The Spanish Civil War - Causes and Legacy
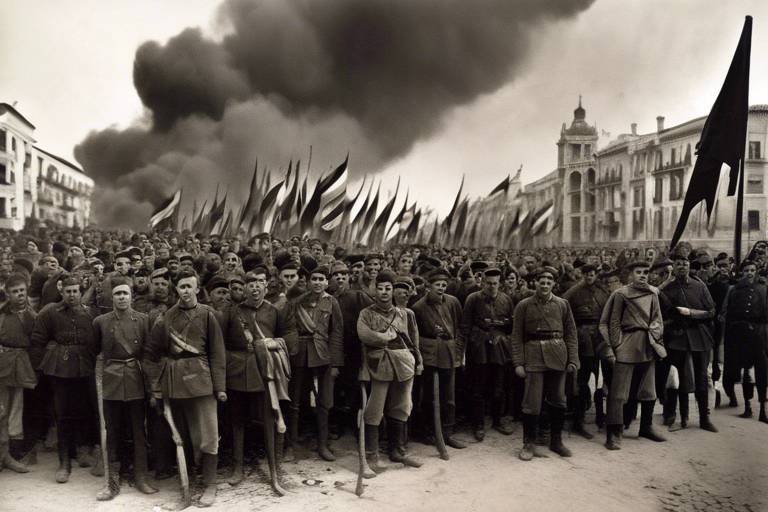
The Spanish Civil War, a tumultuous and tragic chapter in Spain's history, was a conflict born out of deep-rooted political divisions and ideological clashes that tore the nation apart. The causes of the war can be traced back to the early 20th century, as Spain grappled with a complex web of social, economic, and political challenges that ultimately culminated in a violent eruption of hostilities.
Political Landscape in Spain
The political landscape in Spain leading up to the outbreak of the Spanish Civil War was marked by deep divisions and intense ideological conflicts. Various political factions and ideologies vied for power, creating a volatile environment ripe for conflict. On one side, you had the Republicans, a coalition of left-wing groups including socialists, communists, and anarchists, advocating for progressive reforms and social equality. On the other side were the Nationalists, comprised of conservative forces such as monarchists, Falangists, and traditionalists, seeking to uphold the status quo and preserve traditional values.
The clash between these opposing ideologies intensified as tensions escalated, with each side fiercely defending their beliefs and interests. The political turmoil was further fueled by economic disparities, social injustices, and historical grievances, all contributing to the powder keg that eventually exploded into the Spanish Civil War. The struggle for power and control over the direction of the country reached a boiling point, leading to a catastrophic conflict that would shape Spain's destiny for years to come.

International Involvement
International involvement played a pivotal role in the Spanish Civil War, shaping the course and outcome of the conflict. Various foreign powers provided support to the opposing sides, fueling the intensity of the war and deepening the divisions within Spanish society. Germany and Italy backed the Nationalist forces led by General Franco, providing military aid, troops, and strategic guidance. On the other hand, the Soviet Union supported the Republican faction, supplying weapons, equipment, and military advisors.
The involvement of these international powers not only exacerbated the violence on the battlefield but also reflected the broader geopolitical tensions of the time. The Spanish Civil War became a proxy battleground for competing ideologies and interests, with fascist and communist forces vying for supremacy. The influx of foreign fighters and resources further polarized the conflict, turning Spain into a testing ground for new military tactics and strategies.
Moreover, the international dimension of the Spanish Civil War had far-reaching consequences beyond Spain's borders. The conflict drew the attention of the global community, sparking debates and controversies about intervention in civil wars and the moral responsibilities of nations towards conflict-affected populations. The actions of foreign powers in Spain set a precedent for future conflicts and shaped diplomatic relations in the lead-up to World War II.
Overall, international involvement in the Spanish Civil War underscored the interconnected nature of modern warfare and highlighted the complex web of alliances and rivalries that defined the political landscape of the 20th century. The legacy of foreign intervention in the conflict continues to be a subject of historical inquiry and debate, shedding light on the enduring impact of external actors on internal conflicts.

