The Secrets of the Great Wall's Construction
Have you ever wondered about the mysteries shrouding the construction of the Great Wall of China? This ancient marvel stands as a testament to human ingenuity and perseverance, captivating visitors from around the globe with its grandeur and historical significance.
The Great Wall's construction holds a wealth of secrets waiting to be unveiled, each brick and stone whispering tales of the past. From its architectural design to the strategic defense mechanisms embedded within its walls, every aspect of this monumental structure reflects the rich tapestry of Chinese history and culture.
As you delve into the depths of the Great Wall's construction, you will discover a world where laborers toiled tirelessly, where ancient engineering techniques defied the odds, and where the spirit of unity and resilience shaped the very foundation of this iconic landmark.
Step back in time and witness the sheer magnitude of the labor force that dedicated their sweat and blood to erecting this colossal barrier, a symbol of strength and protection for the ancient Chinese civilization.
Marvel at the enduring construction materials that have withstood the test of time, standing firm against the ravages of nature and the passage of centuries. The Great Wall's stones echo with the whispers of generations past, a living testament to the craftsmanship and dedication of those who built it.
But beyond its physical presence, the Great Wall holds a deeper significance as a cultural symbol of unity and pride for the Chinese people. It embodies the resilience of a nation that stood strong in the face of adversity, a beacon of hope and inspiration for generations to come.
Today, as modern conservation efforts strive to preserve this architectural wonder for future generations, the Great Wall continues to stand as a living legacy of human achievement and perseverance. Its towering ramparts beckon travelers from far and wide, inviting them to witness firsthand the secrets of its construction and the stories it holds within its ancient stones.
Join us on a journey through time and space as we unravel the mysteries of the Great Wall's construction, exploring the intricate details and hidden wonders that make it one of the world's most enduring symbols of human achievement.
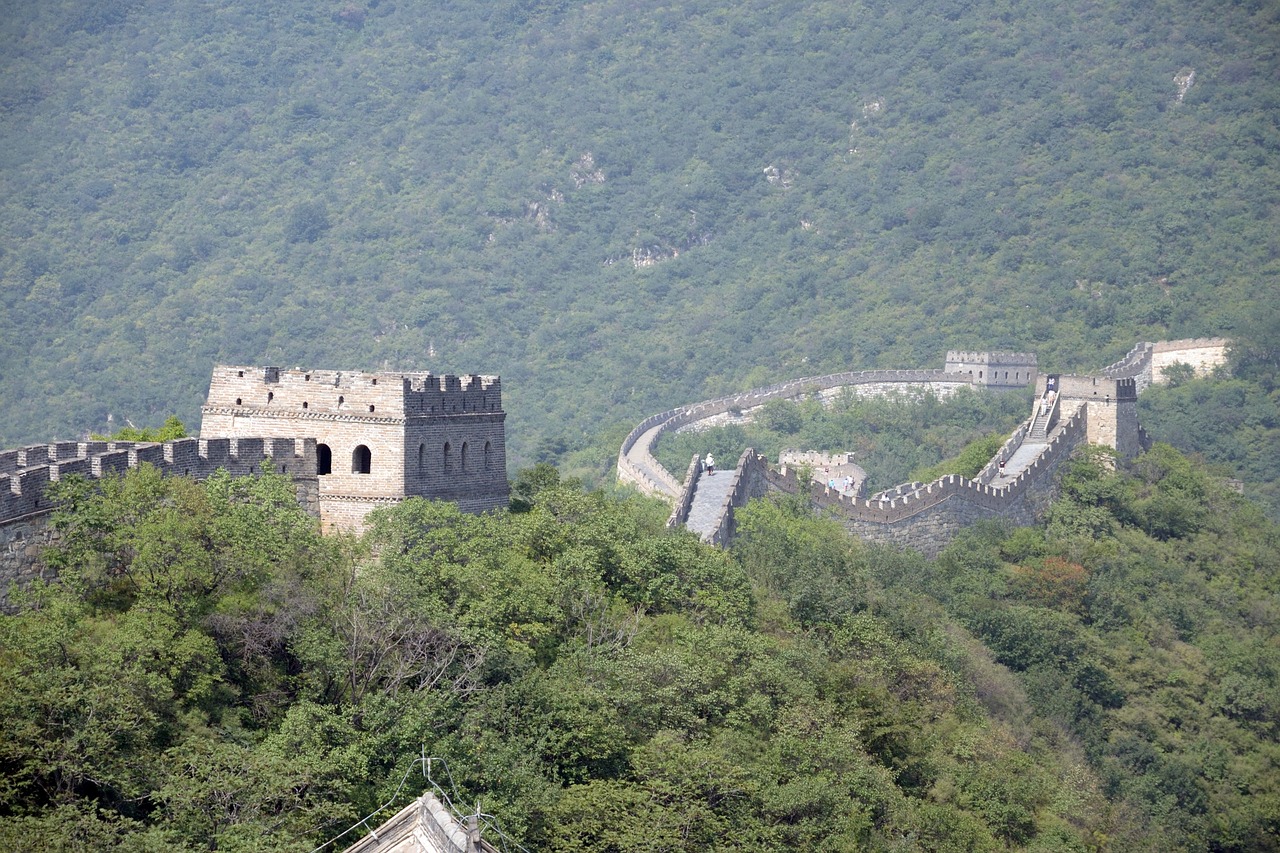

Historical Significance
The Great Wall of China stands as a monumental testament to the rich history and cultural heritage of China. Stretching over thousands of kilometers, this architectural marvel has played a crucial role in shaping the destiny of the Chinese civilization. Built over centuries by various dynasties, the Great Wall symbolizes the resilience and determination of the Chinese people to protect their lands from external threats and invaders. It serves as a tangible link to the past, offering a glimpse into the military strategies and defensive tactics employed by ancient Chinese rulers.
