The Renaissance - Rebirth of Art and Culture
The Renaissance, often referred to as the "Rebirth of Art and Culture," was a transformative period in European history that sparked a revival of creativity and intellectual curiosity. This era was marked by a flourishing of art, literature, and learning, leading to significant advancements and innovations that shaped the course of history.
Originating in Italy during the 14th century, the Renaissance was fueled by a combination of historical, social, and economic factors that set the stage for a cultural revolution. As the movement spread across Europe, it brought about a renewed interest in classical antiquity, humanism, and scientific inquiry.
At the heart of the Renaissance were key figures who played pivotal roles in shaping the artistic and intellectual landscape of the time. Visionaries such as Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Galileo emerged as influential figures, leaving a lasting impact on their respective fields.
Leonardo da Vinci, a true Renaissance polymath, epitomized the spirit of the era with his multifaceted talents in art, science, and engineering. His iconic works like the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper continue to captivate audiences worldwide, showcasing his mastery of both artistic expression and scientific exploration.
The Medici family, prominent patrons of the arts in Florence, played a crucial role in fostering creativity and supporting artists during the Renaissance. Their patronage not only fueled artistic innovation but also contributed to the cultural richness of the period.
The Renaissance was a period of unparalleled artistic innovation, with artists pioneering new techniques and styles that revolutionized the art world. Concepts such as perspective, chiaroscuro, and sfumato became hallmarks of Renaissance art, setting new standards for realism and depth in artistic representation.
Architectural achievements of the Renaissance also left a lasting legacy, with the construction of grand cathedrals, palaces, and public buildings that showcased a blend of classical influences and innovative design principles. These architectural marvels continue to inspire awe and admiration to this day.
The impact of the Renaissance reverberated across art, culture, science, and society, shaping the modern world in profound ways. Its legacy can be seen in the intellectual thought, artistic expression, and cultural values that continue to influence contemporary society.
Reflecting on the enduring legacy of the Renaissance, we can appreciate its profound influence on art, culture, and intellectual thought in the contemporary world. The spirit of creativity, innovation, and humanism that defined this era continues to inspire and resonate with us today, reminding us of the enduring power of artistic expression and intellectual curiosity.

Origins of the Renaissance
The origins of the Renaissance can be traced back to the 14th century in Italy, particularly in the city-states of Florence, Venice, and Rome. This period marked a significant shift from the medieval era, characterized by a renewed interest in art, literature, and humanism. The economic prosperity of Italian cities, fueled by trade and commerce, played a crucial role in fostering a culture of patronage and innovation.
One of the key factors that contributed to the emergence of the Renaissance was the rediscovery of classical texts and ancient knowledge. The fall of the Byzantine Empire in 1453 led to a wave of Greek scholars migrating to Italy, bringing with them valuable manuscripts and intellectual ideas. This influx of new knowledge sparked a cultural revival and inspired artists and thinkers to explore new perspectives and ideas.
The Renaissance was also influenced by the growing emphasis on individualism and human potential. Humanist scholars like Petrarch and Pico della Mirandola promoted the idea of human dignity and the pursuit of knowledge for its own sake. This shift in mindset encouraged artists and intellectuals to break away from traditional constraints and explore the depths of human creativity.
Moreover, the political landscape of Italy, with its decentralized city-states and competitive ruling families, created a fertile ground for artistic and intellectual exchange. The patronage of wealthy families like the Medici in Florence and the Sforza in Milan provided artists and scholars with the financial support and resources needed to pursue their creative endeavors.

Key Figures of the Renaissance
The Renaissance era was marked by the emergence of remarkable individuals who played pivotal roles in shaping the cultural landscape of the time. These key figures of the Renaissance were not only artists but also thinkers and scientists who pushed the boundaries of creativity and knowledge. Among them, Leonardo da Vinci stands out as a true Renaissance polymath, showcasing his talents in art, science, and engineering. His iconic works like the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper continue to captivate audiences worldwide, while his innovative inventions and anatomical studies demonstrate his multidisciplinary genius.