Military Strategies and Tactics
When delving into the tumultuous era of the Spanish Civil War, one cannot overlook the pivotal role played by military strategies and tactics employed by the opposing forces. The conflict was marked by a stark contrast in the approaches taken by the Nationalist and Republican factions, each with its own set of strengths and weaknesses.
The Nationalist forces, led by General Francisco Franco, utilized a combination of traditional military tactics and modern warfare techniques to secure their stronghold. Their emphasis on discipline, hierarchical command structure, and close coordination with their allies, particularly Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy, gave them a strategic advantage on the battlefield.
On the other hand, the Republican side, comprising a diverse coalition of leftist groups, anarchists, and communists, adopted a more decentralized and fragmented approach to military operations. While their commitment to guerrilla warfare and defense of urban centers showcased resilience, the lack of unified command and internal conflicts hampered their overall effectiveness.
Key battles such as the Siege of Madrid and the Battle of the Ebro exemplified the contrasting military strategies at play during the Spanish Civil War. The Nationalists' systematic siege tactics and aerial bombardment tactics proved devastating, while the Republicans' urban warfare tactics and defense of strategic positions demonstrated their determination to resist.
Moreover, the use of propaganda and psychological warfare tactics by both sides further intensified the conflict, shaping public perception and morale. The Nationalists' control over the airwaves and dissemination of propaganda bolstered their image, while the Republicans relied on international brigades and ideological fervor to sustain their fight.
In hindsight, the military strategies and tactics employed during the Spanish Civil War not only influenced the outcome of the conflict but also left a lasting impact on the subsequent development of warfare strategies in the 20th century. The lessons learned from this brutal conflict continue to resonate in the annals of military history, serving as a stark reminder of the devastating consequences of ideological warfare.

Social and Cultural Impact
The Spanish Civil War had a profound impact on the social fabric and cultural heritage of Spain, leaving scars that would endure for generations. The conflict tore apart communities, pitting neighbors and even family members against each other in a brutal struggle for power and ideology. The division between the Nationalist and Republican forces not only led to physical destruction but also deepened existing social rifts, creating a legacy of mistrust and resentment that lingered long after the war ended.
One of the most devastating consequences of the war was the widespread displacement of civilians, as families were uprooted from their homes and forced to flee the violence. The destruction of villages and cities left a trail of devastation in its wake, with many historical landmarks and cultural sites reduced to rubble. The loss of irreplaceable heritage was not just a physical blow but also a cultural one, as Spain's rich history was marred by the destruction wrought by the conflict.
The trauma experienced by the population during the war left deep emotional scars that would shape Spain's collective memory for years to come. Survivors carried the weight of their experiences, haunted by the horrors they had witnessed and the loss they had endured. The psychological impact of the conflict reverberated through Spanish society, influencing attitudes and behaviors in ways that would continue to shape the country's social dynamics long after the war had ended.
Furthermore, the Spanish Civil War had a lasting impact on the cultural landscape of Spain, as artists, writers, and intellectuals grappled with the aftermath of the conflict. Many works of literature, art, and music produced during this period reflected the pain and suffering of war, capturing the raw emotions and turmoil of the time. The war became a central theme in Spanish cultural production, serving as a powerful symbol of resilience and resistance against oppression.
In conclusion, the social and cultural impact of the Spanish Civil War was profound and far-reaching, leaving an indelible mark on the fabric of Spanish society. The scars of the conflict continue to shape Spain's identity and memory, serving as a reminder of the enduring legacy of war and the resilience of the human spirit in the face of adversity.

