The Influence of Ancient Near Eastern Cultures on History
Ancient Near Eastern cultures have left an indelible mark on the tapestry of history, influencing various facets of human civilization in profound ways. From the development of language and writing systems to the establishment of legal frameworks and governance structures, these ancient societies have shaped the course of history in lasting ways.
One of the most significant contributions of ancient Near Eastern cultures lies in the realm of language and writing systems. The emergence of early languages such as Sumerian and Akkadian laid the foundation for written communication, paving the way for the rich literary traditions that followed. The invention of cuneiform script in Mesopotamia revolutionized record-keeping and administration, setting a precedent for future writing systems.
Religious beliefs and practices in ancient Near Eastern societies were equally influential, shaping the spiritual landscape of the ancient world. The worship of deities such as Ishtar and Marduk, along with elaborate rituals and ceremonies, reflected a complex cosmology that permeated all aspects of life. Concepts of the afterlife, divine judgment, and sacred kingship were central tenets of these belief systems.
The establishment of legal systems and governance structures in ancient Near Eastern civilizations marked a pivotal development in the evolution of law and political organization. The Code of Hammurabi, a legal code from ancient Babylon, exemplified the principles of justice and equity that continue to resonate in modern legal systems. The concept of centralized authority and bureaucratic administration laid the groundwork for future systems of governance.
Art, architecture, and technology flourished in ancient Near Eastern cultures, showcasing the creative ingenuity and technical prowess of these societies. From the ziggurats of Sumer to the intricate relief sculptures of Assyria, artistic achievements abounded. Technological innovations such as irrigation systems and metallurgy advanced the material culture of the ancient Near East.
Trade networks and economic systems played a crucial role in the prosperity of ancient Near Eastern societies, facilitating the exchange of goods and ideas across vast distances. The development of commercial hubs such as Ur and Nineveh fueled economic growth and cultural exchange, laying the foundation for interconnected global economies.
Social hierarchies and gender roles in ancient Near Eastern civilizations reflected the complexities of societal structures and cultural norms. Class distinctions between nobility and commoners, as well as gender-based divisions of labor, shaped the social fabric of these ancient societies. The roles of women in religion, politics, and daily life varied across different cultures.
Warfare and military strategies were integral to the power dynamics of ancient Near Eastern civilizations, with conquest and defense playing a central role in shaping regional politics. The chariot warfare of the Hittites, the siege tactics of the Assyrians, and the naval prowess of the Phoenicians exemplified the military innovations of the ancient Near East.
The legacy of ancient Near Eastern cultures endures in contemporary society, with their traditions, beliefs, and achievements continuing to influence the modern world. The enduring impact of Mesopotamian mathematics, Babylonian astronomy, and Assyrian art serves as a testament to the enduring legacy of these ancient civilizations.

Language and Writing Systems
Exploring the profound impact of ancient Near Eastern civilizations on shaping various aspects of history, from language and writing systems to religion, law, and societal structures.
The ancient Near Eastern cultures played a pivotal role in the development of early languages and writing systems, laying the foundation for written communication as we know it today. From the cuneiform script of Mesopotamia to the hieroglyphs of Egypt, these ancient civilizations pioneered the art of recording information and ideas in a tangible form. The intricate symbols and characters they created not only facilitated communication within their societies but also paved the way for the evolution of written expression across different cultures.

Religious Beliefs and Practices
Ancient Near Eastern societies were deeply intertwined with a diverse array of religious beliefs and practices that shaped their worldview and daily lives. The polytheistic nature of many civilizations in the region led to the worship of multiple deities, each associated with various aspects of nature, fertility, war, and the afterlife. Rituals and ceremonies played a significant role in honoring these gods and goddesses, with elaborate offerings, sacrifices, and festivals held to appease and seek favor from the divine beings.
The concept of the afterlife held great significance in ancient Near Eastern cultures, with beliefs in an underworld or realm of the dead where souls journeyed after passing from the physical world. Funerary practices reflected these beliefs, with elaborate burials, tombs, and grave goods provided to ensure a smooth transition to the afterlife. The presence of deities associated with death and the afterlife underscored the importance placed on proper burial rites and commemoration of the deceased.
Moreover, the role of priests and priestesses was pivotal in maintaining religious traditions and performing sacred rituals on behalf of the community. These religious leaders acted as intermediaries between the mortal realm and the divine, interpreting omens, conducting ceremonies, and offering prayers for the well-being and prosperity of the society. Temples served as centers of religious activity, where the faithful gathered to worship, seek guidance, and participate in communal rites that reinforced social cohesion and spiritual unity.
