The Decline of the Roman Empire - An Overview
The decline of the Roman Empire stands as a monumental event in world history, marking the unraveling of a once-mighty civilization that had dominated vast territories for centuries. The fall of Rome was not a sudden cataclysm but a gradual process shaped by a multitude of factors that culminated in its eventual collapse. Understanding the complexities of this decline is crucial in comprehending the lasting impact it has had on the world we live in today.
At the heart of the Roman Empire's downfall were the economic challenges that plagued its foundations. Issues such as rampant inflation, burdensome taxation, and the constant drain on resources caused by incessant warfare all contributed to the empire's financial woes, weakening its once robust economic structure.
Political instability further exacerbated the Empire's decline, with frequent changes in leadership, widespread corruption, and power struggles among competing factions creating a climate of uncertainty and discord. The inability to establish stable governance eroded the empire's ability to effectively govern its vast territories.
Analyzing the military weakness of the Roman Empire reveals a once formidable force that had become overstretched and vulnerable. Factors like overexpansion, difficulties in recruitment, and heavy reliance on mercenaries all played a role in the diminishing strength of Rome's legions, leaving the empire exposed to external threats.
Social unrest simmered within Roman society, fueled by deep-rooted issues such as class disparities, the pervasive institution of slavery, and a gradual erosion of traditional values and civic responsibilities. These internal tensions further weakened the fabric of Roman civilization.
The impact of barbarian invasions on the Roman Empire cannot be understated. The sack of Rome, the mass migrations of tribes, and the gradual erosion of imperial defenses all contributed to the destabilization of the empire, leading to its eventual fragmentation and collapse.
Religious changes also played a significant role in the decline of the Roman Empire, as the rise of Christianity and religious conflicts added another layer of complexity to an already tumultuous period. The influence of religion on societal norms and political dynamics further strained the empire's cohesion.
Cultural transformations within the Roman Empire marked a departure from traditional Roman values, as the adoption of foreign customs, a decline in artistic and literary achievements, and a loss of cultural identity all contributed to the weakening of the empire's cultural fabric.
Despite its eventual collapse, the Roman Empire's legacy endures through its contributions to law, language, architecture, and the valuable lessons learned from its demise. The echoes of Rome's glory and downfall continue to reverberate through the annals of history, shaping the world we inhabit today.

Economic Challenges
The economic challenges faced by the Roman Empire played a significant role in its eventual decline. One of the key issues was inflation, which led to a devaluation of the Roman currency and a decrease in its purchasing power. This economic instability affected all levels of society, from the wealthy elite to the common people, creating widespread financial uncertainty.
Additionally, the Roman Empire struggled with taxation problems, as the heavy tax burden placed on its citizens to fund its vast empire became unsustainable. High levels of taxation not only strained the economy but also fueled resentment among the population, leading to social unrest and dissatisfaction with the imperial government.
Constant warfare also took a toll on the Roman economy, draining valuable resources and manpower. The need to maintain a large military presence across its vast territories put a strain on the empire's finances, contributing to its economic difficulties. The cost of maintaining legions, fortifications, and supplies for military campaigns added to the financial burden already facing the empire.
In conclusion, the economic challenges faced by the Roman Empire, including inflation, taxation issues, and the strain of constant warfare, were significant factors that contributed to its eventual downfall. These financial struggles, combined with other internal and external pressures, weakened the empire's foundations and ultimately led to its collapse.

Political Instability
Political instability was a prominent factor in the decline of the Roman Empire, contributing significantly to its eventual downfall. The empire faced continuous turmoil as power struggles, corruption, and frequent changes in leadership plagued its governance.
The Roman political system, once a model of stability and efficiency, became increasingly fragmented and chaotic. Competing factions vied for control, leading to a series of civil wars and internal conflicts that weakened the empire from within.
Corruption also ran rampant within the political elite, with officials more concerned about personal gain than the well-being of the empire. This lack of integrity and accountability further eroded the trust of the citizens in their leaders, undermining the stability of the government.
Moreover, the constant turnover of emperors and rulers created a sense of uncertainty and unpredictability. Each new leader brought their own agenda and priorities, often resulting in abrupt policy changes and inconsistent governance that destabilized the empire.
As political instability continued to escalate, the Roman Empire struggled to maintain cohesion and unity, making it vulnerable to external threats and internal unrest. The lack of effective leadership and governance exacerbated other underlying issues, hastening the empire's decline.