Economic Consequences
The economic consequences of the Spanish Civil War were profound and far-reaching, leaving a lasting impact on Spain's infrastructure, industry, and agriculture. The conflict, which lasted from 1936 to 1939, devastated the country's economy and hindered its development for years to come.
During the war, vital infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and buildings were destroyed, disrupting transportation and communication networks essential for economic activities. Industrial centers were also heavily targeted, leading to significant damage to factories and production facilities. This destruction not only hampered the wartime economy but also posed challenges for post-war reconstruction efforts.
Furthermore, the agricultural sector, a key component of Spain's economy at the time, suffered greatly during the conflict. Farms were abandoned, crops were left unharvested, and livestock was lost, resulting in food shortages and economic instability. The disruption in agricultural production had long-term consequences for Spain's food security and economic stability.
The Spanish Civil War also exacerbated existing economic inequalities in the country. The conflict deepened the divide between the wealthy elite and the working class, leading to further economic disparities and social unrest. The economic turmoil caused by the war contributed to widespread poverty and unemployment, exacerbating the suffering of the population.
Moreover, the economic repercussions of the Spanish Civil War extended beyond the end of the conflict. The post-war period was marked by economic struggles, as Spain grappled with the immense costs of rebuilding and recovering from the devastation of the war. The country faced challenges in reviving its economy, attracting investments, and restoring stability, hindering its path to recovery.
In conclusion, the economic consequences of the Spanish Civil War were severe, impacting various sectors of the economy and prolonging Spain's recovery process. The scars left by the conflict continued to shape the country's economic landscape for years to come, underscoring the long-term effects of war on a nation's prosperity and development.

Human Rights Violations
During the Spanish Civil War, both the Nationalist and Republican forces were responsible for widespread that left a dark stain on the history of Spain. The conflict saw a multitude of atrocities, including mass executions, forced disappearances, and the suppression of civil liberties by both sides. The brutality of the war extended beyond the battlefield, with civilians often becoming targets of violence and repression.
One of the most infamous instances of human rights abuses during the Spanish Civil War was the mass executions carried out by both factions. Thousands of individuals, including political opponents, intellectuals, and civilians, were summarily executed without due process. These executions were often used as a tool of intimidation and repression to instill fear in the population and eliminate any perceived threats to the ruling powers.
Forced disappearances were another grave violation of human rights that occurred during the conflict. Many individuals simply vanished without a trace, abducted by military or paramilitary groups and never seen again. The families of the disappeared were left in a state of perpetual uncertainty and anguish, never knowing the fate of their loved ones.
The suppression of civil liberties was rampant during the Spanish Civil War, with both sides imposing censorship, arbitrary arrests, and restrictions on freedom of speech and assembly. Dissent was met with harsh reprisals, and any form of opposition to the ruling powers was swiftly quashed.
These not only caused immense suffering during the war but also had long-lasting consequences for Spanish society. The trauma and scars of the conflict continued to haunt the collective memory of the nation, shaping its social and political landscape for decades to come.

Legacy of the Spanish Civil War
The legacy of the Spanish Civil War continues to cast a long shadow over Spain, shaping its political, social, and cultural landscape to this day. The conflict, which tore the country apart in the late 1930s, left deep scars that have yet to fully heal. The repercussions of the war reverberate through generations, influencing the collective memory of the nation and informing contemporary debates on identity and historical responsibility.
One of the most prominent legacies of the Spanish Civil War is the enduring political divisions that persist in Spanish society. The conflict pitted Republicans against Nationalists, leading to a deep-seated ideological rift that has endured through the decades. The legacy of the war is still visible in Spain's political landscape, with echoes of past grievances and allegiances shaping modern politics.
Furthermore, the social impact of the Spanish Civil War is profound and far-reaching. The conflict resulted in widespread displacement of civilians, destruction of communities, and loss of life on a massive scale. Families were torn apart, and the trauma experienced during the war has been passed down through generations, leaving a lasting imprint on Spanish society.
Culturally, the Spanish Civil War also left a significant mark. The destruction of cultural heritage, including historic buildings, artworks, and archives, has deprived Spain of important elements of its past. The war disrupted traditional cultural practices and led to a period of upheaval and uncertainty that continues to influence artistic expression and cultural identity in the country.
Moreover, the economic consequences of the Spanish Civil War were severe. The conflict devastated Spain's infrastructure, industry, and agriculture, plunging the country into economic turmoil that persisted long after the war ended. The reconstruction efforts faced numerous challenges, further exacerbating the economic hardship experienced by the population in the post-war period.
On a human level, the legacy of the Spanish Civil War is marked by the widespread human rights violations that occurred during the conflict. Both sides engaged in atrocities, including mass executions, forced disappearances, and suppression of civil liberties. The legacy of these violations continues to haunt Spain, fueling calls for justice and accountability for the crimes committed during the war.
In conclusion, the legacy of the Spanish Civil War is a complex tapestry of political, social, cultural, economic, and human repercussions that continue to shape Spain's identity and memory. The enduring impact of the conflict serves as a reminder of the fragility of peace and the importance of confronting the past to build a more just and inclusive future.

