The Impact of Climate Change on Historical Sites
Climate change is not just a distant threat looming on the horizon; it is a present danger that is already wreaking havoc on historical sites around the globe. The repercussions of our changing climate are felt deeply in the very foundations of these invaluable remnants of our past. From rising sea levels threatening coastal landmarks to extreme weather events causing irreparable damage, the heritage sites that have stood the test of time are now facing their greatest challenge yet.
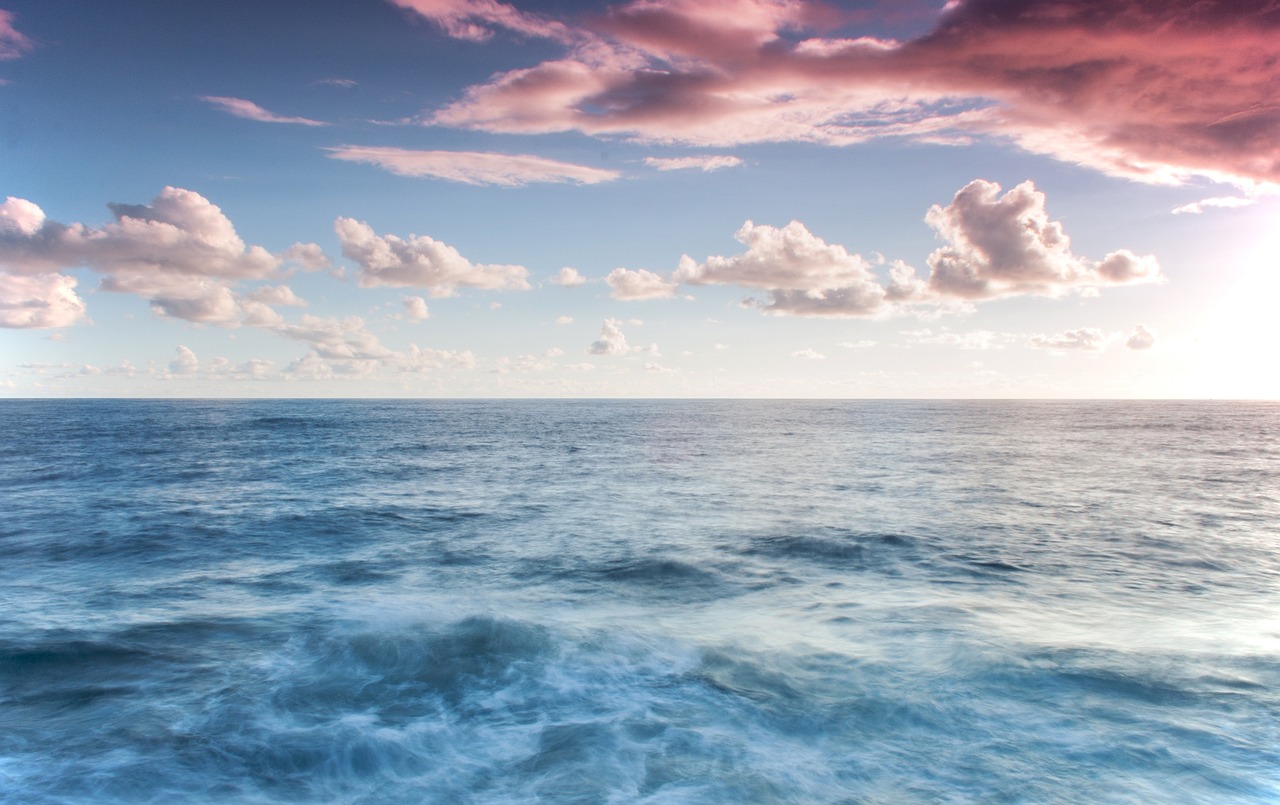

Rising Sea Levels
The impact of rising sea levels on historical sites is becoming increasingly concerning as coastal areas face the threat of erosion and inundation. These rising sea levels, attributed to climate change, pose a significant risk to the preservation of invaluable historical sites located near the shorelines. As the sea encroaches further inland, ancient structures and artifacts are at risk of being lost to the relentless tides, jeopardizing our connection to the past and cultural heritage.
Historic coastal sites such as ancient ports, fortifications, and lighthouses are particularly vulnerable to the destructive forces of rising sea levels. Erosion caused by the encroaching waters can lead to the gradual disintegration of structures, while flooding poses immediate risks to their stability. The delicate balance between the historical significance of these sites and the changing climate demands urgent attention and proactive measures to ensure their survival for future generations.
To combat the threats posed by rising sea levels, various strategies are being implemented to protect coastal historical sites. These include the construction of seawalls and barriers to mitigate erosion, the relocation of vulnerable artifacts to higher ground, and the development of sustainable coastal management plans. By combining scientific research, engineering solutions, and community engagement, efforts are being made to safeguard these precious historical sites from the impacts of climate change.

