The Lost Kingdom of Axum - Trade and Prosperity
Exploring the ancient civilization of Axum, known for its flourishing trade routes and economic prosperity in the Horn of Africa. Uncover the history and significance of this once powerful kingdom that thrived through commerce and cultural exchange.

Ancient Axumite Civilization
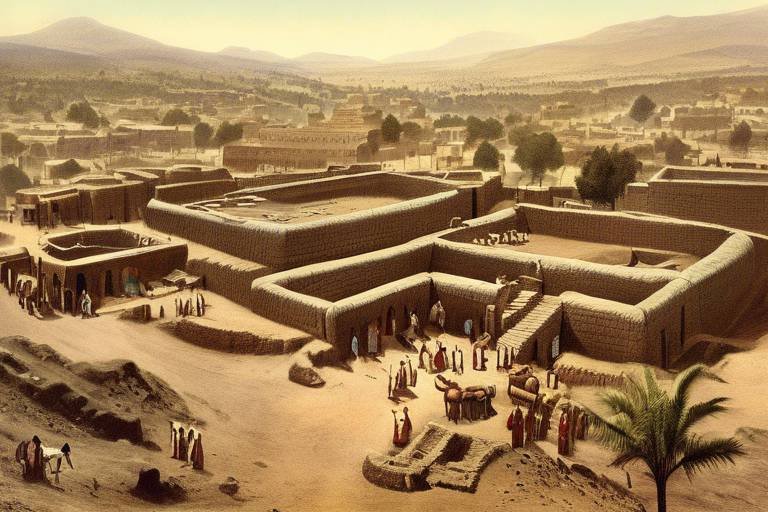
The Ancient Axumite Civilization holds a significant place in the history of Africa, particularly in the region of the Horn of Africa. Originating around the 1st century AD, the Axumite civilization flourished as a powerful kingdom known for its advanced political structure and economic prosperity. At its peak, Axum was a prominent center of trade and culture, attracting merchants and travelers from distant lands.
One of the key factors contributing to the success of the Axumite civilization was its strategic location. Situated in present-day Ethiopia and Eritrea, Axum served as a crossroads for trade between Africa, the Mediterranean, and Asia. This geographical advantage allowed the kingdom to establish lucrative trade routes that brought wealth and influence to the region.
The political structure of Axum was characterized by a strong monarchy, with the king serving as the central authority. The kingdom's rulers, known as neguses, played a vital role in governing the state and overseeing trade relations with foreign powers. Additionally, the Axumite civilization was known for its sophisticated system of coinage, which further facilitated economic transactions and commercial activities.
Moreover, Axum's economic success was closely tied to its control over key resources such as ivory, gold, and frankincense. These valuable commodities were highly sought after in the ancient world, making Axum a prosperous trading hub. The kingdom's ability to extract and trade these resources contributed to its economic growth and political influence in the region.

Trade Routes and Commerce
Trade was the lifeblood of the ancient Kingdom of Axum, fueling its prosperity and influence across the Horn of Africa and beyond. The strategic location of Axum allowed it to establish extensive trade routes that connected the kingdom to distant lands, fostering a vibrant exchange of goods and ideas. The Axumites engaged in commerce with regions as far as the Mediterranean and Asia, importing and exporting a variety of valuable commodities.
One of the key trade routes that bolstered Axum's economic power was the connection between the Red Sea and the interior regions of Africa, with the port city of Adulis playing a crucial role as a bustling maritime hub. Adulis served as the gateway for goods flowing in and out of Axum, facilitating trade with merchants from different parts of the world. The city's strategic position made it a focal point for commercial activities, contributing significantly to the kingdom's wealth.
The trade networks of Axum not only enriched the kingdom economically but also played a vital role in cultural exchange and integration. Through trade, Axumites interacted with diverse peoples, leading to the spread of Christianity and the adoption of various artistic styles and architectural influences. The exchange of ideas and beliefs through commerce shaped the cultural identity of Axum, leaving a lasting impact on its society.
Moreover, the prosperity generated by trade allowed the Axumites to invest in monumental architecture and religious structures, such as the iconic obelisks and churches that symbolized the kingdom's power and spiritual beliefs. These impressive monuments served as testaments to Axum's economic strength and cultural sophistication, showcasing the significance of trade in shaping the kingdom's religious practices and artistic expressions.