Military Weakness
During its peak, the Roman military was a formidable force that conquered vast territories and maintained control over a vast empire. However, as time passed, the military strength of Rome began to wane, leading to significant weaknesses that contributed to the empire's decline. One of the key factors in the military weakness of the Roman Empire was the issue of overexpansion. The empire had stretched its resources thin by trying to control too much territory, making it difficult to defend its borders effectively.
Recruitment problems also plagued the Roman military. As the empire expanded, it became increasingly challenging to find enough qualified soldiers to fill the ranks. This led to a reliance on less experienced and less loyal troops, weakening the overall effectiveness of the army. Additionally, the use of mercenaries became more common, further undermining the cohesion and discipline of the Roman legions.
Furthermore, the Roman military faced internal challenges, including political interference in military matters and corruption within the ranks. Frequent changes in leadership meant that military decisions were often influenced by political considerations rather than strategic needs. This lack of consistency and clear direction hampered the effectiveness of Roman military campaigns.
Overall, the decline of the Roman military was a complex issue that stemmed from a combination of overexpansion, recruitment difficulties, reliance on mercenaries, and internal political turmoil. These weaknesses left the empire vulnerable to external threats and contributed to its eventual collapse.

Social Unrest
Social unrest played a significant role in the decline of the Roman Empire, creating internal tensions that weakened the fabric of society. The empire faced deep-rooted issues such as class inequality, where the gap between the wealthy elite and the impoverished masses widened, leading to widespread discontent among the lower classes. Slavery, a cornerstone of the Roman economy, also fueled social unrest as enslaved individuals endured harsh conditions and limited rights, fostering resentment and resistance.
Moreover, the erosion of traditional values and civic duty further exacerbated social divisions within the empire. As societal norms shifted and moral decay set in, the sense of community and shared purpose that had once bound Roman citizens together began to unravel. This breakdown in social cohesion made it increasingly challenging for the empire to address its mounting challenges effectively, as unity and collective action became elusive goals.

Barbarian Invasions
The marked a pivotal turning point in the history of the Roman Empire. These invasions, characterized by the incursions of various barbarian tribes into Roman territories, inflicted severe damage on the already weakened empire. The sack of Rome in 410 AD by the Visigoths under Alaric was a particularly devastating event that shook the foundations of Roman power.
The migration of Germanic tribes across the borders of the empire further exacerbated the situation, putting immense pressure on the Roman defenses. The inability of the Roman military to effectively repel these invasions highlighted the military weaknesses that had been plaguing the empire for years.
As the barbarian tribes pushed deeper into Roman territory, they brought with them cultural and societal changes that clashed with the established Roman norms. The influx of these tribes disrupted the social order and strained the already fragile cohesion of the empire.
The weakening of imperial defenses in the face of relentless barbarian incursions exposed the vulnerabilities of the Roman Empire. With the traditional structures of power eroding and the once mighty legions struggling to defend the borders, the stage was set for the eventual collapse of Roman authority.
Religious Changes
During the decline of the Roman Empire, one of the significant shifts that took place was in the realm of religious beliefs. The rise of Christianity played a pivotal role in reshaping the spiritual landscape of the empire. As Christianity gained prominence, it sparked conflicts with traditional Roman religions, leading to a clash of ideologies. The spread of Christianity brought about a new set of values and beliefs that challenged the existing social order.
Moreover, the influence of religion extended beyond the spiritual realm and permeated into the political and social fabric of the empire. Religious institutions wielded considerable power and influence, often intersecting with the political sphere. This intertwining of religion and politics created a complex dynamic that shaped the course of events during the empire's decline.
As Christianity gained followers and established itself as a dominant force, it contributed to the fragmentation of the Roman Empire. Religious differences fueled internal divisions and conflicts, weakening the unity of the empire. The emergence of Christianity as a prominent faith marked a profound cultural and societal transformation that reverberated throughout the empire.
Amidst the religious changes, there were also instances of syncretism, where elements of different faiths were blended together. This syncretic approach to religion reflected the diverse and multicultural nature of the Roman Empire, showcasing the adaptability and fluidity of religious practices during a period of transition and upheaval.