Throughout history, the Great Wall has served not only as a physical barrier against invasions but also as a symbol of unity and strength for the Chinese nation. Its construction reflects the collective effort and ingenuity of generations of builders, engineers, and laborers who dedicated their skills and lives to create this iconic structure. The Great Wall has become an enduring symbol of Chinese identity, embodying the spirit of perseverance and endurance that defines the nation's character.
Moreover, the Great Wall's historical significance extends beyond its military and defensive functions. It has become a cultural symbol of China's rich heritage and a source of national pride. The wall's presence in Chinese art, literature, and folklore further underscores its profound impact on the country's cultural landscape. As a UNESCO World Heritage Site, the Great Wall stands as a reminder of China's ancient glory and a beacon of inspiration for future generations.

Architectural Design
When it comes to the Great Wall of China, one cannot help but be amazed by its sheer magnitude and historical significance. Built over centuries, this iconic structure holds secrets of architectural design, strategic defense, and cultural symbolism that have fascinated people around the world. Let's delve into the mysteries behind the construction of this marvel.
The architectural design of the Great Wall is a testament to the ingenuity and engineering prowess of ancient Chinese builders. Spanning over 13,000 miles, this colossal structure is a blend of various construction techniques, including tamped earth, brick, stone, and wood. The wall's design incorporates watchtowers, battlements, and strategic passageways that served both defensive and communication purposes.
One of the remarkable features of the Great Wall's design is its adaptability to the rugged terrain it traverses. The wall follows the natural contours of the landscape, snaking through mountains and valleys with precision. This strategic placement not only enhanced its defensive capabilities but also added to the grandeur of its architectural splendor.
To withstand the test of time and the elements, the builders incorporated advanced techniques such as overlapping bricks and stones, creating a sturdy and resilient structure. The architectural design of the Great Wall stands as a testament to the ancient Chinese craftsmanship and their unparalleled dedication to creating a lasting legacy.

Strategic Defense
Have you ever wondered about the mysteries shrouding the construction of the Great Wall of China? Join us on a journey through time as we unravel the secrets behind this ancient wonder that has stood the test of time.
When it comes to strategic defense, the Great Wall of China stands as a monumental feat of engineering and military foresight. Stretching over thousands of miles, this iconic structure was not merely a physical barrier but a symbol of strength and resilience for ancient China.
