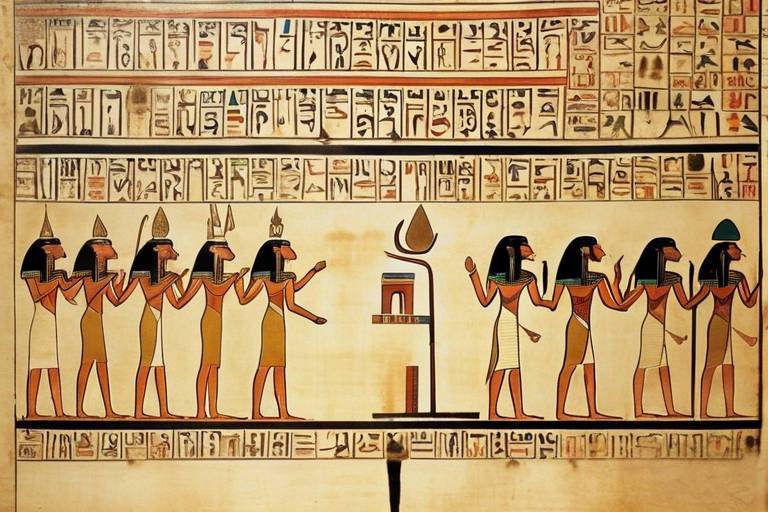
The Significance of Artifacts in Archaeological Research
Artifacts are the tangible remnants of past civilizations that hold immense value in unraveling the mysteries of history. These physical objects, ranging from tools to pottery and jewelry, serve as windows into the lives and cultures of ancient societies. By studying artifacts, archaeologists can piece together the puzzle of human existence and gain profound insights into the ways of the past.
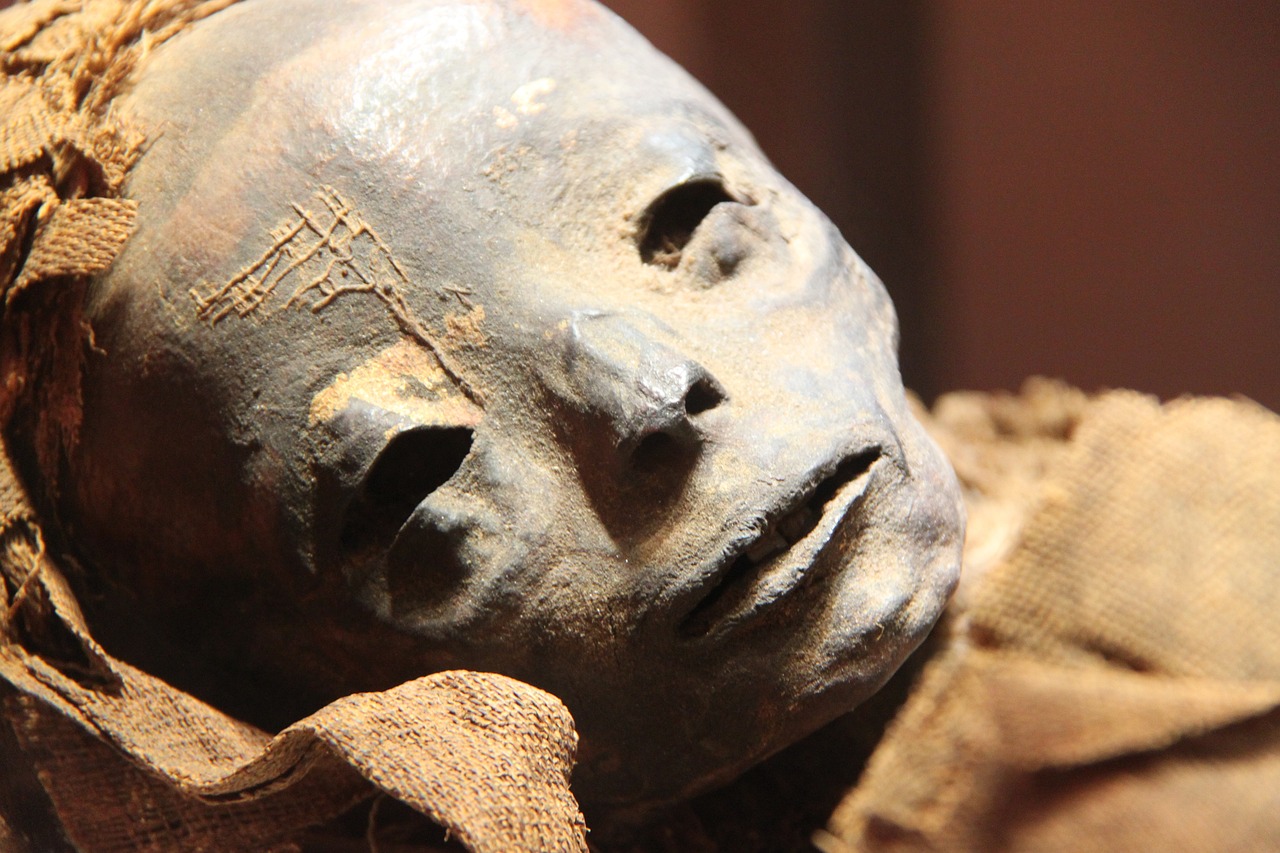