Cultural Transformation
During the decline of the Roman Empire, a significant aspect that played a crucial role was the that took place. This shift in culture marked a departure from traditional Roman values and customs, leading to a gradual erosion of the empire's identity.
One of the key elements of this cultural transformation was the adoption of foreign customs by the Romans. As the empire expanded and came into contact with diverse cultures, there was a growing influence of foreign practices on Roman society. This cultural blending diluted the distinct Roman identity and contributed to a sense of disconnection among the populace.
Furthermore, the decline of Roman art and literature reflected the changing cultural landscape. The once vibrant and innovative Roman artistic scene began to stagnate, with a noticeable decrease in the production of new works. This decline in artistic expression mirrored the broader cultural malaise that was setting in across the empire.
Another significant aspect of the cultural transformation was the loss of identity among the Roman populace. As traditional values and beliefs were challenged by external influences and internal strife, many Romans found themselves adrift in a sea of uncertainty. The strong sense of civic duty and pride in Roman heritage began to wane, further weakening the social fabric of the empire.
In summary, the cultural transformation during the decline of the Roman Empire was a multifaceted process that involved the adoption of foreign customs, the decline of artistic and literary output, and a loss of identity among the populace. These changes contributed to the overall decline of the empire and played a significant role in shaping the world that emerged in the aftermath of Rome's fall.
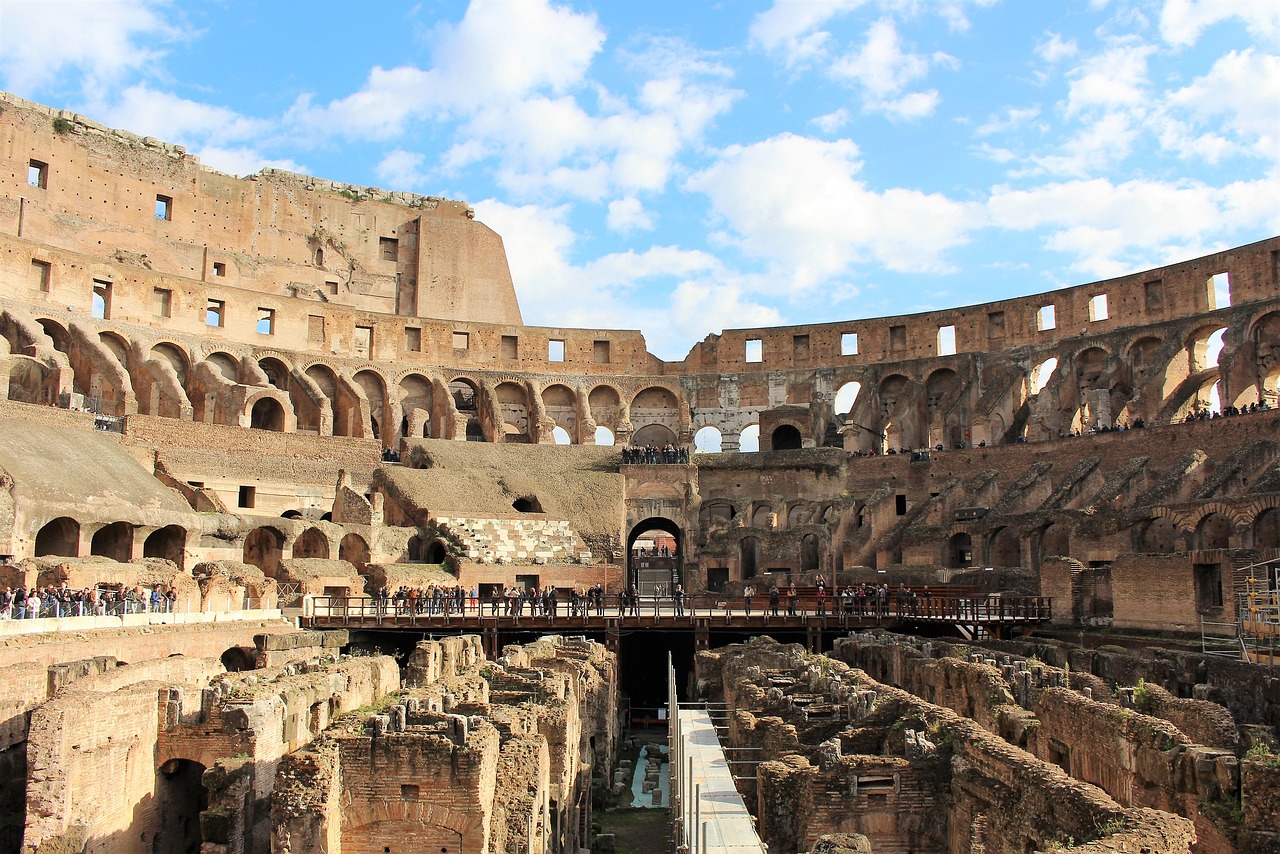