Extreme Weather Events
Exploring how climate change is affecting the preservation and conservation of historical sites worldwide and the measures being taken to mitigate these impacts.
Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and wildfires, pose significant threats to historical sites around the globe. The ferocity of these natural disasters can cause irreparable damage to centuries-old structures and artifacts, erasing valuable pieces of history in the blink of an eye. Imagine a powerful hurricane tearing through a coastal historical site, demolishing buildings that have withstood the test of time for generations. The impact of such events goes beyond physical destruction, as they also disrupt the cultural significance and stories embedded in these sites.

Temperature Changes
Temperature changes play a significant role in the preservation and maintenance of historical sites around the world. As global temperatures continue to rise due to climate change, the structural integrity of historical buildings and monuments is increasingly at risk. Extreme heat can accelerate the deterioration of materials such as stone and wood, leading to cracks, warping, and overall instability.
Historical sites in regions experiencing temperature fluctuations are particularly vulnerable to these changes. For instance, sudden shifts from extreme heat to cold can cause expansion and contraction of building materials, further compromising their structural stability. Moreover, temperature variations can impact the delicate balance of humidity within historical structures, potentially leading to mold growth and decay.
To combat the adverse effects of temperature changes on historical sites, adaptive restoration techniques are being employed. These methods involve implementing climate control systems, such as HVAC systems, to regulate indoor temperatures and humidity levels. Additionally, protective coatings and insulation materials are used to shield historical buildings from extreme temperature fluctuations.
Furthermore, ongoing monitoring of temperature changes within historical sites is crucial for early detection of potential issues. By utilizing advanced sensors and data analysis tools, conservationists can proactively address temperature-related challenges and implement targeted preservation strategies.
In conclusion, understanding the impact of temperature changes on historical sites is essential for ensuring their long-term conservation. By adopting adaptive restoration practices and employing innovative preservation techniques, we can safeguard these invaluable cultural heritage assets for future generations to appreciate and enjoy.

Loss of Biodiversity
Climate change is not only impacting the physical structures of historical sites but also disrupting the delicate balance of ecosystems within these sites. The loss of biodiversity, a direct consequence of climate change, poses a significant threat to the flora and fauna that have coexisted with these historical landmarks for centuries. As temperatures rise and habitats shift, many species face extinction, leading to a domino effect on the entire ecosystem.
Imagine a historical site nestled in a lush forest, teeming with diverse plant and animal life. Now, picture this ecosystem slowly deteriorating as species disappear due to changing climate patterns and deforestation. The once vibrant tapestry of life begins to unravel, leaving behind a fragmented and weakened environment.
Historical sites rely on the intricate web of biodiversity to maintain their ecological balance. Plants play a crucial role in stabilizing soil, preventing erosion, and providing habitats for various organisms. Animals, in turn, aid in pollination, seed dispersal, and controlling pest populations. When biodiversity is compromised, these essential functions are disrupted, jeopardizing the overall health of the ecosystem.
To address the loss of biodiversity at historical sites, conservation efforts must focus on preserving native species, restoring degraded habitats, and creating corridors for wildlife migration. By promoting plant diversity, reintroducing native species, and establishing protected areas, we can help safeguard the biodiversity essential for the long-term sustainability of these sites.

Permafrost Thaw
Exploring how climate change is affecting the preservation and conservation of historical sites worldwide and the measures being taken to mitigate these impacts.
Discussion on how rising sea levels are threatening coastal historical sites and strategies to protect them from erosion and flooding.
Examining the damage caused by extreme weather events like hurricanes and wildfires on historical sites and efforts to enhance resilience.
Exploring the impact of temperature changes on the structural integrity of historical buildings and monuments and adaptive restoration techniques.
Analyzing how the loss of biodiversity due to climate change affects historical sites' ecosystems and steps to promote conservation.
Permafrost thaw poses a significant threat to archaeological sites in cold regions. As the frozen ground thaws, it can lead to the destabilization of structures and artifacts buried within. This process not only compromises the integrity of the sites but also accelerates the degradation of organic materials preserved in the permafrost.
To combat the impact of permafrost thaw on historical sites, preservation efforts focus on implementing innovative engineering solutions such as thermosyphons and insulation to maintain the frozen ground. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and research are essential to understand the changing conditions and adapt preservation strategies accordingly.
Highlighting the role of deforestation in climate change and its impact on historical sites located in forested areas.
Discussing the importance of community involvement in protecting historical sites from climate change effects and fostering sustainable practices.
Exploring the role of policies, advocacy, and international cooperation in safeguarding historical sites from the impacts of climate change.