The intricate mythologies and legends of ancient Near Eastern cultures provided a rich tapestry of stories that explained the origins of the world, the relationships between gods and humans, and the forces of nature. These narratives were passed down through oral tradition and written texts, such as cuneiform tablets and hieroglyphic inscriptions, preserving the collective memory of the society and reinforcing cultural identity through shared beliefs and values.
In conclusion, the religious beliefs and practices of ancient Near Eastern civilizations were integral to the fabric of their existence, influencing every aspect of life from governance and social order to art and daily rituals. The enduring legacy of these spiritual traditions continues to resonate in modern society, offering insights into the human quest for meaning, connection to the divine, and a deeper understanding of the mysteries of existence.

Legal Systems and Governance
Legal systems and governance structures in ancient Near Eastern civilizations played a pivotal role in shaping the foundations of law and political organization that continue to influence societies today. The concept of codified laws, such as the famous Code of Hammurabi in ancient Mesopotamia, provided a framework for justice and governance that set precedents for future legal systems. These early legal codes addressed various aspects of society, including property rights, marriage, and criminal behavior, establishing a sense of order and accountability within communities.
The development of centralized authority and administrative systems in ancient Near Eastern cultures laid the groundwork for organized governance and political institutions. Rulers and officials were tasked with maintaining social order, resolving disputes, and overseeing the implementation of laws. The presence of bureaucratic structures and judicial bodies ensured the enforcement of regulations and the protection of individual rights, fostering a sense of stability and security within these ancient societies.
Moreover, the concept of justice and the rule of law in ancient Near Eastern civilizations reflected the values and beliefs of the respective cultures. Legal decisions were often influenced by religious principles and societal norms, emphasizing the importance of ethical conduct and moral responsibility. The integration of religious beliefs into legal systems underscored the interconnectedness of spiritual and secular authority, shaping the moral fabric of society and guiding the behavior of individuals.
Furthermore, the legacy of legal systems and governance structures from ancient Near Eastern civilizations can be seen in the evolution of modern legal frameworks and political institutions. Concepts such as due process, legal precedent, and the separation of powers have roots in the practices and principles established by these ancient societies. The enduring impact of ancient Near Eastern legal traditions serves as a testament to the enduring legacy of their contributions to the development of legal systems and governance mechanisms.
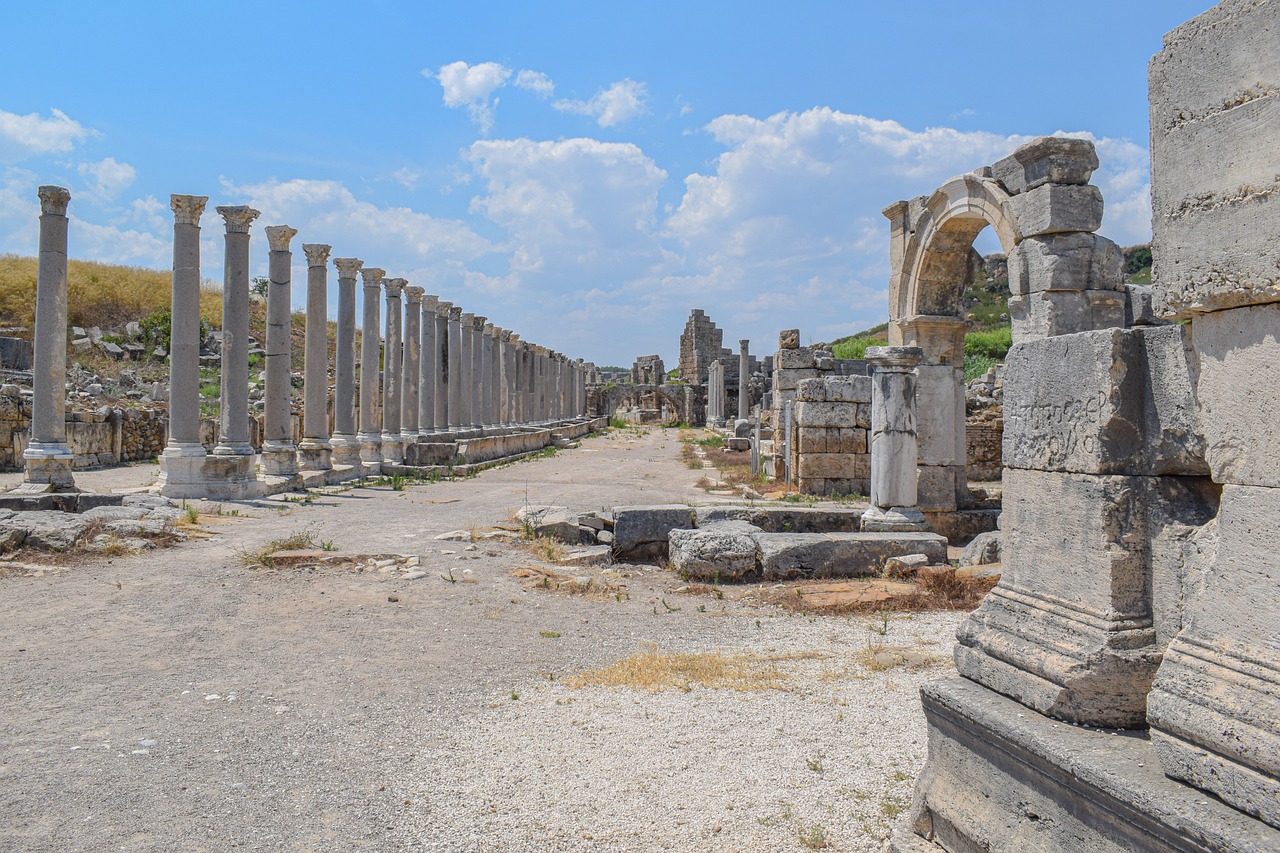

Art, Architecture, and Technology
Exploring the profound impact of ancient Near Eastern civilizations on shaping various aspects of history, from language and writing systems to religion, law, and societal structures.
