The Aesthetics of Sacred Spaces in Different Religions
Exploring the architectural and artistic elements that define sacred spaces in various religions and how they contribute to the spiritual experience of worshippers.
Sacred spaces hold a unique allure, drawing in believers and visitors alike with their captivating designs and profound symbolism. Each religion has crafted its own architectural marvels that serve as gateways to the divine. From the intricate carvings of Hindu temples to the grandeur of Christian cathedrals, these sacred sites are not merely buildings but embodiments of faith and devotion.
Islamic mosques stand out with their elegant minarets, domes, and geometric patterns that symbolize unity and order in the Islamic faith. The calligraphy adorning the walls whispers verses of the Quran, creating an atmosphere of reverence and contemplation. The mihrab, indicating the direction of Mecca, serves as a focal point for prayer, guiding worshippers towards spiritual alignment.
On the other hand, Hindu temples are a riot of colors and shapes, with every inch adorned with intricate carvings depicting gods, goddesses, and mythical creatures. The bustling energy of these temples mirrors the vibrant spirituality of Hinduism, inviting worshippers to immerse themselves in a world of divine beauty and symbolism.
Christian cathedrals soar towards the heavens with their towering spires and awe-inspiring stained glass windows. Light streams through these colorful panes, illuminating the faithful below and casting a kaleidoscope of hues across the sacred space. The altar, adorned with candles and religious artifacts, serves as the focal point for Christian rituals, drawing worshippers into a realm of spiritual transcendence.
Buddhist monasteries, in contrast, exude a sense of tranquility and simplicity. The minimalistic design and serene surroundings create an ideal environment for meditation and introspection. Every element, from the layout of the meditation halls to the Zen gardens outside, is meticulously crafted to promote mindfulness and inner peace.
Jewish synagogues carry the weight of history within their walls, with architectural elements reflecting the trials and triumphs of the Jewish people. The Ark, containing the Torah scrolls, stands as a symbol of the covenant between God and the Jewish community. Intricate mosaics and decorative motifs weave together a tapestry of faith and tradition.
Sikh gurdwaras embody the principles of equality and community, with open spaces and communal dining halls welcoming all who enter. The Golden Temple in Amritsar, with its shimmering waters and gleaming domes, symbolizes the spiritual and temporal aspirations of the Sikh faith. Every corner resonates with the teachings of Guru Nanak, emphasizing service, humility, and unity.
Shinto shrines blend seamlessly into their natural surroundings, with wooden structures nestled among ancient trees and moss-covered stones. The torii gates, marking the transition from the mundane to the sacred, beckon visitors to leave behind their worldly concerns and enter a realm of purity and harmony. Nature itself is worshipped as a divine presence, with every rustling leaf and trickling stream considered sacred.
Bahá'í Houses of Worship stand as beacons of unity and inclusivity, with their intricate lace-like domes and sprawling gardens welcoming people of all backgrounds. The symmetrical design and nine entrances symbolize the oneness of humanity and the interconnectedness of all religions. Visitors are encouraged to reflect on the teachings of Bahá'u'lláh and meditate on the harmony that can be achieved through unity in diversity.
Islamic Mosques
Islamic mosques are not just places of worship but also architectural masterpieces that reflect the rich cultural and religious values of Islam. The design of mosques is characterized by unique features that set them apart from other religious buildings. One of the most striking elements of mosque architecture is the minaret, a tall tower from which the call to prayer is traditionally made. These minarets not only serve a practical purpose but also symbolize the connection between heaven and earth, reminding worshippers of the divine presence.
Another essential feature of Islamic mosque design is the dome, which symbolizes the universe and the heavens. The intricate geometric patterns and Arabic calligraphy adorning the walls and ceilings of mosques create a mesmerizing visual experience for worshippers. These artistic elements not only beautify the sacred space but also serve a spiritual purpose, helping worshippers focus their minds on the divine during prayer.
The mihrab, a niche in the wall indicating the direction of Mecca, is a central feature of mosque architecture. It serves as a focal point for prayer and symbolizes the unity of Muslims around the world facing the same direction in worship. The use of light and space in mosques is also carefully considered to create a sense of tranquility and spiritual serenity, enhancing the overall experience of worshippers.