Imagine standing on the watchtowers of the Great Wall, gazing out into the vast expanse of the Chinese landscape, ready to defend against any potential invaders. The strategic placement of beacon towers, fortresses, and barracks along the wall allowed for swift communication and coordinated defense mechanisms.
The Great Wall was not just a wall; it was a sophisticated system of defense that included traps, obstacles, and strategic points designed to thwart enemy advances. The sheer scale and complexity of the Great Wall's defensive architecture showcased the military prowess and strategic thinking of the ancient Chinese civilization.
Moreover, the Great Wall served as a psychological deterrent, instilling fear in the hearts of potential enemies and projecting an image of invincibility. It was a symbol of China's determination to protect its borders and preserve its sovereignty at all costs.
Despite the passage of centuries, the strategic defense mechanisms of the Great Wall continue to captivate historians, military strategists, and visitors alike, offering a glimpse into a bygone era of warfare and fortification.
Maintenance Challenges
Maintenance of the Great Wall poses significant challenges due to its immense length and age. The wall stretches over thousands of kilometers, making it a daunting task to inspect and repair every section regularly. Weathering and natural erosion have taken their toll on the structure, requiring constant monitoring and upkeep to prevent further deterioration. Additionally, the sheer scale of the Great Wall makes it difficult to allocate resources efficiently for maintenance efforts.
One of the primary challenges in maintaining the Great Wall is balancing preservation with modernization. As the wall attracts millions of visitors each year, there is a need to ensure safety without compromising the historical integrity of the structure. Finding the right balance between conservation and tourism development is crucial in preserving the Great Wall for future generations.
Another maintenance challenge is the invasive plant species that threaten the stability of the wall. Vegetation growth on the wall can weaken the structure by penetrating cracks and crevices, leading to structural instability. Controlling and removing these plants without causing damage to the ancient masonry requires careful planning and expertise.
Furthermore, the Great Wall faces the risk of damage from human activities such as graffiti, vandalism, and illegal construction. Protecting the wall from unauthorized alterations and preserving its original form present ongoing challenges for conservation efforts. Educating visitors about the importance of respecting the historical significance of the Great Wall is essential in safeguarding its legacy.

Cultural Symbolism
The Great Wall of China stands not only as a physical barrier but also as a powerful symbol of Chinese culture and history. Its massive presence and enduring strength have made it a cultural icon representing the resilience and unity of the Chinese people. Just as the wall connects various regions geographically, it also serves to connect the past with the present, bridging generations through its timeless significance. The Great Wall embodies the spirit of perseverance and determination, reflecting the unwavering commitment of the Chinese civilization to protect its homeland.

Construction Materials
When it comes to the construction of the Great Wall of China, the choice of materials played a crucial role in its durability and longevity. The materials used in building this architectural wonder varied depending on the location and the era of construction. One of the primary materials used was bricks, made from a mixture of clay, rice flour, and water. These bricks were then baked in kilns to ensure their strength and durability. Additionally, stone blocks were also utilized in certain sections of the wall, especially in mountainous regions where bricks were not as practical.
Furthermore, wood played a significant role in the construction of watchtowers and gates along the Great Wall. The use of wood provided flexibility and resilience to these structures, allowing them to withstand the test of time. In some cases, earth and gravel were used as fillers between layers of bricks to enhance stability and strength.
It's fascinating to note that the construction materials used in different parts of the Great Wall reflected the local resources available and the strategic importance of each section. The combination of these various materials contributed to the Great Wall's ability to withstand centuries of wear and tear, making it a testament to ancient engineering prowess.