Art, architecture, and technology in ancient Near Eastern cultures were not merely expressions of creativity but also reflections of their advanced civilizations. The intricate designs of Mesopotamian ziggurats, the grandeur of Egyptian pyramids, and the precision of Hittite metalwork all stand as testaments to the skill and innovation of these ancient peoples.
The art of the ancient Near East was not just about aesthetics; it served multiple purposes, from religious symbolism to political propaganda. Sculptures, reliefs, and paintings depicted gods, rulers, and important events, providing a visual narrative of the culture and beliefs of the time.
Architecture in the region was equally impressive, with cities like Babylon and Nineveh boasting massive walls, temples, and palaces that showcased the wealth and power of their rulers. The use of advanced engineering techniques, such as arches and vaults, demonstrated a sophisticated understanding of construction that continues to influence architectural design today.
Technological advancements in ancient Near Eastern cultures were groundbreaking for their time. The invention of writing systems like cuneiform in Mesopotamia and hieroglyphics in Egypt revolutionized communication and record-keeping, laying the foundation for future developments in written language. Additionally, innovations in metallurgy, irrigation, and warfare technology propelled these civilizations to new heights of prosperity and military might.
Stay tuned for the frequently asked questions section!

Trade and Economic Systems
Exploring the profound impact of ancient Near Eastern civilizations on shaping various aspects of history, from language and writing systems to religion, law, and societal structures.
Trade and economic systems in ancient Near Eastern societies played a pivotal role in shaping the dynamics of commerce and economic practices. The exchange of goods and services through extensive trade networks not only facilitated cultural diffusion but also contributed to the economic prosperity of these civilizations. Merchants traversed long distances, connecting distant regions and fostering economic interdependence.
The economic systems of ancient Near Eastern cultures were characterized by a variety of commodities, including precious metals, textiles, spices, and agricultural products. These goods were traded both locally and internationally, leading to the development of sophisticated marketplaces and commercial hubs. The use of standardized weights and measures ensured fair trade practices and promoted economic stability.
Moreover, the establishment of trade routes such as the Silk Road and the Amber Road facilitated the exchange of goods between different regions, enabling the flow of resources and fostering cultural exchange. The economic prosperity resulting from trade allowed for the accumulation of wealth, the growth of urban centers, and the development of specialized crafts and industries.
Ancient Near Eastern societies also engaged in barter systems, where goods were exchanged directly without the use of currency. This practice not only facilitated trade but also fostered social connections and mutual cooperation among individuals and communities. The economic systems of these civilizations were intricately linked to social structures, governance, and cultural practices, reflecting the interconnectedness of economic activities with broader societal dynamics.