Islamic mosques are not only places of prayer but also centers of community life, education, and social gatherings. The design of mosques often includes courtyards, fountains, and shaded areas where worshippers can come together for various activities. The architectural elements of mosques, combined with the spiritual atmosphere they create, play a crucial role in shaping the religious experience of Muslims and fostering a sense of unity and devotion among the community.

Hindu Temples
Hindu temples are architectural marvels that showcase intricate carvings, vibrant decorations, and symbolic motifs, creating an atmosphere of divinity and spirituality for worshippers. These temples serve as sacred spaces where devotees come to connect with the divine and seek inner peace. The design of Hindu temples is deeply rooted in ancient traditions and beliefs, with each element holding symbolic significance.
The layout of a typical Hindu temple is carefully planned to reflect the cosmic order and harmony. The temple complex usually consists of a central sanctum sanctorum, or garbhagriha, where the main deity is housed. Surrounding the garbhagriha are various halls, courtyards, and other structures that lead worshippers through a spiritual journey. The outer walls of Hindu temples are adorned with sculpted figures of gods, goddesses, and mythical creatures, each telling a story from Hindu mythology.
One of the most striking features of Hindu temples is the towering gopurams, or entrance gateways, that are elaborately decorated with colorful sculptures depicting scenes from Hindu epics. These gopurams serve as a threshold between the material world and the divine realm, inviting worshippers to leave their worldly concerns behind and enter a sacred space filled with devotion and reverence.
Inside the temple, the main deity is enshrined in the garbhagriha, surrounded by offerings of flowers, incense, and lamps. The walls and ceilings of the inner sanctum are often adorned with intricate paintings and carvings that depict the stories and teachings of the Hindu scriptures. The atmosphere inside a Hindu temple is filled with the sound of bells, the fragrance of incense, and the sight of colorful decorations, creating a sensory experience that uplifts the spirit and nourishes the soul.