Types of Artifacts
Artifacts play a crucial role in archaeological research by providing insights into ancient cultures, technologies, and daily life. They help archaeologists piece together the puzzle of human history and understand how past societies lived and interacted.
Different types of artifacts, such as tools, pottery, jewelry, and weapons, offer unique perspectives on the lifestyles and practices of ancient civilizations. Understanding the diversity of artifacts helps researchers interpret the past more accurately.
Preserving artifacts is essential to maintain their integrity and ensure future generations can study them. Proper storage, handling, and conservation techniques are crucial in preventing deterioration and loss of valuable historical information.
Archaeologists use various scientific methods, such as carbon dating, x-ray analysis, and microscopic examination, to analyze artifacts. These techniques provide valuable data on the age, composition, and usage of artifacts, enhancing our understanding of the past.
Artifacts often carry symbolic meanings that reflect the beliefs, values, and social structures of ancient societies. Studying these symbols helps archaeologists unravel the cultural significance and rituals associated with different artifacts.
Artifacts can reveal information about ancient trade routes and exchange networks, shedding light on economic systems and interactions between different regions. Studying trade patterns through artifacts provides insights into ancient globalization and cultural diffusion.
Authenticating artifacts is crucial in distinguishing genuine historical items from fakes or forgeries. Through scientific testing and provenance research, archaeologists can verify the authenticity of artifacts and ensure the accuracy of historical narratives.
Ethical issues, such as repatriation of artifacts to indigenous communities and responsible excavation practices, are important in archaeological research. Respecting cultural heritage and collaborating with local stakeholders are essential aspects of ethical artifact studies.
Advancements in technology, such as 3D scanning and virtual reality, are revolutionizing artifact research and public engagement. The future of artifact studies lies in innovative methods that enhance accessibility, conservation, and interpretation of archaeological treasures.

Artifact Preservation
Artifact preservation is a critical aspect of archaeological research, ensuring that valuable historical objects are safeguarded for future study and appreciation. Proper preservation techniques are essential in maintaining the integrity of artifacts and preventing their deterioration over time. By implementing careful storage, handling, and conservation practices, archaeologists can protect these artifacts from environmental factors and physical damage.
One common method of artifact preservation is through the use of specialized storage containers and materials that help regulate temperature, humidity, and light exposure. These controlled environments help prevent degradation and ensure the long-term stability of the artifacts. Additionally, employing conservation treatments, such as cleaning, stabilizing, and repairing damaged artifacts, can prolong their lifespan and enhance their visual appearance for display and research purposes.
Conservation laboratories play a crucial role in artifact preservation, providing controlled settings for in-depth examination and treatment of fragile objects. Highly trained conservators utilize scientific techniques and specialized equipment to analyze, document, and conserve artifacts, ensuring their authenticity and historical significance are preserved for future generations.
Collaboration between archaeologists, conservators, and museum professionals is essential in developing comprehensive preservation strategies that address the unique needs of different types of artifacts. By combining expertise in archaeological research and conservation science, professionals can work together to create sustainable preservation plans that prioritize the long-term care and accessibility of cultural heritage objects.
Artifact Analysis Techniques
When it comes to understanding the past through artifacts, archaeologists employ a variety of sophisticated techniques for analysis. One of the key methods used is carbon dating, which allows researchers to determine the age of organic materials found in artifacts with remarkable accuracy. By measuring the decay of carbon isotopes, scientists can pinpoint the time when an artifact was created or used, providing crucial chronological information.
X-ray analysis is another valuable tool in artifact analysis, offering insights into the composition and structure of materials. By examining the elemental composition of artifacts through X-ray fluorescence, archaeologists can identify the minerals, metals, or other substances used in their production. This technique helps in understanding the technological capabilities of ancient civilizations and tracing the origins of raw materials.
Microscopic examination plays a significant role in artifact analysis by revealing intricate details that are invisible to the naked eye. By magnifying the surface of artifacts, researchers can uncover microscopic traces of wear, tool marks, or manufacturing techniques. This level of scrutiny enables archaeologists to reconstruct past activities, such as tool usage or crafting processes, with precision and accuracy.
Furthermore, isotopic analysis is a powerful method used to study artifacts, especially in determining the geographic origins of materials. Isotopic signatures in artifacts can provide clues about the environmental conditions in which they were produced or the mobility of ancient populations. By analyzing isotopic ratios, researchers can trace the movement of people, animals, or goods across different regions, unraveling complex patterns of migration and trade.