Q: How did trade networks in ancient Near Eastern cultures influence global commerce?
A: Trade networks in ancient Near Eastern cultures facilitated the exchange of goods and ideas across vast regions, contributing to the interconnectedness of diverse societies and the growth of international trade.
Q: What were the key commodities traded in ancient Near Eastern societies?
A: Ancient Near Eastern societies traded a wide range of commodities, including precious metals, textiles, spices, agricultural products, and luxury goods, which played a significant role in economic development and cultural exchange.
Q: How did trade routes like the Silk Road impact economic relations in ancient Near Eastern civilizations?
A: Trade routes such as the Silk Road facilitated the movement of goods between East and West, promoting economic prosperity, cultural exchange, and the diffusion of ideas and technologies among ancient Near Eastern civilizations and beyond.

Social Hierarchies and Gender Roles
Social hierarchies and gender roles in ancient Near Eastern civilizations provide a fascinating glimpse into the intricate fabric of societal structures and cultural norms of the time. These societies were often characterized by complex systems of social stratification, where individuals were placed in various classes based on factors such as wealth, occupation, and lineage. The division between the ruling elite, the middle class, and the lower classes was stark, with each group having distinct rights, privileges, and responsibilities.
Moreover, gender roles played a significant role in shaping the dynamics of ancient Near Eastern societies. Women were typically relegated to domestic roles, responsible for managing household affairs and raising children, while men held positions of authority and power in the public sphere. Despite these traditional gender norms, some women were able to attain positions of influence and prestige, particularly in the realm of religion and royal courts.
Additionally, the concept of gender in ancient Near Eastern cultures was not always binary, with evidence of third gender categories and individuals who did not conform to traditional male or female roles. These individuals, often referred to as eunuchs or gender-nonconforming individuals, held unique positions in society and were sometimes revered for their perceived spiritual or mystical qualities.
Furthermore, social hierarchies in ancient Near Eastern civilizations were intricately linked to religious beliefs and practices. The ruling elite often justified their privileged status through divine mandate, claiming to be descendants of gods or chosen by deities to rule over the masses. This intertwining of religion and governance reinforced existing power structures and perpetuated the stratification of society.
Overall, the study of social hierarchies and gender roles in ancient Near Eastern cultures offers valuable insights into the complexities of human civilization and the enduring impact of historical norms on contemporary society.
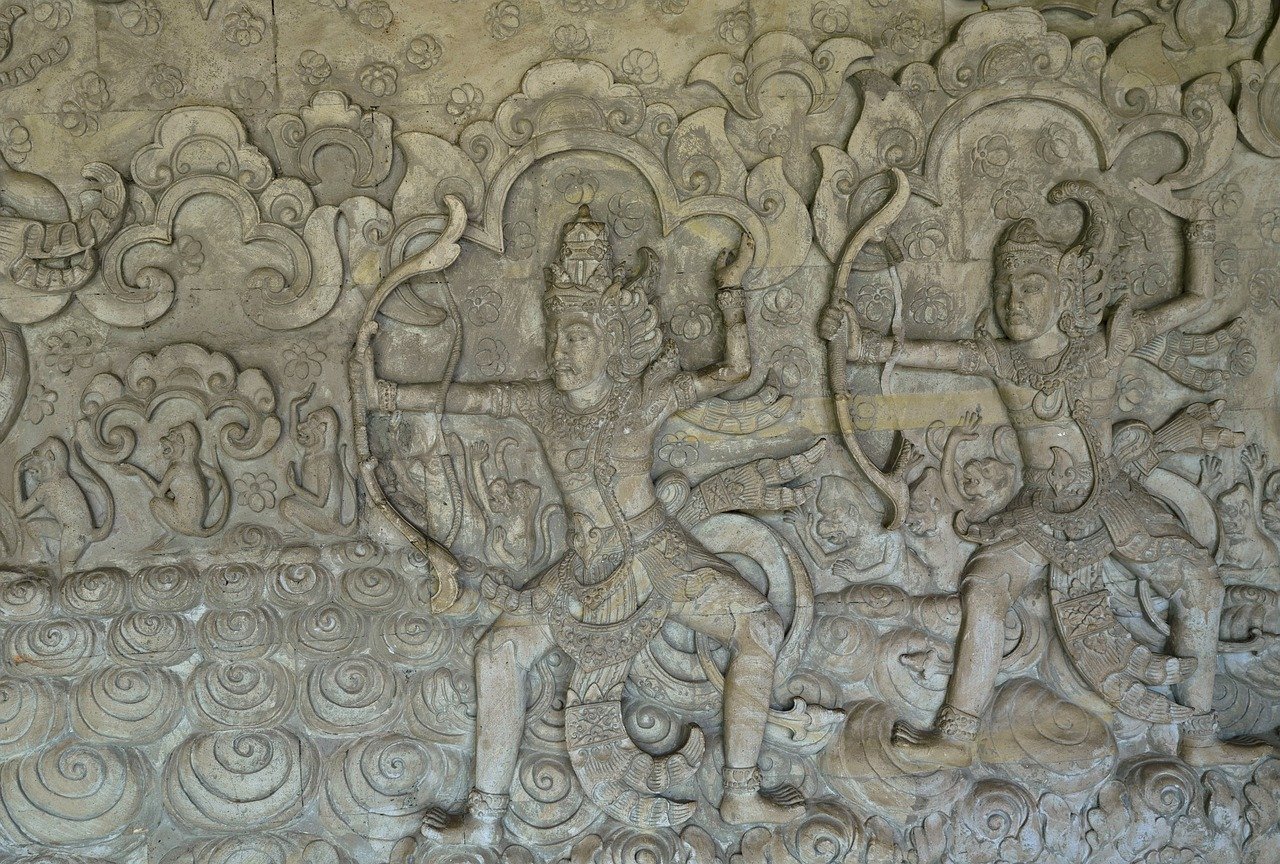

Warfare and Military Strategies
Warfare and Military Strategies in ancient Near Eastern cultures were characterized by a sophisticated understanding of tactics and a strategic approach to conflicts. These civilizations developed advanced military systems that played a crucial role in shaping the outcomes of battles and wars. The use of chariots, cavalry, and infantry units showcased their innovative approach to warfare, allowing them to dominate the battlefield with strategic maneuvers and coordinated attacks.