Devotees visit Hindu temples not only to offer prayers and seek blessings but also to experience a sense of peace and tranquility in the midst of life's chaos. The architecture and design of Hindu temples play a crucial role in facilitating this spiritual experience, providing a sacred space where worshippers can connect with the divine and find solace in their faith.
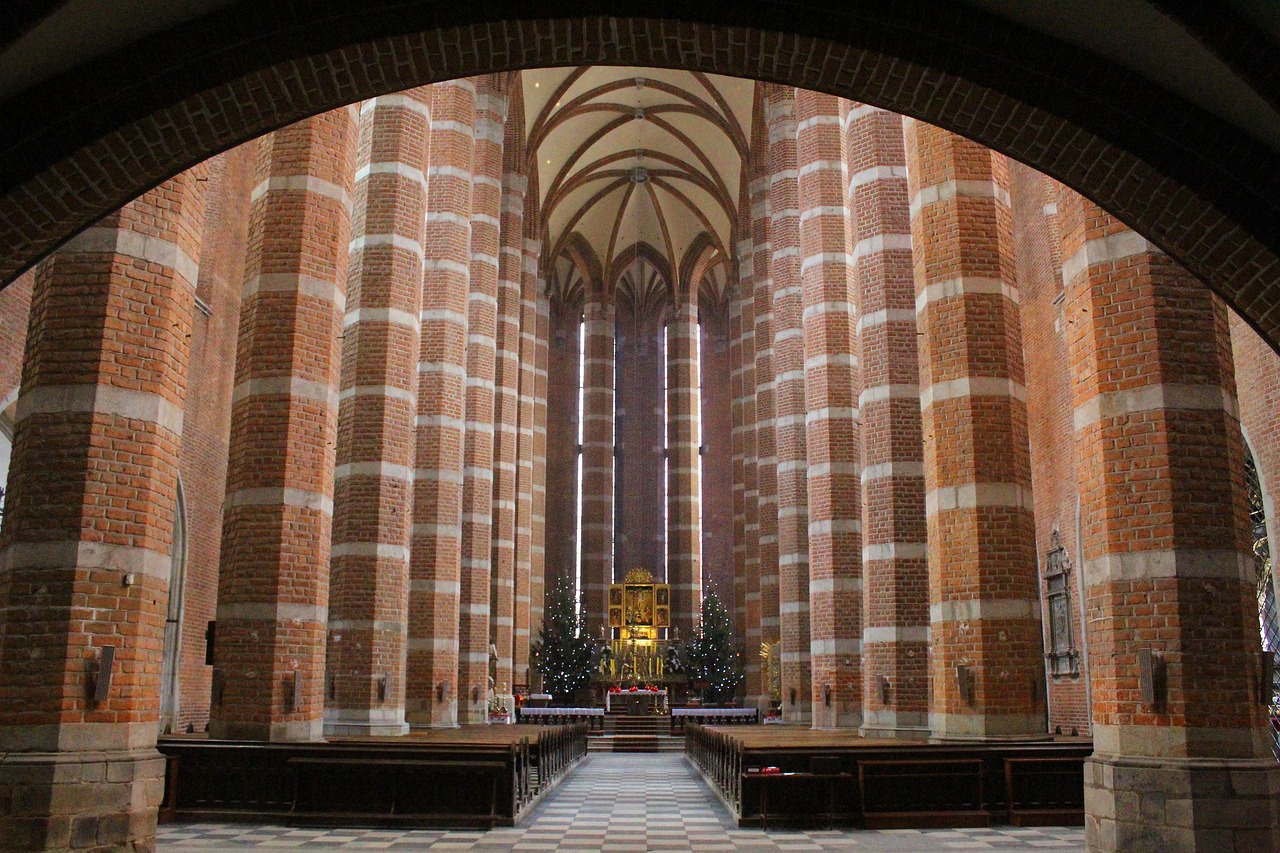

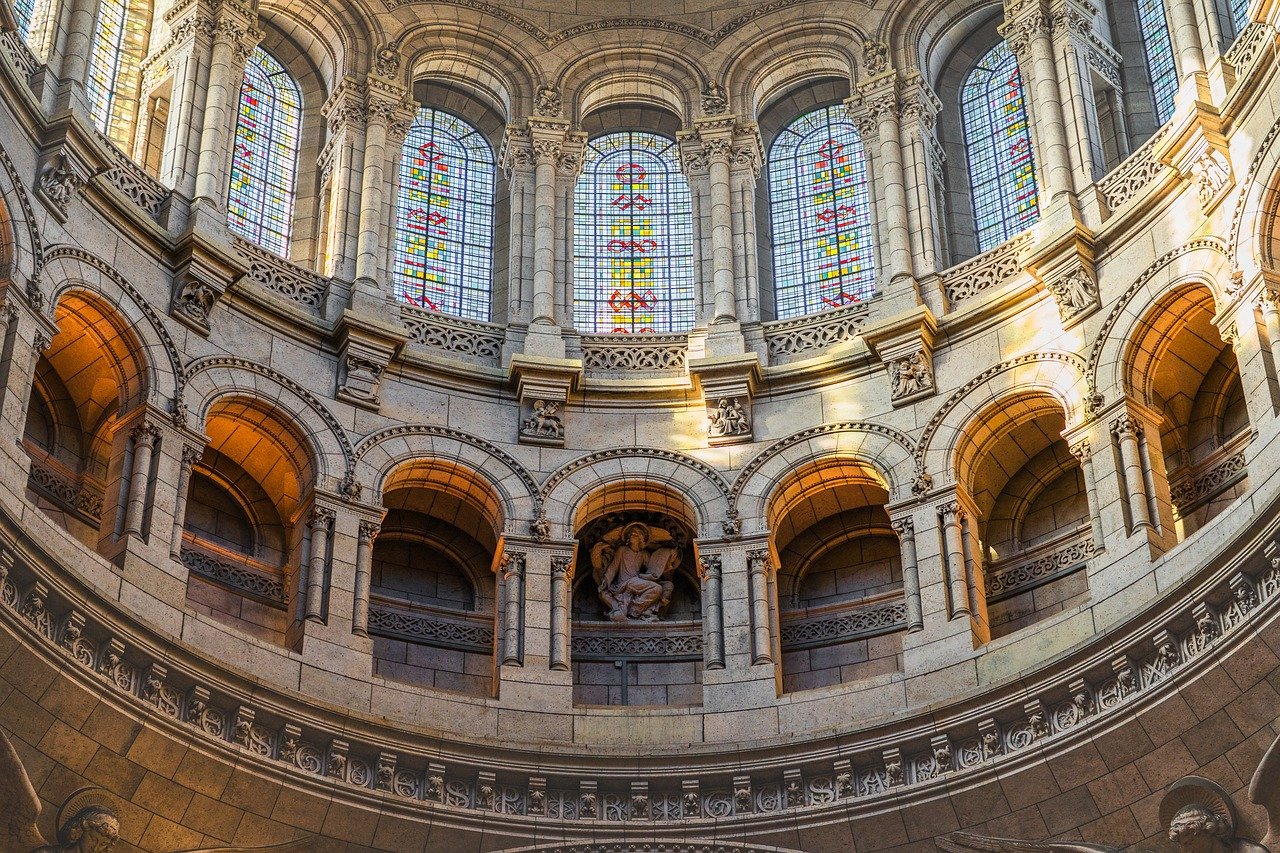
Christian Cathedrals
Exploring the architectural and artistic elements that define sacred spaces in various religions and how they contribute to the spiritual experience of worshippers.
The grandeur and symbolism of Christian cathedrals are a testament to the faith and devotion of believers. These magnificent structures, with their towering spires and intricate details, serve as beacons of spiritual inspiration and reflection.
One of the most striking features of Christian cathedrals is the use of stained glass windows. These colorful panes depict biblical stories, saints, and religious symbolism, casting a kaleidoscope of light that fills the interior with a divine glow. The interplay of light and color creates a mesmerizing effect, drawing worshippers into a state of contemplation and reverence.
Furthermore, the high ceilings of cathedrals symbolize the vastness and grandeur of God, evoking a sense of awe and humility in visitors. The soaring arches and vaulted ceilings seem to reach towards the heavens, reminding worshippers of the transcendent nature of the divine.
Another notable aspect of Christian cathedrals is the ornate altars that serve as the focal point of worship. Adorned with intricate carvings, precious metals, and religious icons, the altar is a sacred space where the Eucharist is celebrated and prayers are offered. The elaborate decorations and symbolic elements create a sacred atmosphere that enhances the spiritual experience of worshippers.