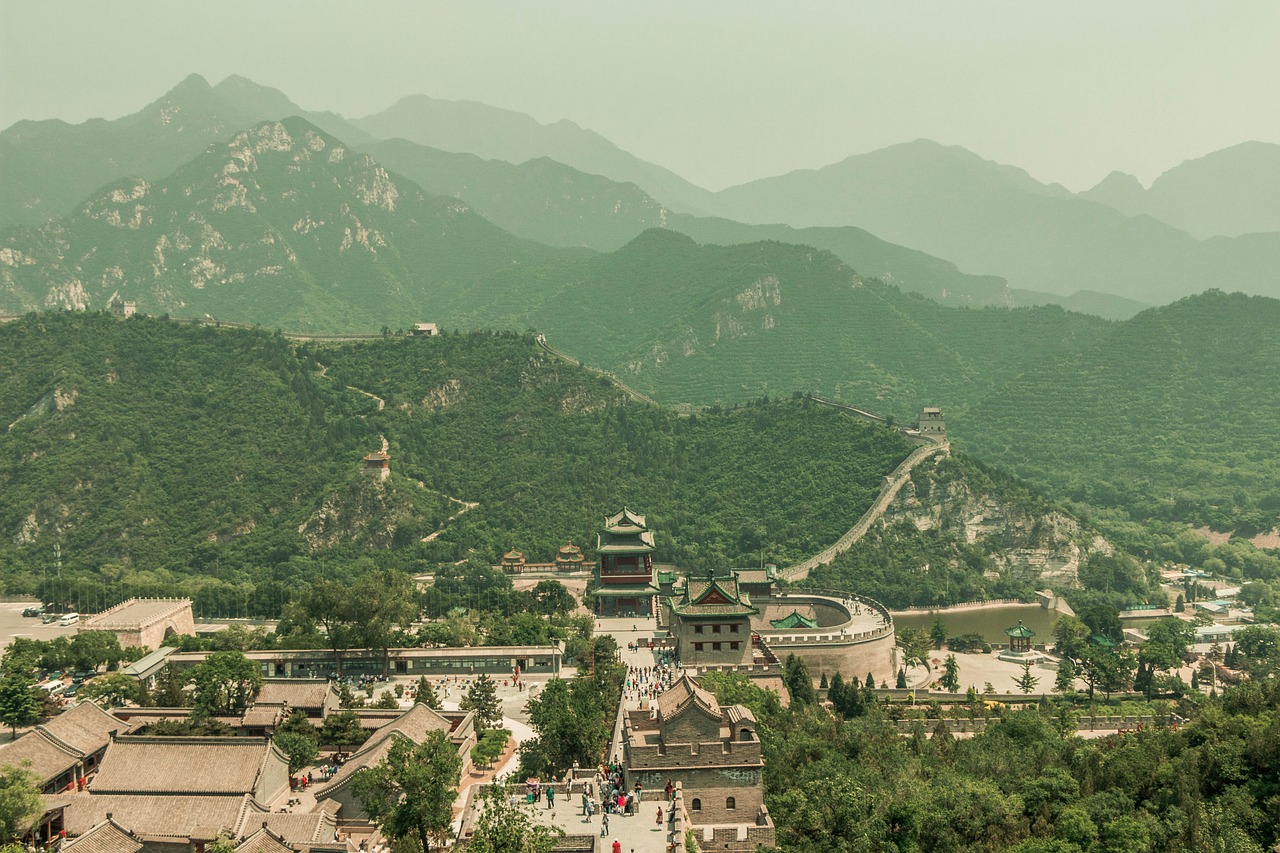

Labor Force
The construction of the Great Wall of China stands as a testament to the sheer magnitude of human effort and labor that went into its creation. Thousands of workers toiled tirelessly, enduring harsh conditions and challenging terrain to erect this monumental structure. The labor force involved in building the Great Wall was not only massive but also diverse, consisting of skilled craftsmen, engineers, soldiers, and ordinary laborers. Each individual played a crucial role in the construction process, from quarrying and transporting materials to laying bricks and fortifying the wall's defenses.
Workers from various regions of ancient China were mobilized to contribute their skills and expertise to the construction efforts. The labor force was organized into teams, each assigned specific tasks and responsibilities to ensure efficient progress. Skilled artisans and craftsmen were responsible for intricate masonry work, carving decorative elements, and designing defensive structures along the wall. Soldiers and guards were stationed at strategic points to protect the workers and fend off potential attacks from invaders.