One of the key military strategies employed by ancient Near Eastern cultures was the use of siege warfare to conquer enemy territories. They constructed fortified city walls and developed siege engines to besiege enemy strongholds, demonstrating their prowess in both offensive and defensive military tactics. The strategic use of archers, spearmen, and siege weapons highlighted their tactical ingenuity in combat situations, enabling them to outmaneuver and outsmart their opponents on the battlefield.
Ancient Near Eastern civilizations also excelled in organizing military campaigns and coordinating large armies to achieve strategic objectives. Military leaders were adept at planning and executing military operations, utilizing intelligence gathering, reconnaissance, and logistics to ensure the success of their campaigns. The establishment of military hierarchies and command structures enabled efficient communication and coordination among troops, leading to effective military engagements and decisive victories.
Moreover, the development of military technologies such as bronze weapons, armor, and chariots revolutionized warfare in ancient Near Eastern cultures. These advancements in military equipment and tactics provided them with a significant advantage on the battlefield, allowing them to assert dominance over rival powers and expand their territorial influence. The strategic use of chariots in battle, for instance, demonstrated their innovative approach to mobile warfare and rapid deployment of forces.
In conclusion, the warfare and military strategies of ancient Near Eastern cultures were characterized by strategic brilliance, tactical innovation, and technological advancements that left a lasting impact on the history of warfare. Their military prowess and strategic acumen influenced the course of conflicts and battles throughout history, shaping the development of military strategies and tactics in subsequent civilizations.
Legacy and Continuity
Exploring the profound impact of ancient Near Eastern civilizations on shaping various aspects of history, from language and writing systems to religion, law, and societal structures.
The legacy of ancient Near Eastern cultures continues to resonate in modern society, leaving an indelible mark on various facets of human civilization. Through their enduring contributions in language, religion, governance, art, and warfare, these ancient civilizations have established a lasting continuity that transcends time.
One of the most remarkable legacies of ancient Near Eastern cultures lies in their linguistic and written heritage. The development of cuneiform script in Mesopotamia and hieroglyphics in Egypt laid the foundation for written communication, influencing the evolution of writing systems across the globe. The legacy of these early scripts can be seen in modern alphabets and languages, underscoring the enduring impact of ancient Near Eastern civilizations on written expression.
Furthermore, the religious beliefs and practices of ancient Near Eastern societies have left a lasting imprint on the spiritual landscape of humanity. The worship of deities such as Ishtar, Marduk, and Ra, along with the concept of an afterlife, has shaped the religious traditions of subsequent cultures. The legacy of these ancient beliefs can be observed in the diverse religious practices and beliefs prevalent in contemporary societies.
