaissance era fostered close collaborations between artists and scientists, leading to cross-disciplinary innovations. Artists often worked closely with anatomists and naturalists, incorporating scientific knowledge into their artworks. This intersection of art and science not only enriched artistic expression but also advanced scientific understanding, laying the groundwork for future discoveries.
Furthermore, the support of patrons extended beyond financial assistance to include intellectual stimulation and social connections. Patrons provided artists and scientists with access to resources, materials, and networks that were essential for their creative pursuits. The relationships forged between patrons and creatives cultivated a culture of exchange and collaboration, driving forward the progress of both art and science.
In essence, Renaissance Artistic Patronage was more than just financial backing; it was a catalyst for innovation and cultural transformation. The patronage system of the Renaissance nurtured a fertile environment where creativity thrived, leading to the remarkable achievements that continue to inspire and influence the world today.

Legacy of the Renaissance
The continues to reverberate through the corridors of time, leaving an indelible mark on the realms of art, science, and society. The innovative spirit that characterized the Renaissance era, with its fervent pursuit of knowledge and creativity, has paved the way for modern advancements and cultural evolution.
Artistically, the Renaissance legacy manifests in the enduring masterpieces that adorn museums and galleries worldwide. The works of iconic figures such as Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael serve as timeless reminders of the period's artistic brilliance and technical mastery. The emphasis on realism, perspective, and human emotion in Renaissance art set a standard that continues to inspire contemporary artists.
Scientifically, the legacy of the Renaissance is equally profound. The empirical approach championed by pioneers like Copernicus and Galileo laid the foundation for modern scientific inquiry. Their bold challenges to prevailing beliefs about the cosmos and the nature of reality sparked a scientific revolution that continues to shape our understanding of the universe.
The interdisciplinary nature of Renaissance innovation, which saw artists collaborating with scientists and philosophers, has left a lasting impact on the way we approach knowledge and discovery. The integration of art and science during the Renaissance not only led to groundbreaking advancements in fields such as anatomy and optics but also fostered a holistic view of the world that transcends traditional disciplinary boundaries.
Moreover, the legacy of the Renaissance extends to the societal realm, influencing concepts of individualism, humanism, and cultural patronage. The emphasis on human potential and the celebration of human achievement that characterized the Renaissance era continue to resonate in contemporary society, shaping our values, aspirations, and understanding of the human experience.
In essence, the Legacy of the Renaissance serves as a testament to the enduring power of human creativity, curiosity, and ingenuity. It reminds us that through bold exploration, collaboration, and a relentless pursuit of excellence, we can push the boundaries of knowledge and imagination, leaving a lasting legacy for future generations to build upon.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What were some key innovations in Renaissance art?
In Renaissance art, notable innovations included the use of perspective to create depth in paintings, the development of chiaroscuro to depict light and shadow realistically, and the exploration of human anatomy in detail.
- How did the Renaissance impact scientific progress?
The Renaissance significantly influenced scientific progress by promoting empirical observation, experimentation, and the questioning of traditional beliefs. This led to groundbreaking discoveries in fields such as astronomy, anatomy, and physics.
- What is the significance of the integration of art and science during the Renaissance?
The integration of art and science in the Renaissance era fostered interdisciplinary collaborations and innovations. Artists and scientists worked together, sharing knowledge and techniques, resulting in advancements that continue to influence modern creativity and scientific inquiry.
- How did Renaissance humanism contribute to artistic and scientific developments?
Renaissance humanism, with its focus on human potential and capabilities, inspired artists and scientists to explore new ideas and push boundaries. This human-centered approach encouraged the pursuit of knowledge in both artistic expression and scientific exploration.
- What role did artistic patronage play in the Renaissance?
Wealthy patrons in the Renaissance played a crucial role in supporting artists and scientists, providing financial backing and resources for creative endeavors. Their patronage enabled the flourishing of artistic and scientific achievements during this period.
- How does the legacy of the Renaissance continue to influence art, science, and society today?
The innovations and ideas of the Renaissance have left a lasting impact on art, science, and society, shaping our modern world. Concepts such as individualism, innovation, and the pursuit of knowledge continue to resonate in contemporary artistic and scientific practices.



