Symbolism and Meaning
Artifacts hold a deeper significance beyond their physical attributes in archaeological research. They serve as windows into the beliefs, values, and societal structures of ancient civilizations. Each artifact carries a unique story, reflecting the cultural context in which it was created. By deciphering the symbolism and meaning behind these objects, archaeologists can unravel the intricate tapestry of ancient societies.
Symbolism in artifacts can manifest in various forms, from intricate engravings on pottery to elaborate designs on jewelry. These symbols often convey religious beliefs, social status, or historical events, providing valuable insights into the mindset of past communities. By analyzing the symbolic language of artifacts, researchers can decode the hidden messages and narratives embedded within these ancient treasures.
Moreover, the meaning attributed to artifacts can transcend their material existence. Objects like ceremonial masks or ritualistic tools carry spiritual significance, connecting individuals to their ancestral roots and cultural heritage. Unraveling the layers of symbolism in these artifacts requires a deep understanding of the historical context and the symbolic language of the civilization that created them.
Through the study of symbolism and meaning in artifacts, archaeologists can reconstruct the spiritual, social, and political landscapes of ancient societies. By piecing together these symbolic fragments, researchers can paint a vivid picture of the beliefs and rituals that shaped the lives of our ancestors.

Trade and Exchange Networks
Trade and exchange networks in ancient civilizations were the lifeblood of economic interactions and cultural diffusion. Through the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies, ancient societies established connections that transcended geographical boundaries. Artifacts discovered along trade routes provide valuable insights into the interconnectedness of different regions and the diversity of goods exchanged.
One of the key aspects of studying trade networks is understanding the types of artifacts found in different regions. By analyzing the distribution of artifacts such as pottery, coins, and exotic materials, archaeologists can map out trade routes and identify major trading hubs. These artifacts act as tangible evidence of long-distance trade and the movement of goods across vast distances.
Moreover, the study of trade and exchange networks through artifacts allows researchers to reconstruct economic systems and commercial activities in ancient societies. By examining the presence of foreign goods in local contexts and vice versa, archaeologists can infer the extent of trade relationships and the impact of commerce on cultural development.
Artifacts not only reveal the economic aspects of trade but also shed light on the cultural exchanges that occurred along trade routes. The presence of foreign pottery styles, architectural influences, and artistic motifs in archaeological finds indicates the transmission of ideas and practices between different civilizations. Through the analysis of artifacts, archaeologists can trace the flow of cultural influences and the adaptation of foreign elements in local contexts.
Furthermore, trade and exchange networks played a significant role in shaping social structures and political dynamics in ancient societies. The accumulation of wealth through trade, the establishment of diplomatic ties, and the formation of alliances based on mutual economic interests are reflected in the artifacts unearthed at archaeological sites. By studying these artifacts, researchers can unravel the complexities of ancient power dynamics and social interactions facilitated by trade networks.

Artifact Authentication
Artifact authentication is a critical aspect of archaeological research, ensuring the credibility and accuracy of historical findings. Through meticulous scientific testing and provenance research, archaeologists can differentiate between genuine artifacts and counterfeit or misrepresented items. By employing a combination of analytical techniques, including carbon dating, material analysis, and stylistic comparison, experts can verify the authenticity of artifacts and validate their historical significance.
One common method used in artifact authentication is carbon dating, which determines the age of organic materials by measuring the decay of radioactive carbon isotopes. This technique is particularly useful for dating ancient artifacts and establishing their chronological context within human history. Additionally, material analysis involves studying the composition of artifacts, such as the type of metal used in a weapon or the clay in pottery, to identify any anomalies that may indicate forgery.
Stylistic comparison is another valuable tool in artifact authentication, where experts compare the design, craftsmanship, and decorative elements of an artifact with known authentic pieces from the same time period or cultural context. This comparative analysis helps archaeologists detect inconsistencies or anachronisms that could suggest a fake artifact. By combining these methods and conducting thorough research on the artifact's origin and history, archaeologists can confidently authenticate valuable historical items.