In conclusion, Christian cathedrals are not just architectural marvels but also spiritual sanctuaries that embody the faith and devotion of believers. Through their grandeur, symbolism, and sacred art, these sacred spaces inspire awe, reverence, and a deep sense of connection to the divine.
- What is the significance of stained glass windows in Christian cathedrals?
- How do the high ceilings of cathedrals contribute to the spiritual experience of worshippers?
- Why are altars in Christian cathedrals considered sacred spaces?
- How do the architectural elements of cathedrals enhance the worship experience?

Buddhist Monasteries
Buddhist monasteries are tranquil sanctuaries designed to foster spiritual growth and contemplation. These sacred spaces are characterized by their minimalist architecture, emphasizing simplicity and harmony with nature. The design of Buddhist monasteries is purposefully kept unadorned to encourage meditation and mindfulness among practitioners. The serene atmosphere created by the clean lines and open spaces promotes a sense of peace and inner reflection.
One of the key features of Buddhist monasteries is their central courtyard, often adorned with a peaceful garden or a simple fountain. These outdoor spaces provide a connection to nature, allowing monks and visitors to find solace in the beauty of the natural world. The layout of the monastery is carefully planned to facilitate movement and flow, with meditation halls positioned to capture natural light and create a sense of serenity.
Inside the monastery, you will find minimalistic decorations, typically consisting of subtle artwork and calligraphy. The focus is on creating a space free from distractions, where individuals can turn their attention inward and cultivate a sense of inner peace. The architecture of Buddhist monasteries embodies the principles of simplicity, humility, and mindfulness, reflecting the core teachings of Buddhism.