Historiographical Debates
Historiographical debates surrounding the Spanish Civil War have been a subject of intense scholarly discussion and disagreement. Historians have grappled with interpreting the complex web of causes and consequences that defined this pivotal moment in Spanish history. One of the key points of contention is the role of external powers in fueling the conflict. Some argue that foreign intervention, particularly from fascist regimes in Germany and Italy, played a decisive role in tipping the scales in favor of General Franco's Nationalist forces. On the other hand, there are scholars who emphasize the internal dynamics of Spanish politics and society as the primary drivers of the war, downplaying the significance of international involvement.
Another hotly debated issue is the ideological underpinnings of the conflict. While some historians view the Spanish Civil War as a struggle between democracy and authoritarianism, others highlight the deep-seated social and economic tensions that underpinned the conflict. The legacy of the war and its impact on Spain's subsequent political development are also subjects of disagreement among historians. Some argue that the Civil War set the stage for the Franco dictatorship that followed, while others see it as a catalyst for the eventual transition to democracy in Spain.
Moreover, the question of how to remember and commemorate the Spanish Civil War continues to be a contentious issue. The competing narratives of the war, shaped by political agendas and collective memories, have led to divergent interpretations of the conflict's significance. Historians grapple with the challenge of reconciling these different perspectives to construct a nuanced understanding of this complex and multifaceted historical event.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What were the main causes of the Spanish Civil War?
The Spanish Civil War was primarily caused by deep political divisions within Spain, including conflicts between Republicans and Nationalists, social unrest, economic instability, and regional separatist movements. These factors culminated in a violent struggle for power and control, leading to the outbreak of the civil war in 1936.
- How did international involvement impact the Spanish Civil War?
International involvement played a significant role in the Spanish Civil War, with countries such as Germany, Italy, and the Soviet Union providing military support to the opposing sides. This foreign intervention intensified the conflict, turning it into a proxy war and further fueling the violence and destruction in Spain.
- What were the key military strategies and tactics used in the Spanish Civil War?
The Nationalist and Republican forces employed various military strategies and tactics during the Spanish Civil War, including guerrilla warfare, aerial bombardment, and sieges of key cities. Battles such as the Battle of Jarama and the Siege of Madrid were pivotal in shaping the outcome of the conflict.
- How did the Spanish Civil War impact Spanish society and culture?
The Spanish Civil War had profound social and cultural repercussions, leading to the displacement of civilians, destruction of historical landmarks, and widespread trauma among the population. The war also polarized Spanish society and left a lasting mark on the country's cultural heritage.
- What were the economic consequences of the Spanish Civil War?
The Spanish Civil War had devastating economic effects on Spain, causing significant damage to infrastructure, industry, and agriculture. The conflict hindered the country's economic development and contributed to its struggles in the post-war period, exacerbating poverty and unemployment.
- What human rights violations occurred during the Spanish Civil War?
Both sides of the Spanish Civil War committed egregious human rights abuses, including mass executions, forced disappearances, and suppression of civil liberties. These violations of human rights led to widespread suffering and loss of life, leaving a dark legacy in the history of Spain.
- How has the legacy of the Spanish Civil War influenced Spain's political and cultural landscape?
The legacy of the Spanish Civil War continues to shape Spain's political and cultural identity, with the memory of the conflict influencing national discourse and historical narratives. The war's impact is still felt in contemporary Spain, reflecting the enduring significance of this tumultuous period in the country's history.
- What are the historiographical debates surrounding the Spanish Civil War?
Historians have engaged in ongoing debates about the causes and consequences of the Spanish Civil War, offering diverse interpretations and perspectives on the conflict. These historiographical debates reflect differing views on the legacy and significance of the war in shaping Spain's history and collective memory.



