Another influential group during the Renaissance was the Medici family, who acted as patrons of the arts in Florence. The Medici's financial support and encouragement of artists such as Michelangelo and Botticelli were instrumental in fostering a thriving cultural environment. Their patronage not only allowed artists to create masterpieces but also contributed to the preservation and promotion of artistic heritage.
Galileo Galilei, a pioneering astronomer and physicist, also left a lasting impact on the Renaissance period. His astronomical observations with the telescope challenged existing beliefs about the universe and laid the foundation for modern observational astronomy. Despite facing opposition from the church, Galileo's contributions to science revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos and paved the way for future scientific advancements.

Leonardo da Vinci: A Renaissance Polymath
Leonardo da Vinci, often hailed as the quintessential Renaissance man, was a true polymath whose talents knew no bounds. Born in Vinci, Italy, in 1452, da Vinci excelled not only as a painter but also as a sculptor, architect, engineer, scientist, and inventor. His insatiable curiosity and relentless pursuit of knowledge set him apart as a visionary ahead of his time.
Da Vinci's artistic prowess is exemplified in masterpieces such as the iconic Mona Lisa, renowned for her enigmatic smile, and the timeless depiction of The Last Supper. His scientific inquiries delved into anatomy, optics, and the natural world, leading to groundbreaking discoveries and sketches that foreshadowed modern inventions.
Furthermore, da Vinci's engineering marvels, including designs for flying machines and war inventions, showcased his innovative spirit and technical acumen. His ability to seamlessly blend art and science epitomized the essence of the Renaissance, where creativity and intellect converged to push the boundaries of human achievement.
As a true polymath, Leonardo da Vinci's legacy transcends disciplines and continues to inspire generations with his multidimensional talents and boundless imagination.
The Medici Family: Patrons of the Arts
The Medici family, renowned as one of the most influential and powerful families in Florence during the Renaissance, played a pivotal role as patrons of the arts. Their unwavering support for artists, thinkers, and scholars not only elevated the cultural landscape of the time but also paved the way for artistic innovation and creativity to flourish.
At the helm of the Medici family stood prominent figures such as Cosimo de' Medici and Lorenzo de' Medici, known for their passion for art and intellectual pursuits. They recognized the value of investing in the arts as a means of showcasing their wealth and power, as well as fostering a cultural renaissance in Florence.
The Medici family's patronage extended to a myriad of artistic disciplines, from painting and sculpture to architecture and literature. Artists like Sandro Botticelli and Michelangelo found patronage under the Medici, enabling them to create masterpieces that have stood the test of time.
Through their generous financial support and encouragement, the Medici family not only commissioned works of art but also provided artists with the resources and freedom to explore new techniques and ideas. This patronage system not only benefited the artists themselves but also enriched the cultural fabric of Renaissance society.
Furthermore, the Medici family's patronage was not limited to established artists but also extended to emerging talents, nurturing a new generation of creative minds. This inclusive approach to supporting the arts ensured a continuous flow of artistic expression and innovation, contributing to the flourishing artistic scene of the Renaissance.