Monks and nuns residing in these monasteries follow a disciplined routine that includes meditation, chanting, and communal gatherings. The design of the monastery plays a crucial role in supporting these practices, with meditation halls designed to enhance concentration and spiritual connection. The overall ambiance of a Buddhist monastery is one of tranquility and introspection, inviting visitors to explore their inner selves and seek enlightenment.
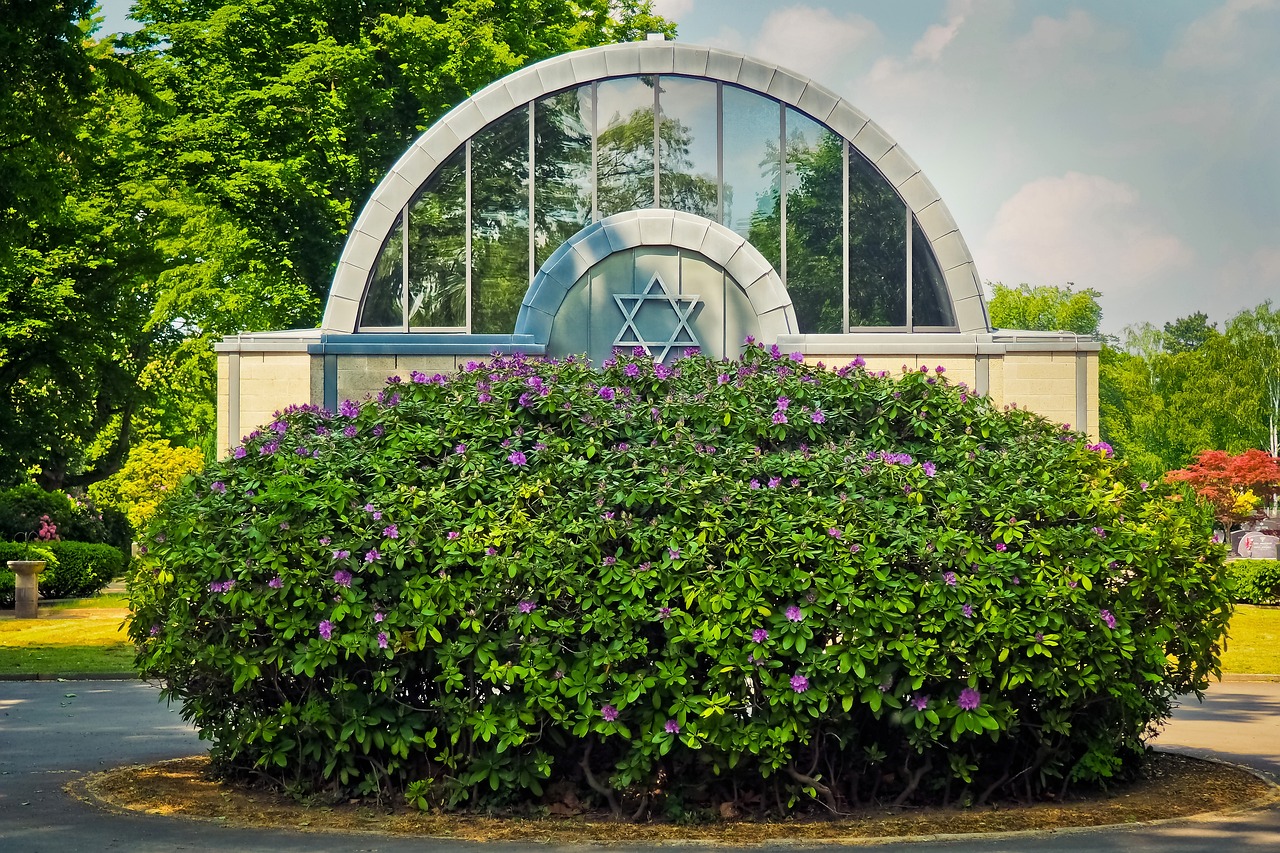

Jewish Synagogues
Jewish synagogues are architectural marvels that serve as spiritual and communal centers for the Jewish community. The design and layout of synagogues are deeply rooted in tradition and symbolism, reflecting the rich history and beliefs of Judaism. One of the most prominent features of a synagogue is the Ark, also known as the Holy Ark or Aron Kodesh, which houses the Torah scrolls. The placement of the Ark, usually facing Jerusalem, symbolizes the eternal connection between the Jewish people and the Holy Land.