Lingering Legacy
The legacy of the Roman Empire continues to echo through the corridors of time, leaving an indelible mark on the world as we know it today. Despite its eventual collapse, the empire's influence can be seen in various aspects of modern society, shaping our laws, languages, and architectural marvels.
One of the most enduring legacies of the Roman Empire is its legal system. The Romans were pioneers in codifying laws and establishing principles of justice that form the basis of many legal systems around the globe. Concepts such as innocent until proven guilty and the right to a fair trial have their roots in Roman jurisprudence.
Furthermore, the Latin language, the linguistic offspring of the Romans, has left an indelible mark on numerous modern languages. From English to Spanish, French to Italian, many languages owe a debt to Latin vocabulary and grammar, showcasing the enduring influence of the Roman Empire.
Architecturally, the Romans were unparalleled in their engineering feats. The legacy of their monumental structures, such as the Colosseum, Pantheon, and aqueducts, stands as a testament to their ingenuity and craftsmanship. Modern architectural marvels often draw inspiration from Roman design principles, showcasing a continuity of influence across the centuries.
As we reflect on the lingering legacy of the Roman Empire, we are reminded of the lessons learned from its collapse. The empire's demise serves as a cautionary tale, highlighting the dangers of overexpansion, internal strife, and societal decay. By studying the fall of Rome, we gain insights into the fragility of civilizations and the importance of maintaining a delicate balance between power, governance, and societal cohesion.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What were the main economic challenges faced by the Roman Empire?
The Roman Empire struggled with issues such as inflation, high taxes, and resource depletion due to continuous warfare, which put a significant strain on its economy.
- How did political instability contribute to the decline of the Roman Empire?
The Roman Empire faced political turmoil marked by frequent changes in leadership, corruption, and power struggles among different factions, leading to instability and weakened governance.
- What role did military weakness play in the fall of the Roman Empire?
The decline of the Roman military, attributed to overexpansion, recruitment problems, and reliance on mercenaries, left the empire vulnerable to external threats and internal unrest.
- What were the key social issues that plagued the Roman Empire?
Social unrest in the Roman Empire was fueled by factors like class disparities, widespread slavery, and the erosion of traditional values and civic responsibilities, contributing to societal tensions.
- How did the barbarian invasions impact the Roman Empire?
The barbarian invasions led to the sack of Rome, the migration of tribes across Roman territories, and the weakening of imperial defenses, ultimately hastening the empire's decline.
- What were the significant religious changes during the decline of the Roman Empire?
The Roman Empire witnessed a shift in religious beliefs, with the rise of Christianity, religious conflicts, and the influence of religion on societal norms and political dynamics.
- How did cultural transformations contribute to the downfall of the Roman Empire?
Cultural changes, such as the adoption of foreign customs, decline in Roman art and literature, and loss of identity, played a role in weakening the empire's cultural cohesion and resilience.
- What is the lasting legacy of the Roman Empire on the world today?
The enduring legacy of the Roman Empire includes its contributions to law, language, architecture, and the valuable lessons learned from its collapse, shaping modern societies and governance systems.



