Port City of Adulis
The holds a pivotal role in the history of the ancient Kingdom of Axum, serving as a bustling hub for maritime trade and cultural exchange. Situated along the Red Sea coast, Adulis acted as a vital link connecting Axum to distant lands and facilitating the flow of goods and ideas across continents. The strategic location of Adulis allowed the Axumites to establish strong trade networks with regions as far as the Mediterranean and Asia, fostering prosperity and growth for the kingdom.
Archaeological excavations in Adulis have unearthed remnants of ancient docks, warehouses, and trading facilities, providing valuable insights into the maritime activities of the Axumites. The city's proximity to the Red Sea enabled easy access to international trade routes, allowing for the exchange of commodities such as ivory, gold, spices, and textiles. Ships laden with exotic goods would dock at Adulis, enriching the kingdom's economy and cultural landscape.
Adulis not only served as a bustling center of commerce but also as a melting pot of diverse cultures and traditions. The cosmopolitan nature of the city attracted merchants, sailors, and travelers from various corners of the ancient world, leading to a vibrant exchange of languages, beliefs, and artistic expressions. The cultural fusion that occurred in Adulis played a significant role in shaping the identity of the Axumite civilization and influencing its artistic and architectural achievements.
Moreover, the maritime activities in Adulis facilitated the spread of Christianity in the region, as evidenced by the presence of early Christian artifacts and inscriptions. The city became a nexus for religious interactions and the dissemination of new faiths, further illustrating the profound impact of trade on cultural and religious dynamics within the Kingdom of Axum.

Cultural Exchange and Influence
Exploring the cultural exchange and influence of the ancient Kingdom of Axum reveals a rich tapestry of interactions that shaped the identity of this vibrant civilization. Through its extensive trade networks, Axum served as a melting pot of diverse cultures, fostering the exchange of ideas, beliefs, and artistic expressions.
One of the most significant aspects of Axum's cultural exchange was the spread of Christianity, which took root and flourished within the kingdom. The introduction of this new religion not only transformed spiritual practices but also influenced the artistic and architectural landscape of Axum. Churches and monasteries were constructed, adorned with intricate carvings and murals that reflected a fusion of Christian and local artistic traditions.
Moreover, Axum's trade connections with distant lands brought a variety of influences to its doorstep. The kingdom embraced and integrated foreign artistic styles, such as Greco-Roman and Arabian motifs, into its own architectural designs. This cultural fusion is evident in the iconic obelisks and stelae of Axum, which exhibit a unique blend of indigenous craftsmanship and external inspirations.
The cultural exchange facilitated by Axum's trade routes extended beyond artistic endeavors to encompass language, cuisine, and social customs. Merchants and travelers from different regions converged in Axum, bringing with them not only goods but also a wealth of cultural practices that enriched the kingdom's social fabric.
Overall, the cultural exchange and influence of Axum were instrumental in shaping the kingdom's identity as a cosmopolitan center of trade and cultural convergence. Through the interplay of diverse traditions and beliefs, Axum emerged as a beacon of cross-cultural exchange in the ancient world, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to resonate in the present day.
Religious Practices and Monuments
Religious practices played a central role in the daily life of the Axumites, shaping their social structure and political dynamics. The Kingdom of Axum was known for its early adoption of Christianity, making it one of the first Christian states in the world. The introduction of Christianity brought about significant changes in religious practices, with the construction of churches and monasteries becoming prominent features of the Axumite landscape.
One of the most iconic religious monuments of Axum is the series of towering obelisks, carved from single pieces of granite, that served as markers of royal burials and religious significance. These obelisks, some reaching over 20 meters in height, symbolized the power and prestige of the Axumite rulers and their connection to the divine. The obelisks also served as focal points for religious ceremonies and rituals, emphasizing the kingdom's spiritual beliefs.
Furthermore, the Axumites built impressive churches, such as the renowned Church of St. Mary of Zion, which is believed to house the Ark of the Covenant according to local tradition. These churches were not only places of worship but also centers of cultural and intellectual exchange, showcasing intricate architectural designs and vibrant artistic decorations that reflected the kingdom's rich heritage.
Religion permeated all aspects of Axumite society, influencing political decisions, social norms, and cultural practices. The construction of religious monuments and the establishment of religious institutions were integral to maintaining the spiritual unity of the kingdom and reinforcing the authority of the ruling elite. The religious landscape of Axum stands as a testament to the enduring legacy of faith and devotion that defined this ancient civilization.