Ethical Considerations
When delving into the realm of archaeological research, ethical considerations play a pivotal role in guiding the actions and decisions of archaeologists. One of the primary ethical concerns in the field is the repatriation of artifacts to indigenous communities. The return of cultural objects to their places of origin fosters respect for the heritage and traditions of indigenous peoples, acknowledging their rights to reclaim and preserve their history.
Furthermore, responsible excavation practices are paramount in ensuring that archaeological sites are treated with care and sensitivity. By employing meticulous techniques and adhering to ethical guidelines, archaeologists can minimize damage to historical sites and artifacts, preserving them for future generations to study and appreciate.
Collaboration with local stakeholders is another critical aspect of ethical artifact studies. Engaging with communities affected by archaeological projects fosters mutual understanding and respect, allowing for the incorporation of diverse perspectives in research endeavors. This inclusive approach promotes transparency and accountability in archaeological practices, enriching the interpretation of artifacts and historical narratives.
Moreover, ethical considerations extend to the dissemination of research findings and the presentation of archaeological discoveries to the public. Ensuring that information is shared responsibly and respectfully, taking into account the cultural sensitivities of affected communities, is essential in upholding ethical standards in the field of archaeology.

Future of Artifact Research
The future of artifact research is an exciting journey into the unknown, fueled by technological advancements and innovative approaches. One of the key developments shaping the future of artifact studies is the integration of 3D scanning technology. This cutting-edge tool allows archaeologists to create detailed digital models of artifacts, enabling closer examination without risking damage to the original pieces.
Furthermore, the rise of virtual reality (VR) applications is revolutionizing how artifacts are studied and presented to the public. Through VR experiences, individuals can immerse themselves in ancient worlds, interact with virtual artifacts, and gain a deeper understanding of historical contexts. This immersive technology opens up new possibilities for education, outreach, and preservation of cultural heritage.
Another significant trend in artifact research is the emphasis on accessibility and inclusivity. Museums and cultural institutions are increasingly digitizing their collections, making artifacts available online for global audiences to explore. This digital democratization of artifacts ensures that knowledge and appreciation of ancient cultures are not limited by geographical boundaries.
Moreover, interdisciplinary collaborations are shaping the future landscape of artifact research. By bringing together experts from diverse fields such as archaeology, chemistry, computer science, and anthropology, researchers can gain multifaceted insights into artifacts and their contexts. This holistic approach fosters a deeper understanding of the past and encourages innovative interpretations of archaeological findings.
In conclusion, the future of artifact research is bright and full of possibilities. By embracing technological advancements, promoting accessibility, fostering interdisciplinary collaborations, and engaging with the public through immersive experiences, archaeologists are poised to unlock new dimensions of ancient civilizations and share their discoveries with the world.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are artifacts in archaeology?
Artifacts in archaeology are objects made or modified by humans that provide valuable insights into past cultures and societies. These can include tools, pottery, jewelry, weapons, and other items from ancient civilizations.
- How do archaeologists analyze artifacts?
Archaeologists analyze artifacts using scientific techniques such as carbon dating, x-ray analysis, and microscopic examination. These methods help determine the age, composition, and use of artifacts, contributing to a better understanding of history.
- Why is artifact preservation important?
Artifact preservation is crucial to maintain the integrity of historical objects and ensure they can be studied by future generations. Proper storage, handling, and conservation techniques help prevent deterioration and loss of valuable information.
- What is the significance of symbolism in artifacts?
Symbolism in artifacts reflects the beliefs, values, and social structures of ancient societies. Studying these symbols helps archaeologists uncover the cultural meanings and rituals associated with different artifacts, providing deeper insights into past civilizations.
- How do artifacts contribute to understanding trade networks?
Artifacts reveal information about ancient trade routes and exchange networks, offering insights into economic systems and interactions between different regions. Studying trade patterns through artifacts helps researchers understand ancient globalization and cultural exchange.