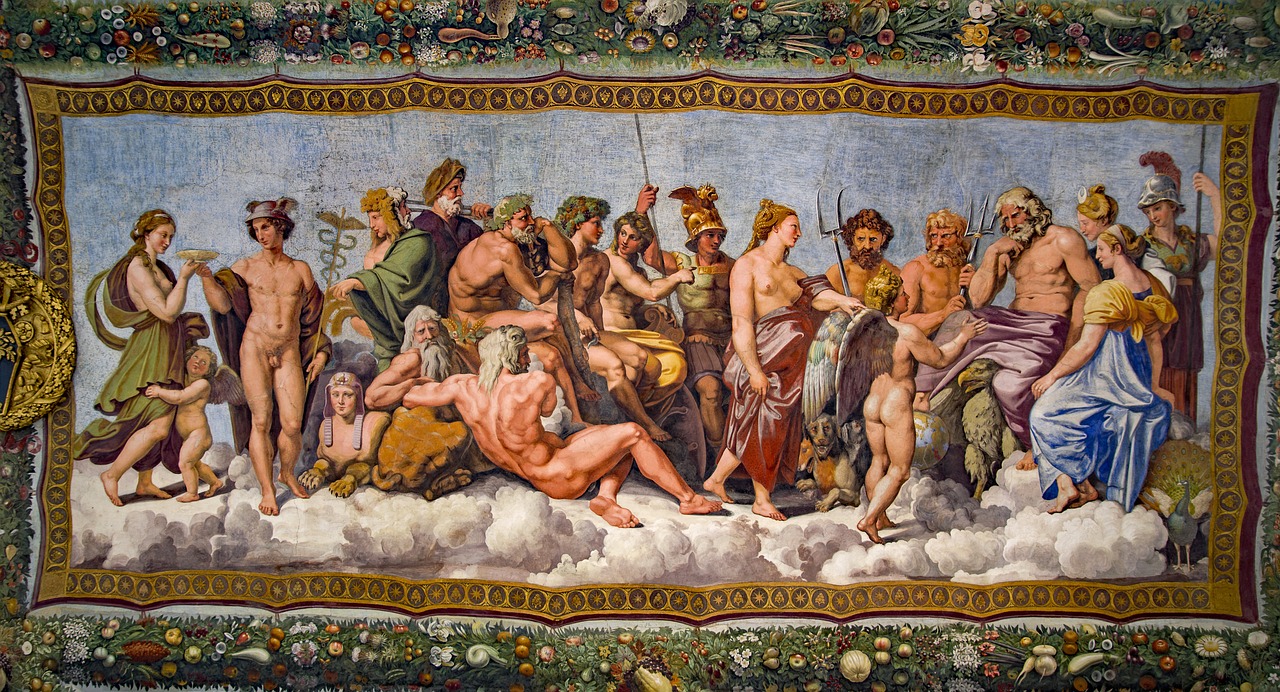

Artistic Innovations and Techniques
The Renaissance period was a time of immense creativity and innovation in the world of art. Artists during this period developed revolutionary techniques that transformed the way art was created and perceived. One of the most significant innovations was the development of perspective, a technique that allowed artists to create more realistic and spatially accurate representations in their works. By using perspective, artists could give the illusion of depth and three-dimensionality, bringing their paintings to life in a way never seen before.
Another important technique that emerged during the Renaissance was chiaroscuro, a method of using strong contrasts between light and dark to create a sense of volume and form in paintings. Artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Caravaggio were masters of chiaroscuro, using it to add drama and intensity to their works. Additionally, the technique of sfumato, which involves the gradual blending of colors and tones to create soft transitions, was perfected during this period, adding a sense of mystery and atmosphere to paintings.
Artists in the Renaissance also experimented with new materials and tools, pushing the boundaries of artistic expression. The use of oil paint became widespread, allowing for greater richness and depth of color in paintings. Artists like Jan van Eyck and Titian were pioneers in the use of oil paint, creating masterpieces that showcased the medium's versatility and vibrancy.
Furthermore, the Renaissance saw a renewed interest in the human form and anatomy, leading artists to study the human body in detail and depict it with greater accuracy. This focus on realism and naturalism revolutionized the way artists approached their subjects, resulting in lifelike and emotionally engaging portraits and sculptures.
In conclusion, the artistic innovations and techniques developed during the Renaissance laid the foundation for modern art and continue to inspire artists to this day. The period's emphasis on realism, perspective, and technical skill transformed the art world and set new standards for creativity and expression.