Decline and Legacy
Investigate the factors that led to the decline of the Kingdom of Axum, including environmental changes, external invasions, and internal conflicts. The once prosperous kingdom faced challenges as its trade routes were disrupted, impacting its economic stability. Environmental factors, such as shifts in climate and agricultural productivity, also played a role in the decline of Axum's power and influence. Additionally, external invasions from neighboring regions and internal conflicts within the kingdom weakened its political structure and overall resilience. Despite its eventual decline, the legacy of Axum continues to resonate in Ethiopian culture and history, serving as a reminder of the kingdom's past glory and the importance of sustainable development.

Archaeological Discoveries
Archaeological discoveries in the ancient kingdom of Axum have provided invaluable insights into the rich history and cultural achievements of this once powerful civilization. Excavations at various sites have unearthed a treasure trove of artifacts, royal tombs, and inscriptions that offer a glimpse into the economic activities and artistic prowess of the Axumites.
One of the most remarkable archaeological finds in Axum is the series of towering obelisks that served as monumental markers of the kingdom's power and prestige. These intricately carved stone pillars, some reaching over 20 meters in height, stand as enduring symbols of Axum's architectural ingenuity and religious significance.
Additionally, the discovery of ancient churches carved out of rock exemplifies the Axumites' dedication to religious practices and their architectural prowess. These rock-hewn churches, adorned with intricate carvings and decorations, highlight the fusion of Christianity with local traditions in Axumite society.
Archaeological excavations have also revealed the presence of elaborate royal tombs containing valuable artifacts such as jewelry, ceramics, and coins, shedding light on the kingdom's economic prosperity and trade connections with distant regions. The inscriptions found in these tombs provide valuable historical records of Axum's rulers and their achievements.
Furthermore, the uncovering of ancient trading posts and marketplaces in Axum underscores the kingdom's pivotal role as a hub of commerce and cultural exchange in the ancient world. The artifacts recovered from these sites, including imported luxury goods and locally produced items, attest to the vibrant trade networks that once thrived in Axum.
In conclusion, the ongoing archaeological discoveries in Axum continue to deepen our understanding of this ancient civilization and its enduring legacy. By piecing together fragments of the past, archaeologists and historians are able to reconstruct the vibrant tapestry of Axumite society and its contributions to the cultural heritage of Ethiopia and the wider region.

Modern Perspectives and Preservation Efforts
Today, the ancient kingdom of Axum stands as a testament to the rich history and cultural heritage of Ethiopia. Designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, Axum continues to captivate visitors and researchers alike with its archaeological wonders and historical significance. Efforts to preserve the legacy of Axum are ongoing, with initiatives aimed at safeguarding the archaeological sites and artifacts that offer a glimpse into the kingdom's past.
One of the key aspects of preserving Axum's heritage is the maintenance and restoration of its iconic monuments, including the towering obelisks and ancient churches that dot the landscape. These structures not only serve as reminders of Axum's former glory but also as symbols of the enduring legacy of the kingdom in Ethiopian culture.
Furthermore, modern perspectives on Axum emphasize the importance of understanding the kingdom's role in shaping the region's history and identity. Scholars and archaeologists continue to study Axumite artifacts and inscriptions, unraveling the mysteries of this ancient civilization and shedding light on its economic and cultural achievements.
Collaborative efforts between local authorities, international organizations, and academic institutions play a crucial role in preserving Axum's heritage for future generations. By promoting awareness and appreciation of Axum's historical significance, these preservation efforts aim to ensure that the legacy of this remarkable kingdom endures for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the significance of the Kingdom of Axum?
The Kingdom of Axum was a powerful ancient civilization known for its flourishing trade routes and economic prosperity in the Horn of Africa. It played a key role in connecting Africa with the Mediterranean and Asia through its well-established trade networks.
- What were the key factors that contributed to Axum's economic success?
Axum's economic success can be attributed to its strategic location along major trade routes, the abundance of valuable resources such as ivory and gold, as well as its control over key ports like Adulis that facilitated maritime trade.
- How did trade impact the wealth of the Kingdom of Axum?
Trade brought immense wealth to Axum by allowing the kingdom to exchange goods like spices, silk, and ivory for valuable commodities. This economic prosperity enabled Axum to flourish culturally and politically.
- What led to the decline of the Kingdom of Axum?
The decline of Axum was influenced by factors such as environmental changes, external invasions, and internal conflicts. These challenges, coupled with the rise of new trade routes, contributed to the eventual downfall of the once-powerful kingdom.
- What is the modern significance of Axum as a UNESCO World Heritage Site?
Axum's designation as a UNESCO World Heritage Site highlights its historical and cultural importance. Efforts to preserve its archaeological sites and cultural heritage serve as a reminder of the kingdom's legacy of trade and prosperity for future generations.



