The labor force faced numerous challenges during the construction of the Great Wall, including harsh weather conditions, rugged terrain, and limited resources. Despite these obstacles, the workers demonstrated remarkable resilience and determination, working tirelessly to fulfill their duties and complete the monumental project. The construction of the Great Wall not only required physical labor but also demanded ingenuity, teamwork, and unwavering dedication from all those involved.
The labor force behind the Great Wall's construction left a lasting legacy on ancient Chinese society, shaping the cultural identity and historical significance of this iconic structure. Their collective efforts symbolize the spirit of unity, perseverance, and sacrifice that defined the construction of one of the world's most remarkable architectural wonders. The labor force's contribution to the Great Wall's creation remains a testament to human ingenuity and the enduring legacy of ancient civilizations.

Modern Conservation Efforts
Modern conservation efforts aimed at preserving the majestic Great Wall of China reflect a global commitment to safeguarding this iconic historical monument for future generations. Through a combination of advanced technologies, dedicated teams of experts, and sustainable practices, ongoing projects strive to maintain the structural integrity and cultural significance of the Great Wall.
One of the key aspects of modern conservation efforts is the use of innovative restoration techniques that balance the preservation of the original construction with the need for structural reinforcement. Conservation teams carefully analyze the condition of the Great Wall sections, identifying areas of weakness and implementing targeted interventions to prevent further deterioration.
Moreover, environmental conservation plays a crucial role in protecting the Great Wall and its surrounding areas. Efforts are made to minimize the impact of tourism on the fragile ecosystem, promote sustainable practices, and raise awareness about the importance of preserving the natural environment alongside the historical monument.
Collaboration between government agencies, heritage organizations, and local communities is essential in ensuring the success of conservation projects. By engaging stakeholders at various levels, conservation efforts can benefit from diverse expertise, resources, and support, fostering a sense of shared responsibility for safeguarding the Great Wall.
Furthermore, educational programs and public outreach initiatives are instrumental in raising awareness about the significance of cultural heritage preservation. By involving schools, universities, and the general public in the conservation process, efforts are made to instill a sense of pride and ownership in protecting this remarkable symbol of China's history and resilience.