Deforestation
Deforestation, a critical issue exacerbated by climate change, poses a significant threat to historical sites nestled within forested regions. The rampant clearing of forests not only contributes to the release of greenhouse gases but also leads to the destruction of habitats and ecosystems that historical sites rely on for their preservation. Imagine a lush forest surrounding a centuries-old temple, providing a natural shield from harsh elements and preserving the site's cultural significance. Now, picture that forest disappearing due to deforestation, leaving the historical site vulnerable to erosion, landslides, and other environmental hazards.
To combat the adverse effects of deforestation on historical sites, conservation efforts must be intensified. Implementing reforestation projects in the vicinity of these sites can help restore lost habitats, enhance biodiversity, and mitigate climate change impacts. Additionally, raising awareness about the link between deforestation, climate change, and historical site preservation is crucial in garnering support for sustainable forestry practices. By engaging local communities, governments, and conservation organizations, we can work towards safeguarding our precious historical heritage for future generations.

Community Engagement
Community engagement plays a crucial role in safeguarding historical sites from the detrimental effects of climate change. When local communities are actively involved in the preservation and conservation efforts, the chances of success significantly increase. By raising awareness and fostering a sense of ownership among residents, historical sites become more than just landmarks; they become integral parts of community identity.
One effective way to engage the community is through educational programs and workshops that highlight the importance of preserving historical sites for future generations. These initiatives not only inform the public about the significance of these sites but also empower individuals to take action in protecting them.
Collaboration with local schools and universities can also be instrumental in promoting community engagement. By integrating historical preservation into educational curricula, young people are instilled with a sense of responsibility towards their heritage, ensuring a sustainable approach to conservation in the long run.
Furthermore, organizing community events such as clean-up campaigns, guided tours, and cultural festivals at historical sites can foster a sense of pride and connection among residents. These activities not only attract visitors but also encourage local support for conservation efforts.
Engaging with indigenous communities and traditional knowledge holders is essential in ensuring that historical sites are preserved in a culturally sensitive manner. By respecting and incorporating indigenous perspectives, conservation initiatives can benefit from centuries-old practices that have sustained these sites for generations.
Establishing partnerships with local businesses and organizations can also enhance community engagement by creating economic incentives for conservation. By highlighting the economic benefits of preserving historical sites, stakeholders are more likely to actively participate in sustainability initiatives.
In conclusion, community engagement is not just a strategy but a fundamental pillar in the protection of historical sites from the impacts of climate change. By involving local residents, educational institutions, indigenous communities, and businesses, we can ensure that these invaluable treasures are preserved for future generations to enjoy.

Policy and Advocacy
Climate change is not only a threat to our environment but also to our cultural heritage. Historical sites around the world are facing significant challenges due to the changing climate, jeopardizing their preservation and conservation. In this article, we will delve into how climate change is impacting these invaluable sites and the measures being implemented to mitigate these detrimental effects.
When it comes to safeguarding historical sites from the impacts of climate change, policy frameworks and advocacy play a crucial role. Governments and organizations worldwide are recognizing the urgent need to address the vulnerabilities of historical sites and are taking proactive steps to ensure their protection.
Through the establishment of robust policies, regulations, and guidelines, authorities aim to integrate climate change considerations into the management and conservation of historical sites. These policies not only focus on immediate preservation efforts but also emphasize long-term sustainability and resilience against future climate challenges.
Advocacy efforts are equally essential in raising awareness about the importance of protecting historical sites from climate change impacts. By engaging with stakeholders, communities, and the public, advocates can mobilize support for conservation initiatives and encourage sustainable practices that contribute to the resilience of these sites.
International cooperation and collaboration are also vital in addressing the transnational nature of climate change impacts on historical sites. By sharing knowledge, resources, and best practices, countries can work together to develop effective strategies for mitigating the effects of climate change and safeguarding our shared cultural heritage.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What historical sites are most vulnerable to the impacts of climate change?
Coastal historical sites are particularly vulnerable to rising sea levels, while those in forested areas face threats from deforestation. Additionally, archaeological sites in cold regions are at risk due to permafrost thaw.
- How can historical sites be protected from rising sea levels?
Protective measures such as building seawalls, implementing beach nourishment projects, and relocating vulnerable structures further inland can help safeguard coastal historical sites from erosion and flooding caused by rising sea levels.
- What can be done to enhance the resilience of historical sites against extreme weather events?
Enhancing the resilience of historical sites involves implementing disaster preparedness plans, conducting regular maintenance and inspections, using resilient building materials, and incorporating sustainable landscaping practices to mitigate the impact of hurricanes, wildfires, and other extreme weather events.
- How do temperature changes affect historical buildings and monuments?
Temperature changes can lead to structural damage in historical buildings and monuments due to factors like thermal expansion and contraction. Adaptive restoration techniques, such as using compatible materials and innovative conservation methods, are crucial in preserving the integrity of these sites.
- Why is community engagement important in protecting historical sites from climate change effects?
Community engagement plays a vital role in raising awareness about the significance of historical sites, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility among local residents, and promoting sustainable practices that contribute to the long-term preservation of these cultural heritage assets.
- What role do policies and advocacy play in safeguarding historical sites from climate change impacts?
Effective policies, advocacy efforts, and international cooperation are essential in establishing regulatory frameworks, securing funding for conservation projects, promoting sustainable development practices, and advocating for the protection of historical sites at the national and global levels.