In terms of governance and legal systems, the organizational structures established by ancient Near Eastern civilizations have influenced the development of modern political institutions and legal frameworks. The codification of laws, administrative procedures, and systems of governance in Mesopotamia and Egypt set a precedent for subsequent societies, highlighting the enduring legacy of these early civilizations in shaping legal and political systems.
Moreover, the artistic achievements, architectural innovations, and technological advancements of ancient Near Eastern cultures continue to inspire awe and admiration. From the ziggurats of Sumer to the pyramids of Egypt, these architectural marvels stand as testaments to the ingenuity and creativity of ancient civilizations. The legacy of their artistic and technological prowess can be seen in the architectural wonders and technological innovations of the modern world.
Additionally, the trade networks, economic systems, and commercial activities of ancient Near Eastern societies have had a lasting impact on global commerce and economic practices. The establishment of trade routes, marketplaces, and economic hubs in Mesopotamia and the Levant laid the foundation for international trade and economic exchange, shaping the trajectory of global economics.
Furthermore, the social hierarchies, class distinctions, and gender roles prevalent in ancient Near Eastern civilizations have influenced the cultural norms and societal structures of subsequent societies. The legacy of these social dynamics can be seen in the complexities of modern societal hierarchies and gender roles, highlighting the enduring impact of ancient Near Eastern cultures on social structures.
Lastly, the military prowess, warfare tactics, and strategic innovations of ancient Near Eastern cultures have left a lasting legacy in the annals of military history. The chariots of the Hittites, the phalanxes of the Assyrians, and the naval fleets of the Phoenicians exemplify the strategic acumen and military might of ancient civilizations, shaping the course of conflicts and battles throughout history.
In conclusion, the legacy of ancient Near Eastern cultures endures in the fabric of contemporary society, weaving a tapestry of traditions, beliefs, and achievements that continue to influence the modern world. Their contributions in language, religion, governance, art, trade, social structures, and military strategies have left an indelible mark on human civilization, underscoring the enduring influence of these ancient civilizations on history.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What were the major contributions of ancient Near Eastern cultures to language and writing systems?
Ancient Near Eastern civilizations laid the foundation for written communication through the development of cuneiform and hieroglyphic scripts. These writing systems not only facilitated record-keeping but also enabled the transmission of knowledge across generations.
- How did religion shape the social fabric of ancient Near Eastern societies?
Religion played a central role in ancient Near Eastern cultures, influencing everything from governance and law to daily rituals and beliefs about the afterlife. The worship of various deities and the performance of religious ceremonies were integral to societal cohesion and identity.
- What impact did the legal systems of ancient Near Eastern civilizations have on modern law?
Ancient Near Eastern legal codes, such as the Code of Hammurabi, set precedents for concepts like justice, punishment, and property rights. These early legal systems laid the groundwork for the development of modern legal principles and governance structures.
- How did ancient Near Eastern cultures contribute to the advancement of art, architecture, and technology?
Ancient Near Eastern societies excelled in artistic expression, architectural design, and technological innovation. Their achievements, such as ziggurats, intricate pottery, and irrigation systems, continue to inspire and influence contemporary artistic and technological practices.
- What role did trade and economic systems play in the prosperity of ancient Near Eastern civilizations?
The trade networks and economic practices of ancient Near Eastern cultures facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies across vast regions. These commercial activities fueled economic growth and cultural exchange, shaping the interconnectedness of the ancient world.
- How were social hierarchies and gender roles structured in ancient Near Eastern societies?
Ancient Near Eastern civilizations exhibited complex social hierarchies based on factors like wealth, status, and occupation. Gender roles were often defined by cultural norms and religious beliefs, influencing the roles and expectations of individuals within society.
- What military strategies and innovations were characteristic of ancient Near Eastern cultures?
Ancient Near Eastern societies developed sophisticated military tactics and technologies to defend their territories and expand their influence. Innovations in warfare, such as chariots and siege warfare, shaped the outcomes of conflicts and battles in the ancient world.
- How does the legacy of ancient Near Eastern cultures continue to impact modern society?
The traditions, beliefs, and achievements of ancient Near Eastern civilizations have left a lasting imprint on contemporary culture, language, and societal structures. Their enduring legacy serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of human history and the enduring influence of ancient civilizations.



