In addition to preservation efforts, research and documentation play a vital role in understanding the Great Wall's construction techniques, historical context, and evolving conservation needs. By continuously studying and documenting the monument, experts can adapt conservation strategies to address new challenges and ensure the long-term sustainability of the Great Wall.
Overall, modern conservation efforts represent a testament to humanity's commitment to preserving cultural heritage and celebrating the legacy of ancient civilizations. By investing in the conservation of the Great Wall, we not only protect a remarkable historical monument but also honor the ingenuity, perseverance, and cultural richness of the past for generations to come.
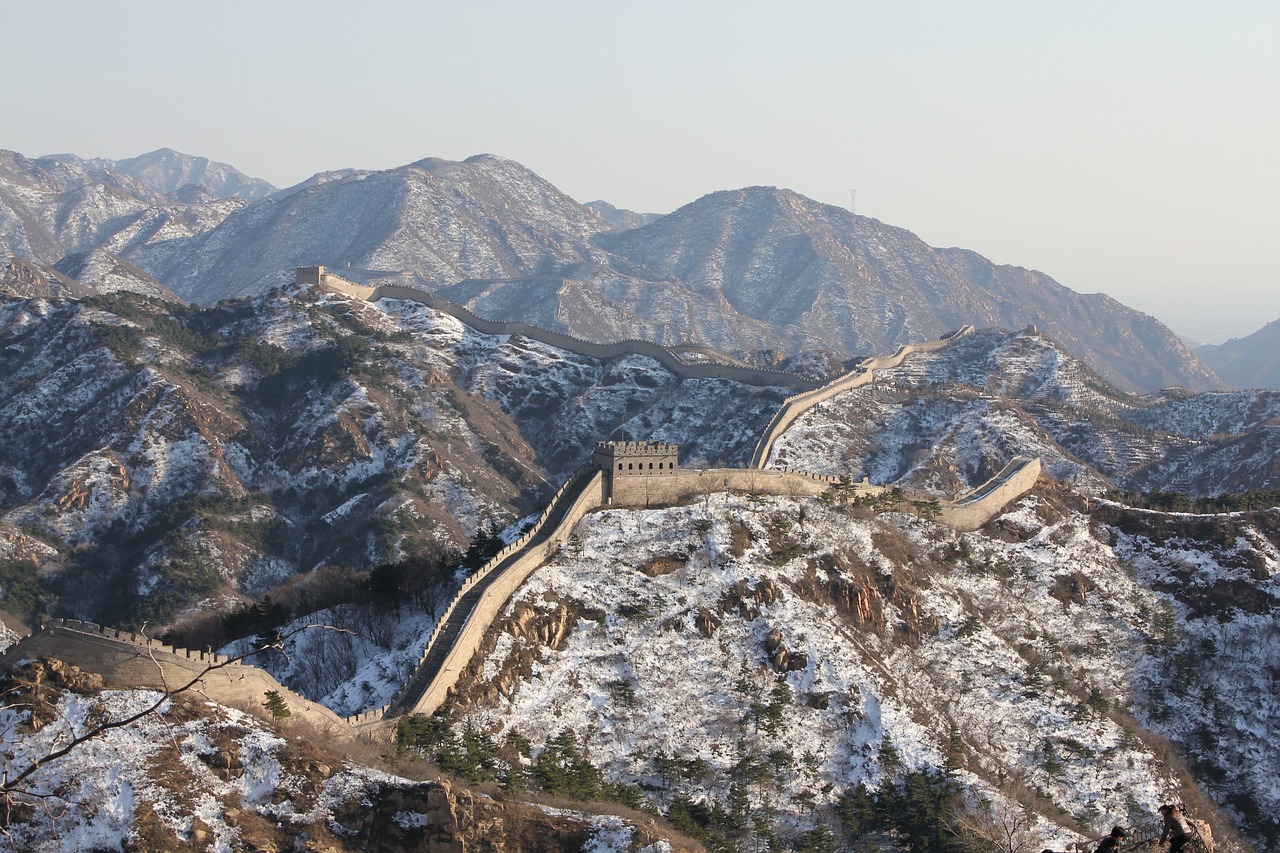

Tourism and Legacy
Tourism plays a significant role in the legacy of the Great Wall, attracting millions of visitors from around the world each year. The awe-inspiring structure, stretching across rugged landscapes and steep mountains, offers a glimpse into China's rich history and architectural prowess. As visitors walk along the ancient fortifications, they are transported back in time, imagining the soldiers who once stood guard against potential invaders. The Great Wall stands as a testament to human ingenuity and determination, leaving a lasting impact on all who behold its grandeur.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the historical significance of the Great Wall?
The Great Wall holds immense historical significance as a symbol of China's strength and resilience. It served as a defensive barrier against invasions, reflecting the strategic military prowess of ancient Chinese dynasties.
- How was the Great Wall constructed?
The Great Wall was built using various construction techniques, including brick, stone, wood, and other materials. It involved a massive labor force and intricate architectural design to create a formidable defense structure spanning thousands of miles.
- What challenges are faced in maintaining the Great Wall?
Maintaining the Great Wall poses significant challenges due to natural erosion, weathering, and human activities. Conservation efforts require careful planning and resources to preserve this ancient marvel for future generations.
- Why is the Great Wall considered a cultural symbol?
The Great Wall symbolizes unity, strength, and Chinese identity. It represents the enduring spirit of the Chinese people and their historical legacy, making it a cultural icon revered both nationally and globally.
- What materials were used in the construction of the Great Wall?
The Great Wall was constructed using a variety of materials, including bricks, stones, earth, and wood. These materials were carefully selected for durability and strength, contributing to the longevity of the wall over centuries.
- How has tourism impacted the Great Wall?
Tourism has brought both opportunities and challenges to the Great Wall. While it has increased awareness and appreciation of this historic site, it has also led to issues of overcrowding and wear and tear on certain sections of the wall.



