Additionally, the Bimah, a raised platform in the center of the synagogue, is where the Torah is read and important prayers are recited. It serves as the focal point of the worship space, emphasizing the importance of communal prayer and study. The intricate designs and decorations inside synagogues often include motifs such as the Star of David, menorahs, and Hebrew inscriptions, all of which carry deep religious significance and cultural heritage.
Moreover, the layout of a synagogue is carefully planned to accommodate various rituals and ceremonies. Separate seating areas for men and women, as well as a designated space for the rabbi and cantor, reflect the traditional roles within the Jewish community. The use of natural light, symbolic artwork, and architectural elements like domes and arches create a sacred atmosphere that enhances the spiritual experience of worshippers.
In summary, Jewish synagogues are not just places of worship but also symbols of Jewish identity, community, and faith. The architectural symbolism and interior decor of synagogues play a crucial role in preserving and passing down the traditions and values of Judaism from generation to generation.

Sikh Gurdwaras
Sikh Gurdwaras hold a unique significance in Sikhism, not just as places of worship but as community hubs promoting equality and inclusivity. The architecture and design of Gurdwaras are deeply rooted in the principles of Sikhism, emphasizing the values of service, humility, and unity.
One of the most distinctive features of Sikh Gurdwaras is the Langar Hall, where free meals are served to all visitors regardless of their background. This communal dining experience symbolizes equality and the importance of sharing with others, fostering a sense of community and togetherness among worshippers.
The central prayer hall of a Gurdwara, known as the Darbar Sahib, is where Sikhs gather for congregational prayers and hymn singing. The Guru Granth Sahib, the holy scripture of Sikhism, is placed on a raised platform under a canopy, signifying its central role in Sikh worship and teachings.
Architecturally, Gurdwaras often feature domes and minarets, reflecting a blend of Islamic and Indian architectural styles. The Golden Temple in Amritsar, India, is a prime example of Sikh Gurdwara architecture, with its stunning golden facade and serene surroundings drawing millions of visitors each year.
Inside a Gurdwara, you will also find a Nishan Sahib, a flagpole with the Sikh flag known as the Khanda, symbolizing the sovereignty of the Sikh community. The flag is a reminder of the values of courage, righteousness, and selfless service that Sikhs strive to uphold in their daily lives.
Overall, Sikh Gurdwaras serve not only as places of worship but as beacons of community service, social justice, and spiritual growth. The architecture and design of Gurdwaras reflect the core beliefs of Sikhism, creating a sacred space where all are welcome to experience the teachings of the Sikh Gurus and connect with the divine.

Shinto Shrines
Shinto shrines are sacred spaces in Japan that encapsulate the essence of harmony between humans and the divine. These shrines are characterized by their natural settings, simple yet elegant architecture, and deep connection to nature. The design of Shinto shrines is carefully crafted to blend seamlessly with the surrounding environment, creating a serene atmosphere that invites worshippers to reflect and find inner peace.
The architecture of Shinto shrines often features wooden structures with sloping roofs and vermillion accents, symbolizing purity and protection. The use of natural materials such as wood and stone enhances the spiritual ambiance of the shrines, allowing visitors to feel a sense of tranquility and reverence in the presence of the kami, the divine spirits worshipped in Shintoism.
One of the distinctive elements of Shinto shrines is the torii gate, which marks the transition from the mundane world to the sacred realm of the shrine. The act of passing through the torii gate is seen as a symbolic purification ritual, cleansing the visitor's spirit before entering the sacred space. The simplicity of the torii gate symbolizes the connection between the physical and spiritual worlds, inviting worshippers to leave behind their worldly concerns and focus on the divine.