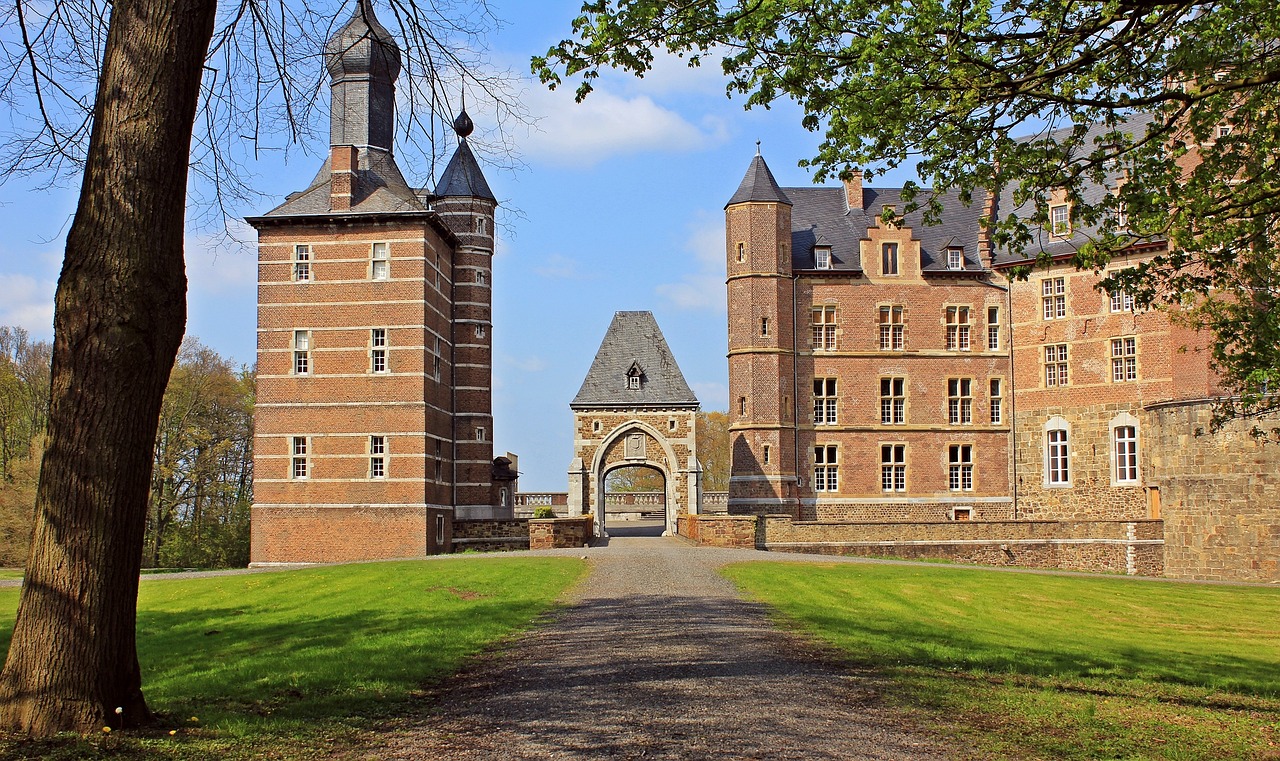

Renaissance Architecture and Design
Renaissance Architecture and Design during the Renaissance period was a remarkable fusion of classical influences and innovative techniques, resulting in iconic structures that still captivate us today. Architects and designers of this era drew inspiration from ancient Roman and Greek styles, incorporating elements such as columns, arches, and domes into their creations. One of the most notable features of Renaissance architecture was the emphasis on symmetry and proportion, reflecting a newfound appreciation for balance and harmony in design.
One of the defining characteristics of Renaissance architecture was the use of perspective to create the illusion of depth and space in two-dimensional artworks. This technique revolutionized the way buildings were depicted, allowing for more realistic and immersive representations. Architects also experimented with new materials and construction methods, leading to the development of innovative structural techniques that enabled the creation of larger and more elaborate buildings.
The Renaissance period saw the construction of magnificent cathedrals, palaces, and public buildings that showcased the wealth and power of the ruling elite. These structures served not only as functional spaces but also as symbols of prestige and cultural sophistication. Architects like Filippo Brunelleschi and Andrea Palladio were instrumental in shaping the architectural landscape of the Renaissance, leaving behind a legacy of timeless masterpieces that continue to inspire architects and designers to this day.

Impact of the Renaissance
The impact of the Renaissance reverberates through history, leaving an indelible mark on art, culture, science, and society. This transformative period sparked a wave of creativity and innovation that reshaped the way people viewed the world and their place in it. The Renaissance not only revitalized artistic expression but also fostered a spirit of intellectual curiosity and exploration that laid the foundation for future advancements.