Shinto shrines are often surrounded by lush gardens, ponds, and sacred trees, further emphasizing the harmony between nature and spirituality. These natural elements are carefully integrated into the shrine's design to create a tranquil environment that encourages contemplation and reverence. Visitors to Shinto shrines are encouraged to take a moment to appreciate the beauty of the natural surroundings and reflect on their connection to the divine.
The rituals and ceremonies performed at Shinto shrines are deeply rooted in tradition and symbolism, reflecting the rich cultural heritage of Japan. From purification rituals to seasonal festivals, each aspect of Shinto practice is imbued with spiritual significance and meaning. Worshippers participate in these rituals to express gratitude, seek blessings, and connect with the kami in a profound and meaningful way.
In conclusion, Shinto shrines embody the spiritual essence of Japan, serving as sacred spaces where individuals can seek solace, find inspiration, and cultivate a deeper connection to the divine. The simplicity, beauty, and harmony of Shinto shrine architecture and design create a profound sense of peace and reverence, inviting worshippers to experience the transcendent beauty of the natural world intertwined with the divine presence.

Bahá'í Houses of Worship
The Bahá'í Houses of Worship, also known as Bahá'í Temples, are architectural marvels that embody the principles of unity and diversity central to the Bahá'í Faith. These sacred spaces are designed to welcome people of all backgrounds and beliefs, symbolizing the oneness of humanity and the interconnectedness of all religions.
One of the most striking features of Bahá'í Houses of Worship is their nine-sided structure, representing the unity of the world's major religions. The intricate design of these temples aims to inspire contemplation and reflection, inviting visitors to connect with their inner selves and the divine essence present in all beings.
Surrounded by beautifully landscaped gardens and set in peaceful environments, Bahá'í Houses of Worship serve as beacons of tranquility and harmony. The architecture of these temples incorporates elements from various cultural traditions, reflecting the Bahá'í belief in the essential oneness of all human creations.
Inside these sacred spaces, natural light filters through intricately designed windows, creating a serene atmosphere conducive to prayer and meditation. The absence of religious symbols or images emphasizes the Bahá'í principle of the unity of God and the spiritual essence shared by all individuals.
Visitors to Bahá'í Houses of Worship are encouraged to engage in silent prayer and meditation, fostering a sense of inner peace and spiritual connection. The open and welcoming design of these temples symbolizes the Bahá'í commitment to inclusivity and the elimination of prejudice in all its forms.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the significance of sacred spaces in different religions?
Sacred spaces play a crucial role in various religions as they provide a physical environment that fosters spiritual connection and worship. These spaces are designed to evoke a sense of awe, reverence, and tranquility, enhancing the religious experience for practitioners.
- How do architectural and artistic elements contribute to the spiritual experience of worshippers?
The architectural and artistic elements of sacred spaces are carefully crafted to reflect the beliefs, values, and cultural identity of a particular religion. These elements, such as intricate carvings, stained glass windows, and symbolic motifs, serve to inspire contemplation, meditation, and a deeper connection to the divine.
- What are some common features of Islamic mosque architecture?
Islamic mosques are known for their distinct architectural features, including minarets, domes, prayer halls, and intricate geometric patterns. These elements not only serve functional purposes but also symbolize the unity, harmony, and transcendence inherent in Islamic teachings.
- How do Hindu temples create a divine atmosphere for worship?
Hindu temples are adorned with colorful decorations, elaborate carvings, and sacred symbols that represent the rich mythology and spiritual beliefs of Hinduism. The vibrant ambiance, combined with the aroma of incense and the sound of prayers, creates a sacred space conducive to devotion and spiritual contemplation.
- What is the significance of stained glass windows in Christian cathedrals?
Stained glass windows in Christian cathedrals are not merely decorative elements but serve as visual narratives of biblical stories, saints, and religious teachings. The colorful light filtering through the glass symbolizes the divine presence and illuminates the spiritual journey of worshippers.



