One of the most significant impacts of the Renaissance was the shift in artistic techniques and styles. Artists during this period began to experiment with perspective, chiaroscuro (the use of light and shadow), and sfumato (the blending of colors), creating a sense of depth and realism in their works that was unprecedented. This revolution in art set the stage for the development of new artistic movements and paved the way for the masterpieces that would define the Renaissance era.
Furthermore, the Renaissance had a profound influence on architecture and design. Architects drew inspiration from classical Roman and Greek styles, leading to the construction of magnificent cathedrals, palaces, and public buildings that showcased a harmonious blend of beauty and functionality. The architectural achievements of the Renaissance continue to awe and inspire observers to this day, serving as a testament to the enduring legacy of this period.
Moreover, the Renaissance catalyzed advancements in science and technology, with figures like Galileo Galilei challenging conventional beliefs and paving the way for modern scientific inquiry. The spirit of inquiry and experimentation that characterized the Renaissance laid the groundwork for the scientific revolution that would follow, forever changing the way humanity understood the natural world.
On a broader societal level, the Renaissance fostered a culture of humanism that emphasized the value of individual achievement and intellectual pursuits. This humanistic philosophy, which placed human beings at the center of the universe, had a profound impact on social structures and institutions, paving the way for the emergence of modern democratic ideals and the promotion of education and literacy.

Legacy of the Renaissance
The legacy of the Renaissance continues to reverberate throughout the annals of history, leaving an indelible mark on art, culture, and intellectual thought. This transformative period not only ushered in a new era of creativity and innovation but also laid the groundwork for the modern world as we know it today. The Renaissance's legacy can be witnessed in a myriad of ways, from the enduring influence of artistic masterpieces to the revolutionary ideas that shaped scientific inquiry and philosophical discourse.
One of the most significant legacies of the Renaissance is its emphasis on humanism, a philosophical approach that prioritizes the value and agency of the individual. This humanistic perspective, championed by thinkers like Petrarch and Erasmus, continues to inform our understanding of human nature and the pursuit of knowledge. The Renaissance's celebration of human potential and creativity has left an enduring legacy that resonates in fields as diverse as literature, art, and ethics.
Artistically, the Renaissance revolutionized the way in which artists approached their craft, introducing innovative techniques and styles that would shape the course of art history. The mastery of perspective, the use of light and shadow (chiaroscuro), and the blending of tones (sfumato) are just a few examples of the artistic innovations that emerged during this period. These techniques not only transformed the visual arts but also influenced future generations of artists, paving the way for movements such as Baroque and Rococo.
Furthermore, the Renaissance's impact on architecture and design can still be seen in the grand cathedrals, palaces, and public buildings that dot the European landscape. Architects like Brunelleschi and Palladio reimagined classical forms and proportions, creating structures that embodied harmony, balance, and beauty. The architectural legacy of the Renaissance endures in iconic landmarks such as the St. Peter's Basilica in Rome and the Palazzo Vecchio in Florence.
Intellectually, the Renaissance laid the foundation for modern scientific inquiry, with figures like Galileo Galilei challenging prevailing beliefs and advancing our understanding of the natural world. The spirit of curiosity and experimentation that defined the Renaissance continues to drive scientific discovery and technological innovation in the present day. The legacy of the Renaissance in the realm of science is a testament to the enduring impact of intellectual curiosity and empirical observation.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What was the Renaissance?
The Renaissance was a transformative period in European history characterized by a revival of art, literature, and learning that led to significant cultural advancements and innovations.
- When did the Renaissance take place?
The Renaissance took place roughly between the 14th and 17th centuries, with its origins in Italy and later spreading across Europe.
- Who were some key figures of the Renaissance?
Some key figures of the Renaissance include artists like Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo, as well as scholars like Galileo who made significant contributions to art, science, and culture.
- What were some artistic innovations of the Renaissance?
The Renaissance saw the development of revolutionary artistic techniques such as perspective, chiaroscuro, and sfumato, which transformed the way art was created and perceived.
- How did the Renaissance impact society?
The Renaissance had a lasting impact on art, culture, science, and society, shaping the modern world and influencing future artistic movements and intellectual thought.



















